Sample Lecturette 10: Poverty | Preparation Tips for SSB Interview - CDS PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Poverty Line and India |

|
| Poverty in India |

|
| Measuring Poverty |

|
| Reducing Poverty |

|
Poverty Line and India
Poverty remains a significant social problem that poses a grave threat to our society. The global economy, which aimed to bring prosperity to all, has unfortunately resulted in widening disparities between the rich and the poor. The eradication of poverty, in all its forms, is the primary goal among the 17 Sustainable Development Goals outlined in the United Nations' 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
What is Poverty
Poverty refers to a state in which individuals or communities lack sufficient resources to attain and maintain a basic standard of living. It is a multifaceted issue that encompasses the absence of fundamental necessities such as food, shelter, and clothing, as well as limited access to healthcare and education. Poverty often manifests as hunger, malnutrition, social exclusion, and discrimination.
Poverty is measured by establishing a minimum level of income or expenditure required to meet the basic standard of living, which is known as the Poverty Line. Individuals living below this line are classified as poor. The World Bank has set the International Poverty Line at $1.90 per day, implying that those earning less than $1.90 a day are considered poor. Each country determines its own poverty line based on its specific standard of living.
Furthermore, the International Day for the Eradication of Poverty is observed annually on 17th October.
Poverty in India
- India has made impressive progress in reducing poverty since gaining independence. During the British colonial period, India's resources were heavily exploited, leaving over 75% of its population in poverty. The latest data shows that approximately 22% of Indians still live in poverty.
- According to the SDG Index 2019 released by NITI Aayog, six states (Andhra Pradesh, Goa, Himachal Pradesh, Kerala, Punjab, and Sikkim) and six Union Territories have successfully achieved the national target of reducing poverty rates to below 10.95% by 2030.
- Among the Indian states, Goa has the lowest poverty rate at 5.09%, while Chhattisgarh has the highest poverty rate at 39.93%.
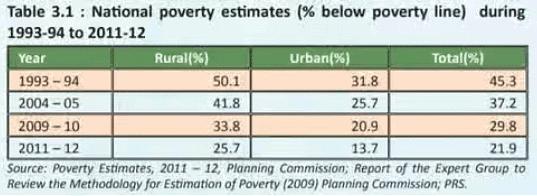
Measuring Poverty
In India, poverty is determined using the consumption expenditure method. The Central Government has established six official committees to estimate the number of Indians living in poverty. These committees are:
- The working group of 1962
- V N Dandekar and N Rath committee (1971)
- Alagh Committee (1979)
- Lakdawala committee (1993)
- Suresh Tendulkar committee (2009)
- Rangarajan committee (2012)
Until the 1990s, the Alagh committee recommended using the calorie method to measure poverty. The committee set a poverty line based on a minimum daily requirement of 2400 and 2100 calories for adults in rural and urban areas, respectively.
The Tendulkar committee (2009) proposed a shift away from the calorie-based approach and introduced a new method that considered expenditure on health, education, sanitation, travel, clothing, etc. The committee set a benchmark daily per capita expenditure of ₹27 in rural areas and ₹33 in urban areas.
In 2014, the Rangarajan Committee recommended raising the daily per capita expenditure to ₹32 for rural poor and ₹47 for urban poor, but these recommendations were not accepted by the government.
Currently, poverty in India is measured according to the criteria established by the Tendulkar committee.
Reducing Poverty
Although India has made significant progress in tackling poverty, a large part of its population still lives in poverty. According to a report by NITI Aayog titled "Eliminating Poverty: Creating Jobs and Strengthening Social Programs," India can overcome poverty by promoting employment-focused sustained high economic growth and effectively implementing anti-poverty initiatives. Additionally, increasing agricultural productivity and related activities can help reduce poverty in rural areas.
The Indian government has introduced several key programmes to address poverty, including the Integrated Rural Development Programme, National Social Assistance Programme, Indira Awas Yojana for rural housing, Annapurna Scheme, Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA), National Old Age Pension Scheme (NOAPS), National Rural Livelihood Mission: Aajeevika, and National Urban Livelihood Mission.
|
99 videos|112 docs|65 tests
|














