UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 25th May 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I
Historic ‘Sengol’ to be installed in new Parliament building

Why in News?
The upcoming inauguration of the new parliament building will also see PM Modi install a historic sceptre from Tamil Nadu next to the Lok Sabha Speaker’s seat.
- The sceptre is known as Sengol — derived from the Tamil word “Semmai”, meaning “Righteousness”.
Sengol
- Known as Sengol, the sceptre is a “significant historical” symbol of Independence as it signifies the transfer of power from the British to the Indians.
- It was presented to Jawaharlal Nehru, India's first prime minister, as a symbol of the transfer of power from the British.
History of Sengol
- Question over nature of ceremony to symbolise the transfer of power from British to Indian hands
- What is the ceremony that should be followed to symbolise the transfer of power from British to Indian hands?
- This was the question posed by the then Viceroy Lord Mountbatten to the to-be Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru.
- Nehru then consulted C. Rajagopalachari, commonly known as Rajaji, who went on to become the last Viceroy of India.
- Chola model was followed
- Rajaji identified the Chola model where the transfer of power from one king to another was sanctified and blessed by a high ruler.
- The symbol used was the handover of ‘sengol’ or sceptre from one king to his successor.
- Making of Sengol
- The Sengol was constructed by two men — Vummidi Ethirajulu and Vummidi Sudhakar, both are still alive and remember making it.
- A golden sceptre was crafted by Vummidi Bangaru Chetty, a famous jeweller in the Madras Presidency.
- The sceptre measures five feet in length and has a ‘Nandi’ bull on top, symbolising justice.
- The Sengol was constructed by two men — Vummidi Ethirajulu and Vummidi Sudhakar, both are still alive and remember making it.
- The ‘handing over’ ceremony that happened on Independence Day eve
- As per the official document, three people brought in the newly-made Sengol from Tamil Nadu.
- These three people were:
- the deputy high priest of Thiruvavaduthurai Adheenam (a 500-year-old Saivaite monastery),
- nagaswaram player Rajarathinam Pillai, and
- an Odhuvar (a person who sings devotional songs in Tamil temples).
- The ceremony was conducted as per Tamil traditions and the sengol was handed over to Nehru at his house.
- During the ceremony, which took place on August 14, 1947, a priest gave the sceptre to Lord Mountbatten and then took it back.
- It was then taken in procession to Pt Jawaharlal Nehru’s house, where it was handed over to him.
- A special song was rendered, as specified by the high priest.
- The song played during the ceremony was composed by the 7th-century Tamil saint Tirugnana Sambandar — a child prodigy who lived only 16 years.
- Thiruvavaduthurai Adheenam
- About
- It is a prominent Shaiva monastic organization or mutt (matha) based in Tamil Nadu, India.
- The mutt is located in Dharmapuram, a town in the Mayiladuthurai district of Tamil Nadu.
- It is one of the oldest and most revered Adheenams (monastic institutions) in the Shaiva tradition.
- It was established in the 10th century by the sage Tirugnana Sambandar, who was one of the four main Nayanars (saints) of Shaivism.
- Features
- The Adheenam is primarily focused on promoting and preserving the teachings, rituals, and practices of Shaivism.
- The Adheenam is involved in publishing Saivite literature, specifically Thevaram and Tiruvasakam and its translations.
- The head of the Thiruvavaduthurai Adheenam holds the title of "Adheenakarthar" and is considered a spiritual leader and guide for the followers.
- About
Source: The Hindu
GS-II
The India SARS-CoV-2 Genomics Consortium (INSACOG)
Why in News?
Sequencing genomes of COVID-19 variants has dipped because fewer samples are being made available to network-labs.
About
- India appears to have slowed down on sequencing genomes of COVID-19 variants.
- The India SARS-CoV-2 Genomics Consortium (INSACOG), has not published a single bulletin since March 27.
- Earlier, the agency would publish reports once a week. Bulletins provided information on the circulating variants of COVID-19, States that were seeing a surge in the contagious variants and information on whether SARS-CoV-2 variants linked to major outbreaks internationally had been found in India.
The India SARS-CoV-2 Genomics Consortium (INSACOG)
- INSACOG is a joint programme initiated by the Union Health Ministry of Health and the Department of Biotechnology with the Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) and the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR).
- It is a consortium of 54 laboratories to monitor the genomic variations in SARS-CoV-2.
- It is a multi-laboratory, multi-agency, pan-India network tasked with sequencing, and keeping an eye out for new, threatening SARS-CoV-2 variants.
The International Pathogen Surveillance Network (IPSN)
- The World Health Organisation (WHO) has warned that countries should not look away from COVID-19 and launched IPSN, a global network to help protect people from infectious disease threats through the power of pathogen genomics.
- IPSN will provide a platform to connect countries and regions, improving systems for collecting and analysing samples, using these data to drive public health decision-making, and sharing that information more broadly.
Source: The Hindu
Highlights of the proposed Digital India Act, 2023

Why in News?
The Digital India Bill, a comprehensive overhaul of Internet laws, will be unveiled in June 2023. This bill represents a significant update since the Information Technology Act of 2000.
What is the Digital India Bill?
- DIA will consist of 4 parts:
- Digital Personal Data Protection Bill,
- DIA rules,
- National Data Governance Policy, and
- Indian Penal Code amendments
Need for such legislation
- India has 850 million internet users, making it the world’s largest “digitally connected democracy.”
- The IT Act, created for the pre-digital era, lacks provisions for user rights, trust, safety, and modern cyber threats.
- Growing cyber crimes, disinformation, and privacy concerns necessitate an updated legislation.
Goals of the Digital India Bill
- Evolvable digital law: Flexible rules adaptable to changing technological trends.
- Adjudicatory mechanism: Accessible mechanism for resolving online civil and criminal offenses.
- Principles and rules-based approach: A legislative framework based on overarching governing principles.
Key components of the DIA
- Open Internet: Promotes choice, competition, diversity, fair market access, and ease of doing business, preventing the concentration of power.
- Online Safety and Trust: Safeguards users against cyber threats, revenge porn, defamation, cyberbullying, and moderates fake news. Advocates for digital rights and protects minors.
- KYC Requirements: Mandates Know Your Customer (KYC) for privacy-invading devices like spy camera glasses.
- Monetization Rules: Overhauls rules for platform and user-generated content to align with the DIA.
Key feature: Reconsideration of Safe Harbour
- The government is reconsidering a key aspect of cyberspace — ‘safe harbour’.
- Safe harbour is the principle that so-called ‘intermediaries’ on the internet are not responsible for what third parties post on their website.
- This is the principle that allows social media platforms to avoid liability for posts made by users.
- Safe harbour has been reined in in recent years by regulations like the Information Technology (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Rules, 2021, which require platforms to take down posts when ordered to do so by the government, or when required by law.
Way Forward
- The detailed timeline is undisclosed, but the government aims to conduct a comparative study of global laws and consult with experts, industry, the public, and relevant forums.
- The draft Bill will undergo consultation, followed by a draft Cabinet note before the final version is released.
Source: The Print
Forum Shopping
Why in News?
Recently, the Chief Justice of India (CJI) DY Chandrachud condemned ‘forum shopping’.
What is Forum shopping?
- When litigants or lawyers attempt to deliberately move their case to a particular judge or Court where they think the judgment could be more favourable, they are said to be “forum shopping.”
- This practice involves choosing a court that is likely to provide the most favourable outcome, rather than following the standard legal process.
- Lawyers think about which is the right forum to approach as part of their litigation strategy. For example, one could directly approach the Supreme Court via a public interest litigation case instead of the concerned High Court because the issue could get more eyeballs.
Issues with Forum Shopping
- It cited the injustice caused to the other party in the case and overburdening some courts over others and interfering with judicial process.
- It circumvents the normal course of justice and may increase the workload on the courts.
- A number of writers recognize that forum shopping may lead to an undesirable lack of decisional uniformity.
- It has no sanction in the law and gives unfair advantage to one party.
SC judgements on ‘Forum Shopping’
- Chetak Construction Ltd. vs. Om Prakash (1998): A litigant cannot be permitted choice of the forum,” and that every attempt at forum shopping “must be crushed with a heavy hand.
- Union of India & Ors. vs. Cipla Ltd (2017): SC laid down a “functional test” to be adopted for forum shopping.
- Vijay Kumar Ghai vs. State of W.B (2022): SC termed forum shopping as a “disreputable practice by the courts” that “has no sanction and paramountcy in law”.
Bench Hunting
- “Bench hunting” refers to petitioners managing to get their cases heard by a particular judge or court to ensure a favorable order.
Source: Indian Express
GS-III
FAME scheme: Will the latest government move kill India's nascent electric vehicles (EVs) boom?
Why in News?
The Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Electric Vehicles (FAME) scheme was launched under the National Electric Mobility Mission, to encourage electric and hybrid vehicle purchase by providing subsidies.
- The government is slashing subsidies for the electric 2-wheelers segment - a regressive step which will drag India's EV revolution.
National Electric Mobility Mission Plan (NEMPP):
- The Ministry of Heavy Industry launched the NEMMP 2020 in 2013.
- Targets:
- Deploying 5 to 7 million EVs in the country by 2020.
- Deploying 400,000 passenger battery electric cars (BEVs) by 2020 in order to avoid 120 million barrels of oil imports and 4 million tons of CO2 emissions.
- Lowering of vehicular emissions by 1.3 to 1.5% by 2020.
- Total investment required - INR 20,000 - 23,000 cr (approx 3 billion USD).
The FAME India Scheme:
- A part of NEMPP, the Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Electric and Hybrid Vehicles in India (FAME India) scheme, has been administered by the Ministry of Heavy Industry since 1st April 2015.
- Under the scheme, subsidies are being given to promote manufacturing of electric and hybrid vehicle technology and to ensure sustainable growth of the same.
- Subsidies are meant to bring a price parity between vehicles that have electric motors and fossil fuel-run engines, thereby nudging buyers to go for the cleaner option.
- Its first phase - FAME I, ran for four years until 2019.
- Under the FAME II (which ends this financial year - March 2024), companies can offer a discount of up to 40% on the cost of locally manufactured vehicles and claim it as a subsidy from the government.
- Under this scheme, the subsidies could range from ₹15,000-60,000 for a two-wheeler.
What is Driving the EV Revolution in India?
- The share of EVs in total vehicle sales in India is currently around 5%. Cumulative sales of EVs in India crossed the 1 million milestone for the first time in 2022-23.
- 2-wheelers accounted for more than 60% of all EV sales with an increase of 183% over 2021-22. A major reason for the rise in electric two-wheeler sales is subsidies.
- The government target for EV sales by 2030 is 30% of private cars, 70% for commercial vehicles and 80% for two and three-wheelers.
How and why the Government is Reducing Subsidies?
- Under the FAME-II scheme, the government is increasing the outlay for 2-wheelers but cutting the subsidy per vehicle.
- The budgetary allocation for electric 2-wheelers has been enhanced to around Rs 3,500 crore from Rs 2,000 crore, but the subsidy per unit is being reduced to 15% of the ex-factory price from 40% at present.
- Earlier, the government had announced that since it was about to achieve the target of 1 million sales in four years, the subsidies may not continue.
Possible Impacts on the EV revolution in India:
- The sudden reduction of subsidies could lead to a rise in per-unit cost for consumers.
- Rise in per-unit cost for consumers may lead to a major decline in EV adoption, impacting the entire industry.
Way Ahead:
- A gradual transition with sustained subsidies would have been ideal to ensure market growth and reach the international benchmark of 20% EV adoption.
- Production-Linked Incentive scheme in automobile and battery cells will help to bring enhanced investments and will bring down costs for manufacturers.
- The 2-wheeler makers are looking to tweak products and prices to stay competitive. For example, leading manufacturers have launched lower-spec variants by reducing features and size of batteries.
Source: Indian Express
Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism
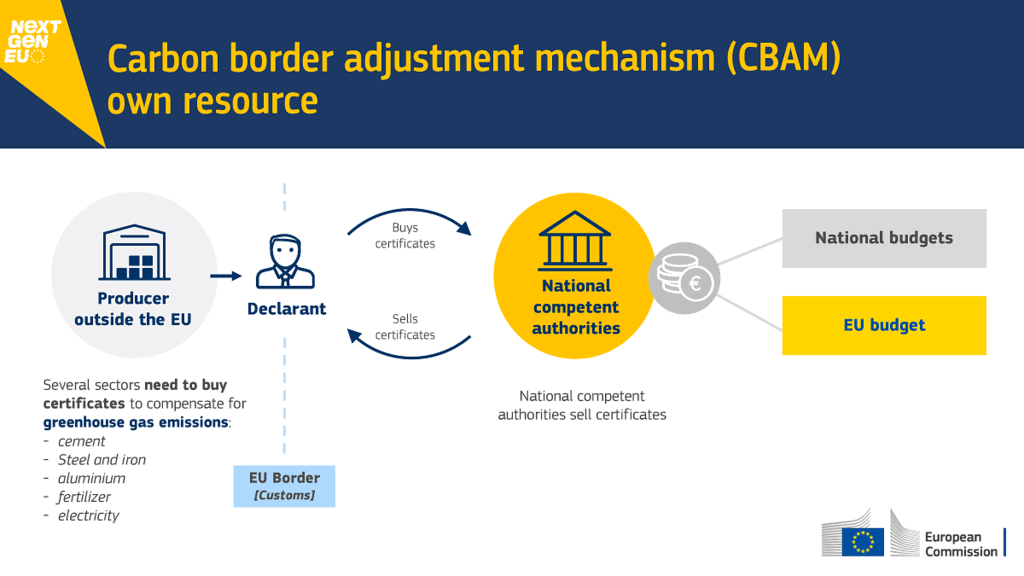
Why in News?
Recently the co-legislators at the European Commission signed the Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM).
About
- It has been described as a “landmark tool” to put a “fair price" on the carbon emitted during the production of carbon intensive goods that are entering the EU, and to encourage cleaner industrial production in non-EU countries.
- The reporting system under the regulation would be enforced from October 1 for certain goods to facilitate a smooth roll out and dialogue with third countries. Importers would start paying the financial levy from 2026.
What is the CBAM?
- CBAM is one of the elements of the EU Green Deal, the goal of which is to reduce GHG emissions by 55% by 2030.
- CBAM is aimed at equalizing the price of carbon paid for EU products operating under the EU Emissions Trading System (ETS) and imported goods.
- It refers to a phenomenon where a EU manufacturer moves carbon-intensive production to countries outside the region with less stringent climate policies. Its primary objective is to avert ‘carbon leakage’.
- The CBAM will initially apply to imports of the following goods, these sectors have a high risk of carbon leakage and high carbon emissions.
- Cement
- Iron and steel
- Aluminium
- Fertilisers
- Electricity
- EU importers will have to buy carbon certificates corresponding to the carbon price that would have been paid in the EU, if the goods had been produced locally.
- The price of the certificates would be calculated according to the auction prices in the EU carbon credit market.
- Once a non-EU producer can show that they have already paid a price for the carbon used in the production of the imported goods in a third country, the corresponding cost can be fully deducted for the EU importer.
- CBAM will apply on: In principle, imports of goods from all non-EU countries will be covered by the CBAM. Certain third countries who participate in the ETS or have an emission trading system linked to the Union's will be excluded from the mechanism. This is the case for members of the European Economic Area and Switzerland.
Didn’t the EU already have a mechanism in place?
- The gradual introduction of the CBAM would be in parallel with the phasing out of the allocation of free allowances given out under the EU Emissions Trading System (ETS), which was also aimed at supporting the decarbonisation of the region’s industries.
- The ETS had set a cap on the amount of greenhouse gas emissions that can be released from industrial installations in certain sectors.
Significance
- CBAM will avert the possibility of carbon leakage alongside encouraging producers in non-EU countries to green their manufacturing processes.
- Moreover, it will ensure a level playing field between imports and EU products. This would also form part of the continent’s broader European Green Deal which endeavours to achieve 55% reduction in carbon emissions compared to 1990 levels by 2030 and become a climate neutral continent by 2050.
How will it impact other countries?
- In 2021, the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) had concluded that Russia, China and Turkey were most exposed to the mechanism.
- Considering the level of exports to the union in these sectors, it stated India, Brazil and South Africa would be most affected among the developing countries. Mozambique would be the most exposed least-developing country.
- Countries in the EU combined represent about 14% of India’s export mix for all products, steel and aluminium included.
- EU being India’s third largest trade partner and given the latter’s projected growth trajectories, the size of exports (including in the CBAM sectors) will invariably rise.
- CBAM’s scope would expand beyond its current ambit to include other sectors as well.
- Given India’s products have a higher carbon intensity than its European counterparts, the carbon tariffs imposed will be proportionally higher making Indian exports substantially uncompetitive.
- And finally, international climate policies (including CBAM) will compel other countries to impose similar regulation eventually translating to “a significant impact” on India’s trading relationships and balance of payments.
Source: The Hindu
What is NASAMS (National Advanced Surface-to-Air Missile System)?

Why in News?
The United States recently announced the approval of a $285 million sale of a NASAMS air defense system and related equipment to Ukraine.
About NASAMS (National Advanced Surface-to-Air Missile System):
- It is a medium-range ground-based air defense system.
- It is designed to engage air targets at low and medium altitudes in all weather conditions.
- It was designed and developed jointly by Raytheon (United States) and Kongsberg Defence & Aerospace (Norway).
- It is used by Norway, the United States, Canada, Chile, Finland, Indonesia, Netherlands, Oman, Qatar, Spain, the United Kingdom, and Ukraine.
- It is best suited to defend important stationary assets, such as key military assets, infrastructure, or cities.
- It has been integrated into the S. National Capital Region’s air defense system since 2005.
- Features:
- It is the world's first networked short- and medium-range air defense system that could integrate with other equipment and air defense systems.
- It features an X-Band, 360-degree phased array air defense radar with a 75-kilometer (approximately 47-mile) range to identify targets.
- The NASAMS is armed with three launchers, each carrying up to six missiles.
- The system can engage 72 targets simultaneously in active and passive modes.
- It uses AIM-120 AMRAAM air-to-air missiles, which have been modified for ground launch and have an engagement range of about 30 kilometers.
Source: The Hindu
|
38 videos|5293 docs|1118 tests
|


















