Class 11 Exam > Class 11 Notes > Venation & Modification of Leaves - Rough
Venation & Modification of Leaves - Rough - Class 11 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Venation |

|
| (1) Reticulate |

|
| (2) Parallel |

|
| Types of Leaf |

|

|
|
| (1) Simple Leaf |

|
| (2) Compound Leaf |

|
| Modifications of Leaves |

|
Understanding the different types of venations is important as it helps in plant identification and classification. Additionally, venation plays a role in understanding the adaptations of plants to their environment, as the pattern of veins affects the distribution of resources within the leaf.
Venation
The arrangement of veins and veinlets in lamina or leaf blade of a leaf. It plays a crucial role in the transport of water, nutrients, and sugars within the leaf.
It is of two types.
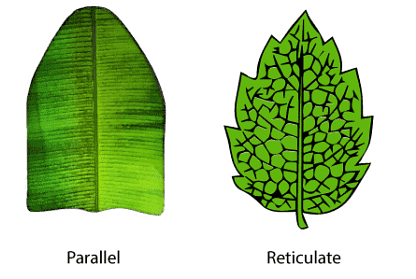
(1) Reticulate
- In this type of venation many veins are divided into various branches (veinlets) and form a net-like structure.
- Many smaller veins called veinlets arise from larger veins, creating an web like network.
- It is found in dicots.
- *Exception – Calophyllum (It has parallel venation)
(2) Parallel
- In this type of venation, all veins run parallel to each other, and they do not form network.
- They extend from the base of the leaf to the tip, maintaining a consistent distance between each other.
- It is found in monocots.
- Exception(*) – Smilax (It has reticulate venation)
Question for Venation & Modification of Leaves - Rough
Try yourself:Venation is the ________________.
View Solution
Types of Leaf
leaves are one of the most important plant organs involved in photosynthesis, gas exchange, and transpiration.
There are two types of Leaves(1) Simple Leaf
- Simple leaves are those that have only one lamina and are connected to the main stem by a petiole. The petiole is a slender stalk that joins the leaf blade to the main stem or branch of the plant. It acts as a support structure, allowing the leaf to be positioned optimally for light absorption during photosynthesis.
- It is characterized by having only one leaf blade or lamina, which is not divided into smaller leaflets.
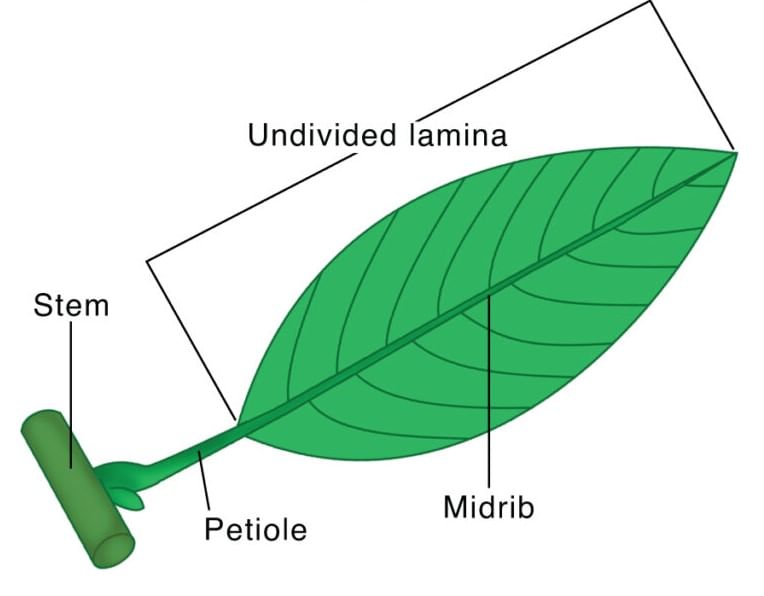
- The lamina of a simple leaf never gets divided into smaller leaflets.
Examples: Maples, Oregano, Banana, Guava, Mango, Black Cherry.
(2) Compound Leaf
- A compound leaf is composed of multiple leaflets attached to the midvein, having their own stalks.
- Each leaflet of a compound leaf remains attached to the main stem by a short stem-like structure called the rachis.
- Each leaflet is similar to a small leaf, but they are not individually connected to the stem.
- Examples: Neem, Clover, Rose, Hickory, Walnut, Pecan.
There are two types of compound leaves

 |
Download the notes
Venation & Modification of Leaves - Rough
|
Download as PDF |
Download as PDF
a) Pinnately Compound
- Number of leaflets are present on a common axis called rachis.
- In pinnately compound leaves, multiple leaflets are arranged along a central stalk called the rachis.
- The arrangement of leaflets resembles the shape of a feather or a pinnate structure, hence the name "pinnately compound.
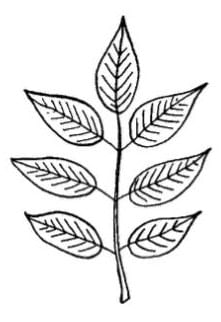 Pinnately Example - Neem, Rose plants, Walnut trees, and Pecan trees.
Pinnately Example - Neem, Rose plants, Walnut trees, and Pecan trees.
b) Palmately Compound
- The leaflets are attached at a common axis at the tip of petiole.
- The arrangement resemble the shape of an open palm or hand, hence the name "palmately compound.
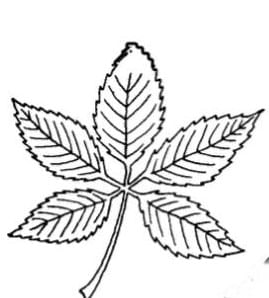 PalmatelyExample - Silk Cotton
PalmatelyExample - Silk Cotton
Question for Venation & Modification of Leaves - Rough
Try yourself:Q4. What is the structure called that attaches each leaflet to the main stem in a compound leaf?
View Solution
Modifications of Leaves
When leaf is modified in a different structure to perform functions other than photosynthesis is called modification of leaf.
Leaf tendril: In this, whole leaf is modified into a wire-like structure helping leaves to climb which is called leaf tendril
Example: Lathyrus aphaca (wild pea)- Leaf spine - Leaves or any part of leaflet are modified into pointed spine for defense function.
Example: Opuntia , Aloe, Argemone . - Leaf scale - In this leaves become thin, dry and form a membrane or paper-like structure and serve to protect axillary buds or store food and water as in onion.
Example: Ficus and Tamarix , Ruscus. - Leaf pitcher - Leaves of some plants are modified to pitcher shape.
Example: Nepenthes, Dishidia.
Note: Dionaea (Venus flytrap) is insectivorous plant and they also have modified leaves.
Question for Venation & Modification of Leaves - Rough
Try yourself:Q4. What is the function of a leaf spine when a leaf is modified into a pointed spine?
View Solution
Download as PDF
Top Courses for Class 11
Related Searches