MCAT Exam > MCAT Notes > Biology for MCAT > Cellular Organelles and Structure
Cellular Organelles and Structure | Biology for MCAT PDF Download
Introduction
Cell organelles play a crucial role in the intricate machinery of both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. These specialized structures, enclosed by membranes, are responsible for carrying out specific functions necessary for cell survival and optimal functioning. By understanding the diverse types of cell organelles and their unique characteristics, we can unravel the complexities of cellular processes such as energy production, protein synthesis, and waste disposal. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of cell organelles, exploring their structure, function, and significance within the cellular realm.
What are Cell Organelles?
Cell organelles are the components within a cell that carry out specialized functions. These organelles can be categorized into membrane-bound and non-membrane-bound structures, each with its distinct structure and function. Working in harmony, these organelles contribute to the overall functionality and integrity of the cell. Some organelles aid in maintaining cell shape, while others facilitate cell motility or reproduction. They can be classified into three categories based on their membrane composition.
- Organelles Without Membrane: The cell wall, ribosomes, and cytoskeleton are examples of non-membrane-bound organelles. Present in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, these structures contribute to cell shape maintenance, protein synthesis, and the facilitation of cellular movement.
- Single-Layer Membrane Organelles: Eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bound organelles encompassed by a single layer. Examples of such organelles include vacuoles, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and the endoplasmic reticulum. Each of these organelles performs specific functions such as storage, protein modification and transport, waste removal, and lipid metabolism.
- Double-Layer Membrane Organelles: Certain organelles are enclosed by a double-layered membrane. These include the nucleus, mitochondria, and chloroplasts. The nucleus houses the genetic material of the cell and plays a vital role in maintaining cellular activities. Mitochondria, often referred to as the powerhouse of the cell, are responsible for energy production through aerobic respiration. Chloroplasts, found in plant cells, are the sites of photosynthesis, utilizing light energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose.
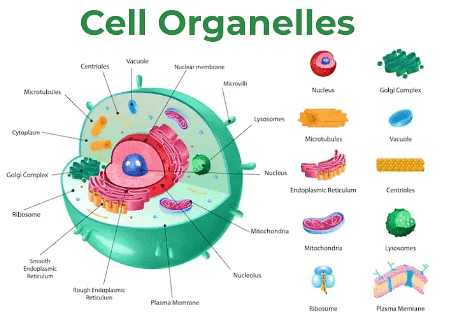
Cell Organelles and Their Functions
A diverse array of cell organelles contribute to the intricate workings of a cell. Here, we will explore some of the key organelles and their functions.
- Plasma Membrane: Also known as the cell membrane or cytoplasmic membrane, the plasma membrane forms a selectively permeable barrier composed of a lipid bilayer and proteins. It regulates the movement of specific molecules into and out of the cell, contributing to cell shape maintenance and providing structural support (in animal cells).
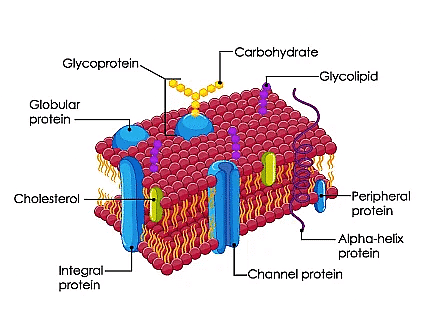
- Cytoplasm: The cytoplasm is a jelly-like substance present between the nucleus and the plasma membrane in both plant and animal cells. Composed of water, organic compounds, and inorganic substances, it serves as the site for numerous metabolic reactions and houses various cell organelles.
- Nucleus: The nucleus, found in all eukaryotic cells, is a double-membraned structure that contains the cell's genetic material. Within the nucleus, the nucleolus houses chromosomes, which carry genes responsible for transmitting hereditary information from parents to offspring. The nucleus plays a crucial role in maintaining cellular integrity and regulating metabolic activities.
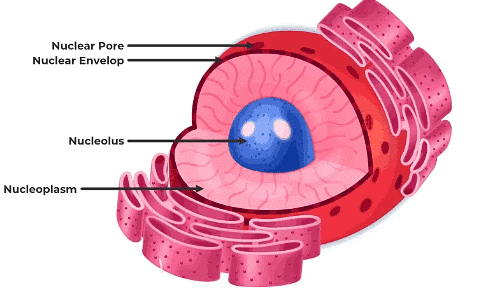
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): The endoplasmic reticulum is a membranous structure composed of tubules filled with fluid and cristae. It acts as the cell's transport system, facilitating the movement of proteins and enzymes within and outside the cell. There are two types of ER: rough ER, involved in protein synthesis, and smooth ER, responsible for storage and lipid synthesis.
- Mitochondria: Mitochondria are double-membraned, semiautonomous organelles found in all eukaryotic cells. They possess their own set of genes, but some proteins are still synthesized in the cell nucleus. Mitochondria serve as the powerhouses of the cell, generating energy through aerobic respiration, which fuels various cellular activities.
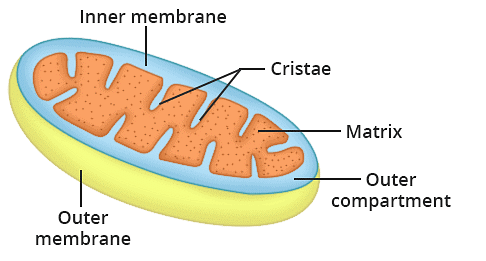
- Plastids: Plastids are large, membrane-bound organelles that contain pigments. They are categorized into three types based on the type of pigments present. Chloroplasts, found in the leaf mesophyll cells, contain chlorophyll and are involved in photosynthesis. Chromoplasts provide colorful pigments, such as carotene and xanthophylls, giving plants their vibrant hues. Leucoplasts are colorless plastids that store nutrients like starch, proteins, or oils/fats.
- Ribosomes: Ribosomes, composed of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and ribosomal proteins, are non-membrane-bound organelles. They can be found either attached to the endoplasmic reticulum or freely floating in the cytoplasm. Ribosomes play a crucial role in protein synthesis, decoding the genetic information from mRNA and synthesizing proteins accordingly.
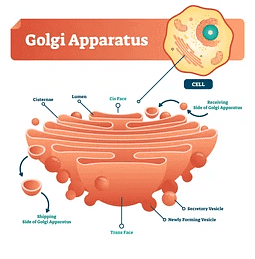
- Golgi Apparatus: Also known as the Golgi complex, the Golgi apparatus is a membrane-bound organelle comprising flattened stacked pouches called cisternae. It plays a vital role in modifying, packaging, and transporting proteins and lipids to their target destinations within the cell or outside of it.
- Cytoskeleton: The cytoskeleton is a proteinaceous structure present throughout the cell, from the cell membrane to the nucleus. It provides structural support to the cell, helps maintain cell shape, and facilitates cell movement. Composed of various proteins, the cytoskeleton assembles and disassembles according to the cell's requirements, contributing to mechanical resistance and cellular motility.
- Cilia and Flagella: Cilia and flagella are hair-like projections found on the outer part of the cell wall. Cilia, smaller in size, aid in the movement of cells or extracellular fluid. Flagella, larger than cilia, exhibit a whip-like motion and are involved in cell movement. Both cilia and flagella possess microtubule-based structures called axonemes, which contain nine microtubule doublets and a set of central microtubules. Centrioles, basal bodies for cilia and flagella, are composed of microtubules and assist in their formation.
- Centrosomes and Centrioles: Centrosomes are formed when two perpendicular centrioles come together. Each centriole consists of nine microtubules, and they play a crucial role in organizing the microtubule network within the cell. Centrioles are also essential components of the basal bodies found in cilia and flagella.
- Vacuoles: Vacuoles are single-membrane structures found in cells, with plant cells often having the largest vacuoles. They serve as storage organelles for various compounds, including nutrients, waste products, and ions. The number and shape of vacuoles vary depending on the cell type.
The document Cellular Organelles and Structure | Biology for MCAT is a part of the MCAT Course Biology for MCAT.
All you need of MCAT at this link: MCAT
|
233 videos|16 docs|32 tests
|
Related Searches
















