States of matter | Chemistry for EmSAT Achieve PDF Download
Introduction
There are three primary states of matter: solids, liquids, and gases. A substance can typically exist in any of these states, depending on the temperature and pressure conditions. State changes occur at specific points, namely the melting point and the boiling point, which depend on whether the substance is being heated or cooled.
At the melting point:
- Heating up causes a solid to melt into a liquid.
- Cooling down causes a liquid to freeze into a solid.
At the boiling point:
- Heating up causes a liquid to boil and transform into a gas.
- Cooling down causes a gas to condense back into a liquid.
It's important to note that individual atoms do not possess the same properties as bulk matter. To represent the three states of matter, a simple model can be used, where particles are depicted as small solid spheres.
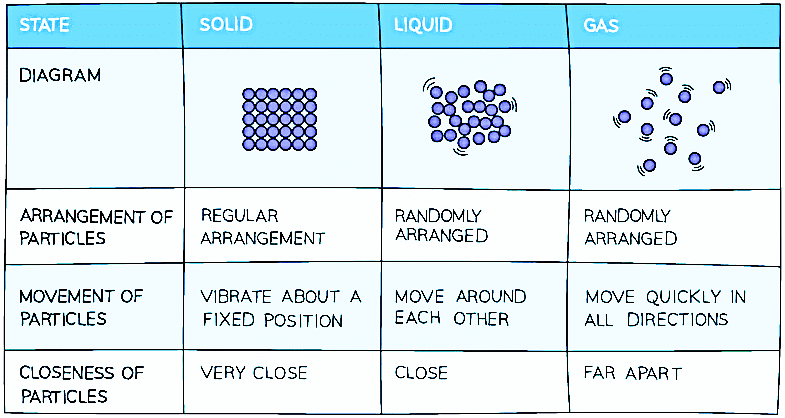
Summary of the Properties of Solids, Liquids and Gases
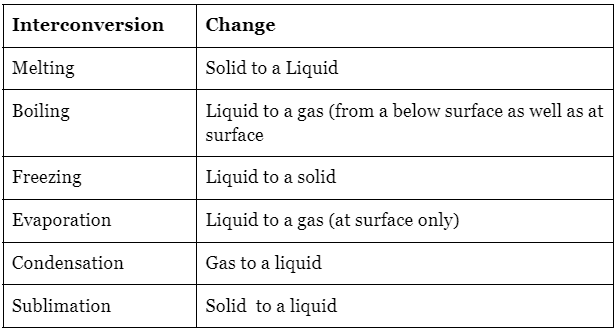
Interconversion Between the States of Matter
The transition between different states of matter is influenced by the amount of energy required to overcome the forces between particles. The strength of these forces determines the energy needed for a state change. Consequently, substances with stronger interparticle forces have higher melting and boiling points.
When matter undergoes a change in state due to variations in temperature or pressure, it is referred to as an interconversion of state. This is a physical change that involves modifications in the forces between particles, while the particles themselves and the chemical properties of the substance remain unchanged.
Physical changes, such as interconversions of state, are generally reversible as they do not involve the formation of new substances. There are specific terms to describe these interconversions, including:
- Solid to liquid: Melting
- Liquid to solid: Freezing
- Liquid to gas: Vaporization or evaporation
- Gas to liquid: Condensation
- Solid to gas: Sublimation
- Gas to solid: Deposition
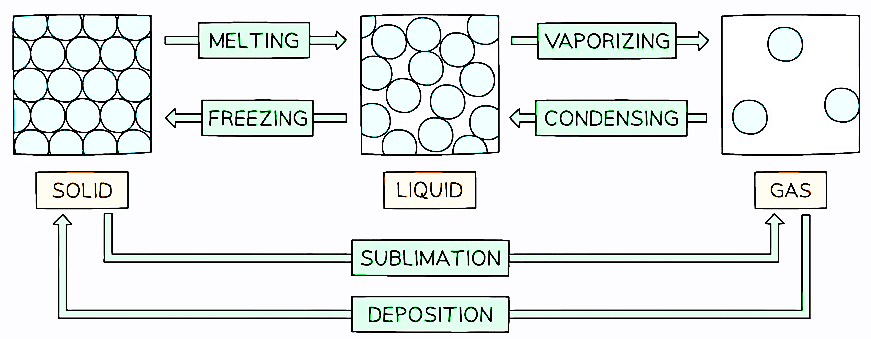
A Summary of State Changes
Melting:
- Melting is the process in which a solid substance changes into a liquid state. It occurs when heat energy is applied, causing an increase in kinetic energy and enabling the particles to move more freely. Each pure solid has a specific temperature called the melting point at which melting occurs.
Boiling:
- Boiling is the transformation of a liquid into a gas state. It requires the application of heat, leading to the formation of gas bubbles within the liquid. These bubbles allow the liquid particles to escape from both the surface and the interior of the liquid. Similar to melting, each pure liquid has a distinct temperature known as the boiling point at which boiling occurs.
Freezing:
- Freezing is the reverse process of melting, where a liquid substance changes into a solid state. It occurs at the same temperature as the melting point, resulting in the freezing and melting points of a pure substance being identical. For instance, water freezes and melts at 0°C. Freezing requires a significant decrease in temperature and has a specific temperature unique to each pure substance.
Evaporation:
- Evaporation is the conversion of a liquid into a gas state, but it takes place only at the liquid's surface. High-energy particles near the surface can escape and enter the gas phase, even at temperatures below the boiling point. The rate of evaporation is influenced by factors such as the surface area and temperature of the liquid. While evaporation can occur over a range of temperatures, heating accelerates the process as it provides the particles with the necessary energy to escape from the surface.
Condensation:
- Condensation is the transition from a gas to a liquid state, typically occurring when a gas is cooled. As gas particles lose energy upon cooling, they come into contact with other particles and lack the energy to bounce away. Consequently, they group together, forming a liquid.
Sublimation:
- Sublimation is the direct conversion of a solid into a gas state without passing through the liquid phase. Only certain solids, such as iodine or solid carbon dioxide (dry ice), undergo sublimation. The reverse process is known as desublimation or deposition.
|
191 videos|265 docs|160 tests
|
















