Law of Definite Proportion & Conservation of Mass | Chemistry for EmSAT Achieve PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Law of Definite Proportion (Law of Constant Composition) |

|
| Law of Conservation of Mass |

|
| Relationship between the Two Laws |

|
Introduction
- In chemistry, understanding how matter behaves in chemical reactions is crucial, and two fundamental laws, the Law of Definite Proportion and the Law of Conservation of Mass, provide the foundation for this understanding.
- The Law of Definite Proportion, proposed by Joseph Proust, states that a given chemical compound always contains the same proportion of elements by mass, regardless of the sample's size or source.
 Law of Definite Proportion
Law of Definite Proportion
- The Law of Conservation of Mass, formulated by Antoine Lavoisier, asserts that mass is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. The mass of the reactants equals the mass of the products, emphasizing the conservation of matter.
 Law of Conservation of Mass
Law of Conservation of Mass
- Together, these laws are essential in explaining chemical interactions, ensuring consistency in compound composition, and maintaining the balance of matter during chemical reactions.
Law of Definite Proportion (Law of Constant Composition)
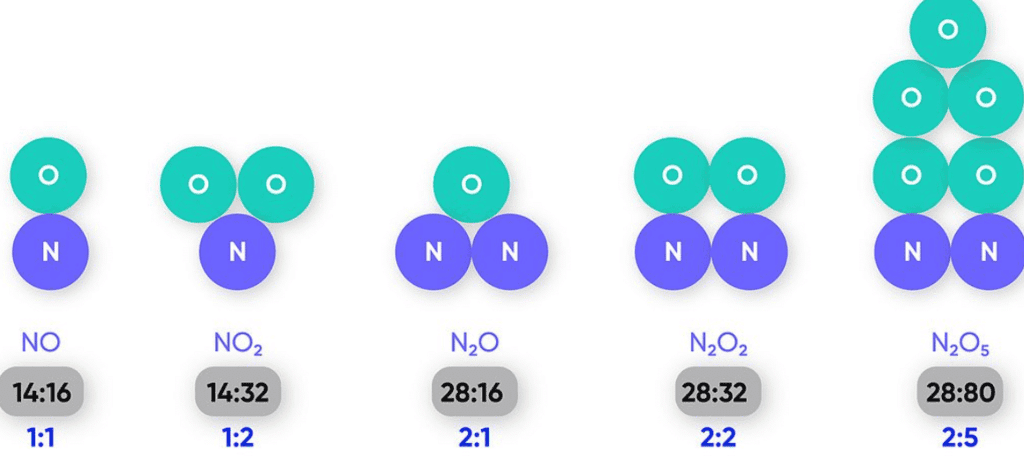
The Law of Definite Proportion, first proposed by Joseph Proust in 1797, states that a given chemical compound always contains the same elements in exactly the same proportion by mass, no matter how the compound is prepared or where it is sourced.In other words, no matter the size of the sample or how it is synthesized, a specific compound will always have a fixed ratio of the elements that make it up.
Detailed Explanation:
This law implies that the chemical composition of a compound is consistent and predictable. The ratio of the elements in the compound is a constant value, which can be determined by careful measurements of the compound's mass and the masses of its individual elements.
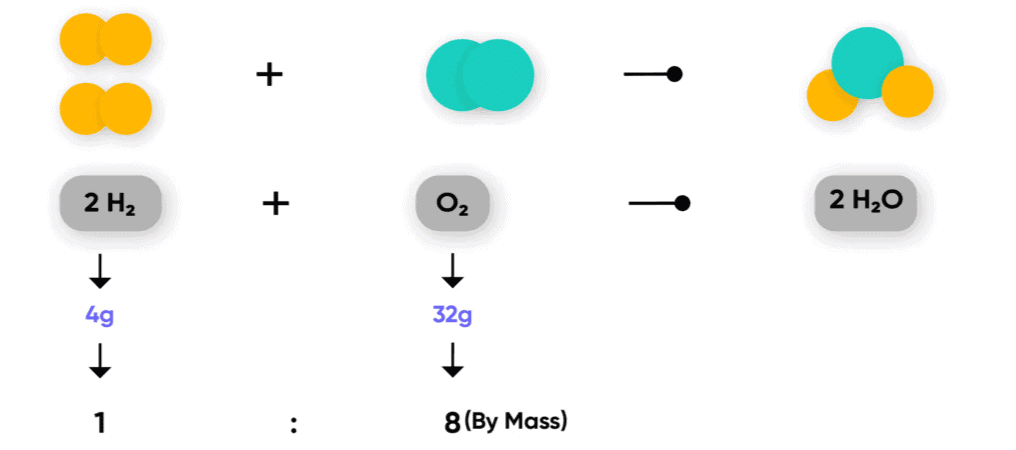
For example, water (H₂O) is composed of two elements: hydrogen and oxygen. In every sample of water, the mass ratio of hydrogen to oxygen is always the same, which is 1:8 by mass. This means that no matter how much water you have or where it is sourced from (river, ocean, distilled water, etc.), the proportion of hydrogen and oxygen remains constant.
 Law of Definite Proportion
Law of Definite Proportion
Example: In the compound carbon dioxide (CO₂), for every 12 grams of carbon, there will always be 32 grams of oxygen. The ratio of carbon to oxygen by mass in CO₂ is always 12:32, which simplifies to 3:8.
The key takeaways from this law are:
- Each compound has a specific, fixed ratio of elements.
- This ratio does not change regardless of the compound's source or quantity.
Importance:
- The Law of Definite Proportion was crucial in the development of atomic theory because it supported the idea that compounds are made up of atoms combined in fixed proportions.
- It helped scientists understand that chemical reactions occur in specific, measurable ratios, which led to the development of stoichiometry.
Start Test Start TestLaw of Conservation of Mass
The Law of Conservation of Mass, proposed by Antoine Lavoisier in 1789, states that mass is neither created nor destroyed during a chemical reaction. The total mass of reactants before the reaction is equal to the total mass of products after the reaction.
Detailed Explanation:
This law emphasizes that in a closed system (where no mass can enter or leave), the amount of matter remains constant during any chemical reaction. In other words, the mass of the reactants (the substances you start with) must equal the mass of the products (the substances formed) because no mass is lost in the reaction.
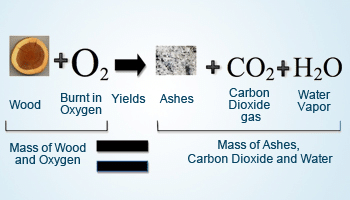
Example 1: when wood burns in oxygen, it produces carbon dioxide and water vapor. The mass of the wood and oxygen before combustion equals the mass of the carbon dioxide and water produced after combustion, as long as no mass is lost to the surroundings (e.g., through ash blowing away).
 Law of Conservation of Mass
Law of Conservation of Mass
Example 2:
- Suppose 10 grams of hydrogen reacts with 80 grams of oxygen to form water (H₂O). According to the law, the mass of the water produced will be 90 grams (10g of hydrogen + 80g of oxygen = 90g of water).
Key Concepts:
- Closed System: The law applies in a closed system where no external forces can alter the system's mass.
- No Mass Loss: In any chemical reaction, mass is not lost or gained; it is simply rearranged.
- Applications: This law is foundational in the study of chemical reactions, balancing chemical equations, and understanding how atoms are conserved through reactions.
Importance:
- The Law of Conservation of Mass provided the basis for modern chemistry by demonstrating that chemical reactions are just rearrangements of atoms, rather than the creation or destruction of matter.
- It is a fundamental principle in chemical engineering, laboratory work, and industrial processes, ensuring accurate calculations for the amounts of reactants and products.
Relationship between the Two Laws
Both the Law of Definite Proportion and the Law of Conservation of Mass are key to understanding the behavior of matter in chemical reactions.
- Law of Definite Proportion tells us that in a compound, the elements are always present in fixed proportions by mass.
- Law of Conservation of Mass ensures that, during a chemical reaction, the mass of the reactants is conserved and remains constant throughout the reaction process.
 Difference Between Law of Conservation of Mass and Law of Constant Proportion
Difference Between Law of Conservation of Mass and Law of Constant Proportion
Together, these two laws help chemists understand how substances combine to form compounds and how they break down during reactions, while maintaining a constant mass in the system.
|
193 videos|226 docs|153 tests
|
FAQs on Law of Definite Proportion & Conservation of Mass - Chemistry for EmSAT Achieve
| 1. What is the principle of conservation of mass? |  |
| 2. How does the conservation of mass apply in chemical reactions? |  |
| 3. Can you provide examples of conservation of mass in everyday life? |  |
| 4. How is conservation of mass relevant in environmental science? |  |
| 5. What are some common misconceptions about the conservation of mass? |  |






















