Plants Chapter Notes | Science Olympiad Class 4 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Parts of Plants |

|
| Roots |

|
| Stem |

|
| Leaves |

|
| Flowers |

|
Introduction
Plants are essential living organisms crucial for life on Earth. They produce food and oxygen, which are necessary for all other living beings. Plants can be found in various environments such as land, mountains, deserts, and water bodies. Understanding the structure and function of plants is fundamental to basic science. This article will explore the different parts of plants and their significance.
Parts of Plants
A typical plant consists of several important parts: roots, stem, leaves, flowers, and fruits. Each part has a specific role that contributes to the plant's overall functioning. Let's take a closer look at each part:Roots
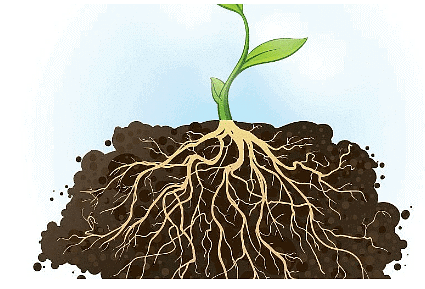
The root system is the underground part of a plant's body. Roots grow towards the force of gravity and serve multiple purposes. They anchor the plant firmly in the soil and absorb water and vital minerals from it. Additionally, roots store excess food, ensuring a steady supply of nutrients for the plant. There are two primary types of roots:
(a) Tap Root
- A tap root system consists of a single, thick primary root that grows deep into the soil, with smaller lateral roots branching off from it.
- The primary root is responsible for anchoring the plant firmly in the ground and accessing water and nutrients from deeper soil layers.
- Examples of plants with a tap root system include:
- Carrot: The tap root stores carbohydrates and sugars, making it a popular vegetable.
- Beet: Sugar beets have a large tap root that stores sugar, which is extracted for commercial use.
- Radish: Radishes have a swollen tap root that stores water and nutrients, making them a fast-growing vegetable.
- Turnip: Turnips have a thickened tap root that stores starch, and they are often used in cooking.
- Sweet potato: Although not a true tap root, sweet potatoes develop thickened roots that store carbohydrates, making them a nutritious food source.
(b) Fibrous Root
- A fibrous root system consists of many thin, hair-like roots that spread out from the base of the stem. These roots are usually similar in size and form a dense network just below the soil surface.
- This type of root system is effective for absorbing water and nutrients from the topsoil and provides good stability for the plant.
- Examples of plants with a fibrous root system include:
- Grass: Most grass species have a fibrous root system that helps prevent soil erosion and provides a stable base for the plants.
- Wheat: Wheat plants have a fibrous root system that helps them absorb water and nutrients from the topsoil, supporting their growth and development.
- Rice: Rice plants have a fibrous root system that helps them thrive in flooded conditions, as the roots can access nutrients from the waterlogged soil.
- Corn: Corn plants have a fibrous root system that helps them absorb water and nutrients efficiently, supporting their rapid growth.
- Sugarcane: Sugarcane plants have a fibrous root system that helps them absorb water and nutrients from the soil, contributing to their high sugar content.
Functions of Roots
Roots have vital functions that contribute to the overall health and stability of the plant:
- Support: Roots anchor the plant securely in the ground, providing stability and preventing it from being uprooted.
- Absorption: Root hairs, which are tiny structures on the roots, absorb water and essential minerals from the soil and transport them to the stem for the plant's use.
- Storage: Certain roots, such as those of carrots and radishes, store food reserves for the plant.
- Preventing Soil Erosion: Roots play a crucial role in binding the soil together, which helps prevent erosion caused by wind or water.
Stem
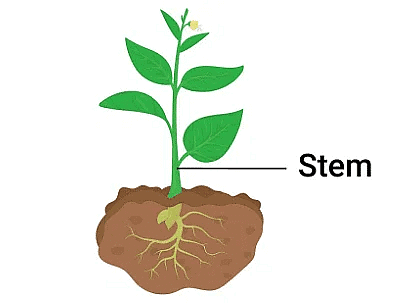
The stem is the main part of a plant that grows above the ground. It has several important roles:
- Support: It holds the plant upright.
- Transportation: It carries nutrients and water between the roots and leaves.
- Food Storage: It can store food for the plant.
Different plants have various types of stems:
- Woody Stem: Trees like neem, mango, and peepal have thick, strong, and woody stems known as trunks.
- Herbaceous Stem: Some plants, such as bananas, have thick but soft stems.
- Weak Stem: Climbers and creepers, like watermelon and money plant, have soft, green, and weak stems.
Functions of Stem
The stem plays several important roles in the plant's overall functioning:
- Support: The stem provides essential structural support to the plant, holding up branches, leaves, buds, flowers, and fruits.
- Transportation: The stem is responsible for transporting water and minerals from the roots to other parts of the plant and also for moving food produced by the leaves to different areas of the plant.
- Food Storage: Some plants, like sugarcane, potatoes, and ginger, have underground stems that store food.
Leaves

Leaves are essential for photosynthesis, the process by which plants produce their food. They come in various shapes and sizes, each with distinct parts:
- Leaf Blade or Lamina: The broad, flat part of the leaf that contains veins responsible for transporting nutrients and water.
- Stomata: Tiny openings on the surface of the leaf that facilitate gas exchange.
- Petiole: The stalk that connects the leaf blade to the stem, providing support and stability.
- Leaf Margin: The edges of the leaf, which can vary in shape and are useful for identifying different types of leaves.
Functions of Leaves
Leaves play a crucial role in keeping the plant healthy because they are the primary site for photosynthesis.
- Photosynthesis: Leaves are responsible for photosynthesis, a process essential for life on Earth. They contain chlorophyll, a green pigment that captures sunlight. Using this sunlight, leaves convert water and carbon dioxide into sugar and oxygen. This process not only provides food for the plant but also releases oxygen into the atmosphere, which is vital for the survival of most living organisms.
- Food Storage: In addition to photosynthesis, some leaves have the capability to store food. This stored food can be used by the plant when needed, providing an essential reserve of nutrients.
In summary, leaves are essential for a plant's survival as they enable photosynthesis and can also act as storage for important nutrients.
Flowers
Flowers are the most beautiful and interesting part of a plant. They come in many different shapes, colors, and smells. Flowers grow from buds and eventually become fruits that contain seeds. Some fruits have just one seed, while others have many.
Uses of Flowers

Apart from their aesthetic value, flowers serve various practical purposes:
Flowers are not just pretty; they are also very useful in many ways. Here are some of the ways we use flowers:
- Perfumes: Many flowers, like roses and jasmine, are used to make sweet-smelling perfumes.
- Edible Flowers: Some flowers, such as marigold, hibiscus, and nasturtium, are safe to eat and can add flavor to dishes.
- Spices: Certain spices come from flowers, like saffron, which is made from the crocus flower, and cloves, which are dried flower buds.
- Decoration: Flowers are often used to decorate at special events, and they are also used to make bouquets, garlands, and rangoli.
Understanding the different parts of plants and their functions provides valuable insights into the complex mechanisms that sustain life on Earth. By studying plants, students can develop a deeper appreciation for the natural world and gain a solid foundation in science.
|
53 videos|76 docs|59 tests
|
FAQs on Plants Chapter Notes - Science Olympiad Class 4
| 1. What are the main functions of roots in plants? |  |
| 2. How does the stem of a plant support its functions? |  |
| 3. What role do leaves play in the life of a plant? |  |
| 4. Why are flowers important for plants? |  |
| 5. How do different parts of a plant work together to ensure its survival? |  |















