Cultural Relativism | Psychology and Sociology for MCAT PDF Download
Introduction
Defining Culture- Beyond Ethnicity and Society: Culture is a fascinating and complex concept that encompasses the beliefs, behaviors, objects, and other characteristics shared by groups of people. While we often associate culture with ethnicity or society, it goes beyond these conventional boundaries. In today's interconnected world, one can claim to be influenced by internet culture, emphasizing the fluid nature of cultural identity.
Cultural Dimensions: Varied and Diverse
- Exploring Cultural Objects and Artifacts: Culture can manifest in various dimensions, including shared ethnicity, gender, customs, values, and even objects. Cultural objects hold significant value in many societies, such as ceremonial artifacts, jewelry, and clothing. For instance, Christmas trees symbolize both Western religious and commercial holiday culture, serving as cultural and ceremonial objects.
- Behavioral Patterns and Norms: Moreover, culture reflects the way a group thinks, their practices, behavioral patterns, and their worldview. Cultural norms can vary greatly across different societies. For example, in some countries like China, staring at others in public or standing close to strangers is considered acceptable. In contrast, in the United States, a study on Greyhound bus trips revealed that sitting next to another person when other seats are available is often viewed as socially awkward. These cultural norms highlight the vast differences in societal expectations and customs.
Culture Shock: Navigating Unfamiliar Territory
- Embracing Cultural Relativism: Encountering unfamiliar cultural norms can lead to a phenomenon known as culture shock. Picture yourself walking into a nearly empty movie theater in a foreign country and choosing not to sit next to the only person there. In such cases, someone may confront you for being rude, leaving you confused and anxious. This disorientation is a prime example of culture shock, highlighting the importance of understanding and respecting cultural differences.
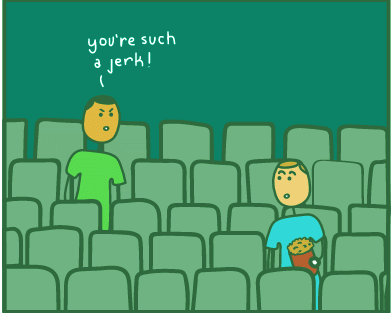
Cultural Relativism: An Inclusive Perspective
- Challenging Ethnocentrism: To avoid ethnocentrism, the tendency to judge or make assumptions about other cultures based on our own norms and values, cultural relativism offers an inclusive approach. Cultural relativism encourages us not to judge other cultures by our own standards of right or wrong, but to seek understanding within their unique cultural contexts. By adopting cultural relativism, we can foster empathy, appreciation, and respect for diverse cultural practices.

- Exploring Alternative Perspectives: Instead of dismissing cultural practices that may seem strange or unfamiliar, cultural relativism prompts us to delve deeper. For instance, rather than labeling fried crickets as disgusting, we can inquire about the reasons behind their consumption in certain cultures. By doing so, we may learn that fried insects are rich in protein and have been a healthy food source in Oaxaca, Mexico, for thousands of years. This broader perspective challenges our preconceived notions and promotes cultural understanding.
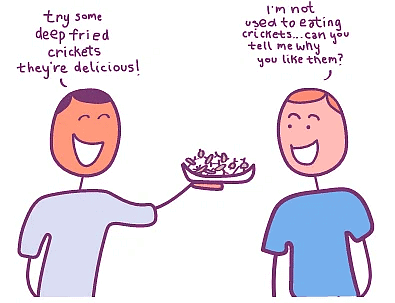
The Challenges of Cultural Interpretation
- The Dilemma of Cultural Practices: While cultural relativism provides a valuable framework, it can also raise challenging questions. One such question revolves around determining moral cultural behaviors. Different cultures may have conflicting viewpoints on practices such as whaling or female genital cutting. Environmental concerns clash with cultural traditions, necessitating a thoughtful examination of the balance between preserving cultural heritage and addressing ethical considerations.
- Impact of Language on Cultural Perspectives: Language plays a crucial role in shaping our perception of the world, as demonstrated by the Sapir-Whorf hypothesis. Linguistic relativism suggests that our thoughts are heavily influenced by our native language and its cultural context. For instance, the Hopi Indians' lack of words distinguishing between past, present, and future challenges our understanding of tense. Language reflects cultural experiences and influences the way we think about various aspects of life.
- Beyond Words: Unveiling Cultural Contexts: Learning a language goes beyond acquiring words; it involves grasping the cultural contexts embedded within the language. For instance, American high school clichés portrayed in movies may be bewildering to someone from a different cultural background. Explaining the nuances and meanings behind these groupings becomes challenging without a shared linguistic cultural context. Understanding language and culture is essential for effective communication and fostering cross-cultural appreciation.
Embracing Diversity: A Path to Cultural Understanding
- Celebrating Multiculturalism: In a globalized world, embracing cultural diversity is crucial for building inclusive societies. By adopting a cultural relativist perspective, we can learn to appreciate and understand the rich tapestry of human experiences. Recognizing that cultural practices differ and are shaped by unique historical, social, and linguistic contexts paves the way for empathy, respect, and meaningful intercultural exchanges.
- The Journey of Learning and Growth: Exploring cultural relativism enables us to broaden our perspectives, challenge assumptions, and embark on a journey of personal growth. By embracing diversity, valuing different cultural expressions, and seeking to understand rather than judge, we contribute to a more harmonious and inclusive global community.
Conclusion
Cultural relativism encourages us to embrace diversity, understand cultural differences, and challenge our preconceived notions. By adopting this approach, we can navigate the complexities of a globalized world, fostering empathy, respect, and appreciation for the richness of human cultures. Language and culture are intertwined, shaping our thoughts and perceptions. As we embark on the journey of cultural understanding, let us celebrate our shared humanity while recognizing and valuing the unique expressions of diverse cultures around the world.
|
339 videos|20 docs|42 tests
|















