Transformations and Natural Laws | General Chemistry for MCAT PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| The Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics |

|
| The First Law of Thermodynamics |

|
| The Second Law of Thermodynamics |

|
| The Third Law of Thermodynamics |

|
| Conclusion |

|
Introduction
Thermodynamics, an enthralling field encompassing physics and chemistry, holds immense significance in our understanding of energy, its conversions across different forms, and its ability to perform work. As we embark on this enlightening article, prepare to delve into the depths of thermodynamics, appreciating its relevance in our daily lives. Witness how the laws of thermodynamics seamlessly operate in the world around us, unraveling the secrets of energy and its behavior.
The Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics
What is Thermal Equilibrium?
Thermal equilibrium refers to the state of two systems that are in contact with each other, with no energy exchange occurring between them. In simpler terms, both systems have reached the same temperature. Explore how this concept, integral to our daily lives, impacts various phenomena.
Embracing Thermal Equilibrium: An Everyday Example
Discover how thermal equilibrium manifests in our day-to-day experiences, such as observing the cooling of a bowl of hot soup placed in a freezer. Gain a deeper understanding of how heat flows between systems of different temperatures until they reach thermal equilibrium, where no further heat exchange takes place.
The Zeroth Law: A Fundamental Connection
Unveil the Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics, which states that if two systems are in thermal equilibrium with a third system, they are also in thermal equilibrium with each other. This law underscores the crucial relationship between temperature and heat flow, as well as its implications in various contexts.
The First Law of Thermodynamics
Introduction to the First Law
Embark on a journey into the realm of energy conservation, as we explore the First Law of Thermodynamics. Learn that energy cannot be created nor destroyed, only transformed from one form to another. Witness the profound implications of this law on the internal energy of systems.
Understanding Internal Energy
Delve into the concept of internal energy, which comprises the kinetic and potential energies of molecules, as well as intermolecular forces. Grasp the intricate balance between energy transfer, heat, and work, shaping the internal energy of a system.
The First Law's Equation
Unearth the conventional statement of the First Law: "The change in internal energy of a closed system is equal to the heat added to it (Q) plus the work done on the system (W) by the surroundings." Dive into the mathematical representation of this law and comprehend its implications.
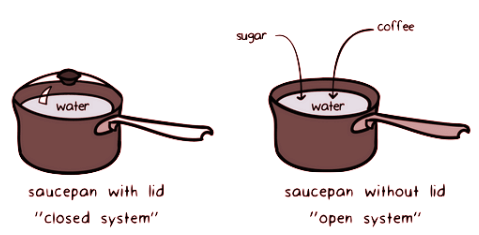
Exploring Closed and Open Systems
Differentiate between closed and open systems, shedding light on their distinct energy and matter exchange capabilities. Envision scenarios where a system solely interacts with its surroundings through energy exchange or facilitates both energy and matter transfers.
Sign Conventions and Real-World Applications
Master the sign conventions associated with the First Law of Thermodynamics, distinguishing positive and negative values for heat flow and work. Engage with a practical example of a gas in a sealed container, where heat energy causes expansion and work is performed.
The Second Law of Thermodynamics
Entropy: The Measure of Disorder
Unravel the concept of entropy, the measure of a system's disorder or randomness. Witness how natural processes tend to gravitate towards increased entropy, ultimately leading to a state of higher disorder. Gain insights into the irreversible nature of such processes.
The Second Law Unveiled
Explore the profound principle of the Second Law of Thermodynamics, which asserts that the total change in entropy of a system and its with the cutoff set at 4096 characters surroundings is always greater than or equal to zero. Discover the implications of this law in various domains, from heat engines to the arrow of time.

Heat Engines and Efficiency
Delve into the world of heat engines, devices that convert thermal energy into mechanical work. Learn about the Carnot cycle, a theoretical construct that represents the most efficient heat engine possible. Explore the concept of efficiency and the role of entropy in determining the maximum efficiency attainable.
Entropy and Irreversibility
Witness the connection between entropy and irreversibility in natural processes. Understand how the increase in entropy is a fundamental characteristic of irreversible processes, such as the dissipation of heat or the mixing of substances. Gain a deeper appreciation for the role of entropy in shaping the behavior of our universe.
Entropy and the Arrow of Time
Contemplate the intriguing concept of the arrow of time, which relates to the irreversibility of certain processes. Explore how the increase in entropy aligns with our perception of time flowing in a particular direction, leading to the past being distinguishable from the future. Marvel at the profound implications of this connection.
The Third Law of Thermodynamics
The Quest for Absolute Zero
Embark on a journey towards absolute zero, the lowest attainable temperature in the universe. Learn about the fascinating experiments and discoveries that led scientists to approach this extreme limit. Understand the significance of absolute zero in the context of the Third Law of Thermodynamics.
The Third Law Defined
Unveil the Third Law of Thermodynamics, which states that as the temperature of a system approaches absolute zero, its entropy approaches a minimum or zero value. Delve into the implications of this law in understanding the behavior of matter at extremely low temperatures.
Quantum Mechanics and Zero-Point Energy
Explore the realm of quantum mechanics and its connection to the Third Law of Thermodynamics. Gain insights into the concept of zero-point energy, where even at absolute zero, particles possess a minimum amount of energy due to quantum fluctuations. Witness the interplay between quantum mechanics and thermodynamics in extreme temperature regimes.
Conclusion
As we conclude our journey into the mysteries of thermodynamics, we have gained a profound understanding of the fundamental laws governing energy transformations and the behavior of systems. The Zeroth Law establishes the concept of thermal equilibrium, paving the way for the First Law's conservation of energy. The Second Law emphasizes the universal trend towards increased entropy and irreversibility, while the Third Law sheds light on the behavior of matter at absolute zero. With this knowledge, we can better comprehend the world around us, appreciate the beauty of natural laws, and unlock new frontiers in energy utilization and sustainability.
|
164 videos|11 docs|16 tests
|














