UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 13th June 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I
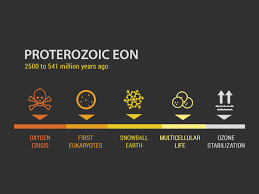
Proterozoic Eon
Why in News?
Recently discovered molecular fossils from the Proterozoic Eon may open the window to the ‘lost world’ of primordial life.
About Proterozoic Eon:-
- Proterozoic Eon was the last aeon of the Precambrian supereon.
- Precambrian era: it spans Era (4500–544 Ma) and includes almost 90% of Earth’s history.
- Eon (or aeon): is a term in Earth science for the longest periods of time.
- Era: it is a very long span of geologic time; the second longest portion of geological time.
- It spans from the time of the appearance of oxygen in Earth’s atmosphere to just before the proliferation of complex life (such as corals) on the Earth.
Major Events in the Proterozoic Eon:-
- Bacteria began producing oxygen, leading to the sudden rise of life forms.
- Eukaryotes (have a nucleus), emerge, including some forms of soft-bodied multicellular.
- Earlier forms of fungi formed around this time.
- The early and late phases of this aeon may have undergone Snowball Earth periods.
- Snowball Earth periods: when Earth suffered below-zero temperatures, extensive glaciation and as a result drop in sea levels.
- It was a very tectonically active period in the Earth’s history.
- It featured the first definitive supercontinent cycles and modern mountain buildings.
- It is believed that 43% of modern continental crust was formed in the Proterozoic, 39% formed in the Archean and only 18% in the Phanerozoic.
- In the late Proterozoic (most recent), the dominant supercontinent was Rodinia.
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
Cyclone Biparjoy

Why in News?
Developed in the Arabian Sea, cyclone Biparjoy is heading towards the northern Gujarat coast, with landfall expected on June 15.
About Tropical Cyclone:
- Tropical Cyclone is a weather phenomenon.
- A tropical cyclone is formed only over warm ocean waters near the equator.
- Warm, moist air rises up and away from the ocean surface, creating an area of low pressure.
- It causes the air from surrounding areas with higher pressure to move towards the low-pressure area.
- This leads to warming up of air and causes it to rise above.
- As the air rises & cools, the water in the air forms clouds.
- This complete system of clouds and wind spins & grows, along with the ocean’s heat.
- As the wind rotation speed increases, an eye gets formed in the middle.
What is an Extratropical Cyclone?
- Extratropical cyclones are low-pressure areas which are generally formed outside the tropics with a latitude range between 30 degrees and 60 degrees.
- They are also known as temperate cyclones.
- These low-pressure systems are associated with cold fronts, warm fronts, and occluded fronts.
How an Extratropical Cyclone is Formed?
- In the Northern hemisphere, cold air blows from the north of the front and warm air blows from the south.
- When the pressure descents along the front, the cold air move towards the south, and the warm air moves northwards setting in motion an anticlockwise cyclonic circulation.
- The cyclonic circulation results in a well-built extratropical cyclone, with a cold front and a warm front.
- There are pockets of warm air compressed between the forward and the rear cold air.
- The warm air climbs over the cold air and a series of clouds appear over the sky ahead of the warm front and cause rainfall.
- The cold front approaches the warm air from behind and pushes the warm air up.
- As an outcome, cumulus clouds develop along the cold front.
- The cold front moves faster than the warm front eventually surpassing the warm front.
- The warm air is entirely lifted and the front is occluded and the cyclone dissipates.
- They can originate over the land and sea and cover a larger area.
Source: The Hindu
Lower Subansiri Hydroelectric Power Project
Why in News?
State-run hydropower company NHPC Ltd. Will soon start trial runs for the Subansiri Lower project.
About Lower Subansiri Hydroelectric Power Project:
- It is the biggest hydroelectric project undertaken in India so far.
- It is a run-of-river scheme on river Subansiri.
- Location: The Project is located near North Lakhimpur on the border of Arunachal Pradesh and Assam.
- Capacity:2000MW
- It is a concrete gravity dam 116 m high from river bed level.
- It is being developed by the state-run National Hydro Power Corporation (NHPC).
Key facts about the Subansiri River:
- It originates in the Tibet Plateau and is the largest tributary of the Brahmaputra River.
- The high topographic variation makes this river a potential zone for harnessing it for the hydropower.
What is a Gravity dam?
- Gravity dams are massive structure dams which are constructed of concrete or stone masonry.
- Concrete gravity dams usually run in a straight line across a broad valley and resist the horizontal thrust of the retained water entirely by their own weight.
- This type of structure is durable and requires very little maintenance.
Source: Financial Express
GS-II
US to rejoin UNESCO

Why in News?
The UN cultural and scientific agency UNESCO announced that the US plans to rejoin — and pay more than $600 million in back dues.
- US has retreated after a decade-long dispute sparked by UNESCO’s move to include Palestine as a member.
UNESCO (United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization) | |
| Established | November 16, 1945 |
| Headquarters | Paris, France |
| Membership | 195 member states and 10 associate members |
| Mandate | Promoting international cooperation in education, science, culture, and communication |
| Objectives |
|
| Notable Programs and Activities |
|
A quick recap
- US and Israel’s withdrawal: Last December, the United States and Israel decided to leave UNESCO.
- Historical trajectory of engagement: The decisions should be viewed within a longer historical context.
Reasons for Withdrawal
- Anti-Semitic resolutions: The US and Israel cited several resolutions that they perceived as biased against Israel.
- Disdain for multilateralism and ‘America First’ policy: The US demonstrated a lack of interest in multilateral organizations and prioritized its own interests.
- Mounting arrears: The decision was based on mounting arrears, the need for reform, and perceived anti-Israel bias.
- Lack of interest in paying UNESCO debts: The Trump administration had little incentive to pay off debts accumulated since the Obama administration froze contributions.
Implications of the withdrawal
- Impact on UNESCO’s daily workings: The departure of the US and Israel impaired the organization’s operations.
- Limited consequence for Palestinians: The diplomatic victory for the Palestinian Authority was of little political or economic significance for Palestinians living under occupation.
Why is the US now joining back?
- Counterbalance China’s influence: The US aims to counterbalance China’s growing influence in shaping global policies on artificial intelligence and technology education.
- Protect and promote US interests: Rejoining allows the US to protect and advance its interests in cultural heritage preservation, climate change initiatives, and girls’ education.
- Reforms and diplomatic efforts: UNESCO’s management reforms and efforts to address concerns have contributed to the US decision to rejoin.
- Bipartisan support for engagement: The decision to rejoin UNESCO has received bipartisan support within the US, ensuring long-term engagement regardless of future political changes.
- Financial considerations and commitment: The US plans to fulfill financial obligations to UNESCO, including paying dues and arrears, demonstrating a commitment to supporting key initiatives within the organization.
Conclusion
- The decision of the United States to rejoin UNESCO reflects a strategic effort to counterbalance China’s influence, protect and promote American interests, and engage in international efforts for cultural preservation, climate change, and education.
Source: The Hindu
Global Slavery Index: Controversies with modern Metric
Why in News?
Report published: Published last week, the global slavery index provides an overview of modern slavery.
- 50 million people in modern slavery: The report reveals that approximately 50 million individuals were living in “modern slavery” on any given day in 2021.
- Existing slavery: Out of the 50 million affected, 28 million suffer from forced labor, while 22 million experience forced marriages. Shockingly, 12 million of those impacted are children.
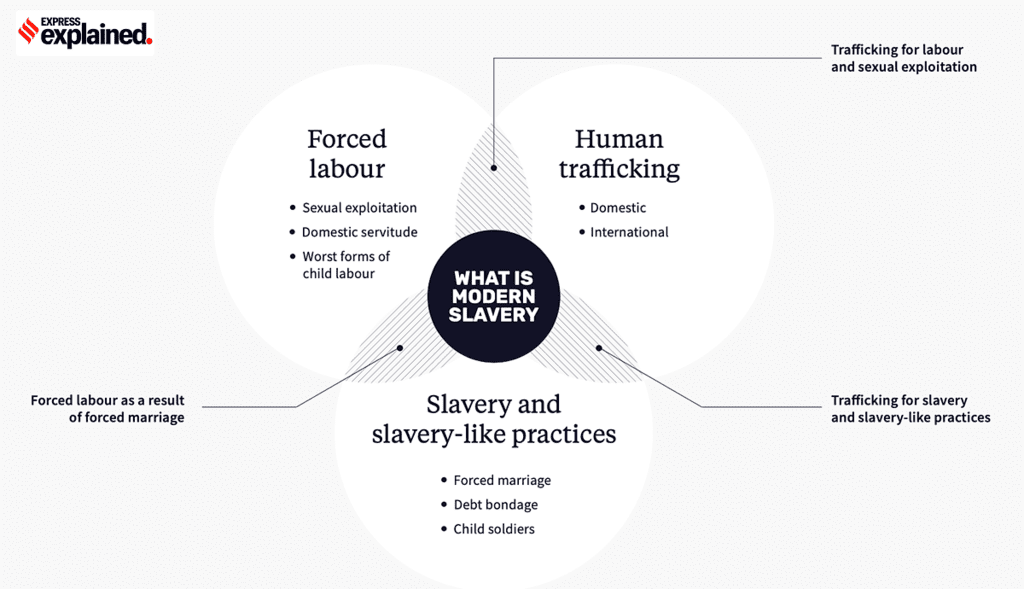
Definition of Modern Slavery
- Exploitation and inability to refuse or leave: “Modern slavery” encompasses situations where individuals are exploited and cannot decline or escape due to threats, violence, coercion, deception, or abuses of power.
- Broad range of abuses: Modern slavery is an umbrella term that covers various forms of exploitation, including forced labor, forced marriage, debt bondage, sexual exploitation, human trafficking, slavery-like practices, forced or servile marriage, and the sale and exploitation of children.
What is Global Slavery Index?
- Constructed by Walk Free: The Index is created by Walk Free, a human rights organization.
- Based on Global Estimates of Modern Slavery: The index relies on data provided by the Global Estimates of Modern Slavery, which is produced by the International Labour Organization (ILO), Walk Free, and the International Organization for Migration (IOM).
- Fifth edition: The recently published Global Slavery Index is the fifth edition and is based on the estimates from 2022.
- Country-wise estimates: While initial estimates are regional, the index employs representative surveys to determine country-specific estimates.
- Metrics: The index examines the prevalence of modern slavery by calculating the incidence per 1000 population.
Country-wise Findings
- Highest prevalence of modern slavery: The following ten countries have the highest prevalence: North Korea, Eritrea, Mauritania, Saudi Arabia, Turkey, Tajikistan, United Arab Emirates, Russia, Afghanistan, and Kuwait.
- Countries with lowest prevalence: Switzerland, Norway, Germany, Netherlands, Sweden, Denmark, Belgium, Ireland, Japan, and Finland have the lowest prevalence of modern slavery.
- Countries hosting the most people in modern slavery: The top ten countries are India, China, North Korea, Pakistan, Russia, Indonesia, Nigeria, Turkey, Bangladesh, and the United States.
Criticisms of the Index
- Lack of internationally agreed definition: One criticism is the absence of a universally accepted definition for modern slavery, unlike trafficking in persons which has an agreed-upon definition.
- Calculation based on “risk score”: Factors determining the risk often align with those used to classify countries as developed or developing, potentially leading to biased conclusions.
- Discrepancies in statistics: For instance, the index highlights the UK as having the “strongest government response to modern slavery,” but later mentions a decline in the UK’s overall response and potential violation of international law.
Challenges faced by developing countries
- Workers in countries like India: Countries such as India face significant challenges concerning modern slavery, as evidenced by the hardships experienced by workers during the COVID lockdown and subsequent reverse migration.
- Status of women: Women, particularly in terms of economic freedoms, face significant disparities, contributing to issues related to modern slavery.
Addressing the Issues
- Importance of addressing worker precarity: It is crucial to address the precarious situations faced by workers, particularly in the post-pandemic era and during G20 presidencies.
- Responsibilities of countries: Countries, especially G20 nations, bear the responsibility to combat issues like trafficking and modern slavery, rather than stigmatizing poorer nations and absolving richer nations of their obligations.
India’s measures against on modern slavery
- India has passed laws like the Bonded Labour Abolition Act of 1976 to address modern slavery.
- However, implementation challenges, corruption, legal loopholes, and lack of political hinder effective enforcement of these laws.
- Moreover, there are lacunas in the proper identification and enumeration of people trapped in modern slavery conditions.
Way forward
- Strengthen Measures and Legislation: Enact stronger laws to prevent the sourcing of goods and services associated with modern slavery.
- Embed Anti-Slavery Measures in Climate Change Plans: Integrate anti-slavery efforts into sustainability plans, acknowledging the link between climate change and vulnerability to modern slavery.
- Enhance Education and Tighten Regulations: Provide accessible education while tightening regulations on forced labor, child marriage, and exploitative practices.
- Prioritize Rehabilitation and Support: Prioritize comprehensive support systems for the rehabilitation of bonded laborers, including financial aid, education, job security, and fair compensation.
- Hold G20 Nations Accountable and Foster Cooperation: Ensure accountability among G20 nations and promote collaborative efforts to eliminate modern slavery.
Source: Indian Express
GS-III
Agency for New and Renewable Energy Research and Technology (ANERT)

Why in News?
The Kerala State government has recently, nominated the Agency for New and Renewable Energy Research and Technology (ANERT) as the State-level nodal agency for Green Hydrogen initiatives.
About Agency for New and Renewable Energy Research and Technology (ANERT):-
- ANERT is the single nodal agency for drafting and publishing the Green Hydrogen policy for the state of Kerala.
- A Chief Executive Officer (CEO) appointed by the Government heads ANERT.
- ANERT is also the Nodal Agency for the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy Sources (MNRE), Govt. of India, to carry out the National Programmes in Kerala.
- Chairman: Minister for Electricity
- Supervision: ANERT is guided by a:-
- Governing Body- chaired by the Minister for Electricity, Kerala and
- Executive Committee- chaired by the Additional Chief Secretary to Government/ Principal Secretary.
- Power Department, Government of Kerala provides guidelines for ANERT’s activities in various energy-related areas.
Objectives of ANERT:-
- To identify, formulate, implement and implementation of projects aimed at providing energy requirements of the State of Kerala.
- Evolving long-term plans based on harnessing solar energy, wind energy, wave energy, biogas, biomass, energy plantations, micro and mini hydel projects, improved chulahs etc.
- To identify, formulate, implement and support the implementation of a broad-based energy conservation program including the conservation of energy at the source of generation, at the state of distribution and/ or its utilization.
- To provide technical, financial or other assistance for popularization and creation of awareness on alternative sources of energy, energy conservation and rural technologies.
- To undertake or sponsor training programs, seminars workshops etc. on non-conventional sources of energy, energy conservation, and rural technology.
- To sponsor, co-ordinate or promote research programs or projects of a development nature involving the development of prototypes, pilot plant investigation in the area of alternative and new sources of energy and rural technologies, and
PROGRAMMES under ANERT:-
- Solar Photovoltaic Programmes
- Wind energy
- Solar Thermal Programme
- Improved chulhas
- Training and extension
- Other programmes
- Bioenergy
Green Hydrogen
- Green Hydrogen is produced by electrolysis using renewable energy.
- Electricity splits water into hydrogen and oxygen.
- By Products: Water, Water Vapor.
- It is called ‘green hydrogen’ because has no carbon footprint. (UPSC CSE: G)
- Other Types of hydrogen:-
- Brown hydrogen: produced using coal where the emissions are released into the air.
- Blue hydrogen: produced from natural gas, where the emissions are captured using carbon capture and storage.
Significance of Green Hydrogen for India:-
- Green hydrogen can drive India’s transition to clean energy and combat climate change.
- Green hydrogen energy is vital for India to meet its Nationally Determined Contribution (INDC) Targets.
- Under the Paris Climate Agreement, India pledged to reduce the emission intensity of its economy by 33-35% from 2005 levels by 2030.
- It will reduce import dependency on fossil fuels.
- The localisation of electrolyser production and the development of green hydrogen projects can create a new green technologies market in India worth $18-20 billion and thousands of jobs.
Advantages of green hydrogen:-
- Environment Friendly: Green Hydrogen as an energy source is seen as the next big thing as its usage would lead to zero emissions
- Potential to decarbonise various sectors: It is a clean burning molecule, which can decarbonise a range of sectors including iron and steel, chemicals, and transportation.
- Efficient utilization of Renewable Energy: Renewable energy that cannot be stored or used by the grid can be channelled to produce hydrogen.
Applications of green hydrogen:-
- It can be used in fuel cells to generate electricity, or power and heat.
Source: The Hindu
Chikungunya
Why in News?
According to a recently published research paper, a human clinical trial of a vaccine candidate to prevent chikungunya has returned a 99% immune response.
About Chikungunya:
- It is a viral disease transmitted to humans through the bites of mosquitoes infected with the chikungunya virus.
- The word comes from the African Makonde language and means "bent over in pain."
- It is most commonly transmitted by mosquitoes, Aedes (Stegomyia) aegypti and Aedes (Stegomyia) albopictus, which can also transmit dengue and Zika viruses.
- It was first described during an outbreak in southern Tanzania in 1952 and has now been identified in nearly 40 countries in Asia, Africa, Europe and the Americas.
- Symptoms:
- Symptoms usually begin 4 to 8 days after a mosquito bite but can appear anywhere from 2 to 12 days.
- The most common symptom is an abrupt onset of fever, often accompanied by joint pain.
- Other symptoms include muscle pain, headache, nausea, fatigue, and rash.
- Serious complications are uncommon, but atypical severe cases can cause long-term symptoms and even death, especially in older people.
- Treatment:
- There is currently no approved vaccine or specific treatment for chikungunya virus infections.
- The goal of treatment for the infection is to relieve symptoms with rest, fluids and drugs.
Source: Hindustan Times
|
38 videos|5293 docs|1118 tests
|























