UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Psychology for UPSC Optional (Notes) > Prejudice and Discrimination in Psychology
Prejudice and Discrimination in Psychology | Psychology for UPSC Optional (Notes) PDF Download
Introduction
Prejudice and discrimination are significant topics within the field of psychology, shedding light on the unjustified and negative attitudes people hold towards individuals based on their social group membership. This article explores the concepts of prejudice and discrimination, highlighting their differences, various explanations for their existence, and the impact of social norms on shaping these behaviors.
Understanding Prejudice and Discrimination
- Prejudice: Prejudice refers to an unfair or incorrect attitude held by an individual towards another person solely based on their membership in a particular social group. For instance, prejudice can manifest as racism, sexism, or other forms of biased views. Prejudice encompasses three components of an attitude: affective (emotional), behavioral, and cognitive.
- Discrimination: Discrimination involves the negative behavior or actions directed at an individual or a group, often based on factors such as sex, race, social class, and more. Unlike prejudice, discrimination solely focuses on the behavioral aspect and excludes the emotional and cognitive components of attitude.
Differences Between Prejudice and Discrimination
It is important to note that a person can hold prejudiced views without necessarily acting upon them, thus not engaging in discriminatory behavior. This means that someone can harbor prejudice against a particular group but refrain from discriminating against them. Discrimination is a specific manifestation of prejudice and involves observable actions or behaviors.
Explanations for Prejudice and Discrimination
Several theories and frameworks have been developed to explain the origins and perpetuation of prejudice and discrimination. The following are four main explanations:
- Authoritarian Personality: This theory suggests that individuals with an authoritarian personality are more prone to prejudice and discrimination. Such people adhere to strict social hierarchies and are likely to submit to authority figures, leading to biased attitudes and behaviors towards certain social groups.
- Realistic Conflict Theory – Robbers Cave: The realistic conflict theory posits that prejudice and discrimination emerge from competition between groups for limited resources. The famous Robbers Cave experiment demonstrated how intergroup conflict can foster prejudice and discrimination, emphasizing the role of competition in fueling biased attitudes.
- Stereotyping: Stereotyping involves categorizing individuals into groups based on certain characteristics and attributing generalized traits to all members of the group. These stereotypes often oversimplify complex social identities and contribute to prejudice and discrimination.
- Social Identity Theory: Social identity theory proposes that individuals derive part of their self-esteem and identity from the groups they belong to. This theory suggests that prejudice and discrimination can arise when people identify strongly with their own group and perceive other groups as threats or competitors.
Conformity as an Explanation of Prejudice and Discrimination
Conformity, the tendency to adopt the behavior and beliefs considered "normal" within a specific group or society, can also provide insight into prejudice and discrimination. Individuals may conform to social norms and exhibit prejudiced behavior due to influences from peers, parents, and other group members. Social norms define the accepted behaviors within a social group, and conforming to these norms can perpetuate prejudiced attitudes.
The Effect of Social Norms on Prejudice
- An influential study conducted by Minard (1952) explored how social norms influenced prejudice and discrimination. The research observed the behavior of black and white miners in a southern United States town, both above and below ground. Underground, where the social norm promoted friendly interactions between miners, 80% of white miners displayed friendliness towards their black counterparts. However, above ground, where the social norm encouraged prejudiced behavior, only 20% of white miners maintained friendly interactions. These findings revealed that individuals conformed to different norms depending on the social context, demonstrating the impact of social norms on prejudiced behavior.
- Pettigrew (1959) further investigated the role of conformity in prejudice. His study found a positive correlation between higher levels of conformity and greater levels of prejudice among white South African students. Similarly, the prevalence of prejudice against black people was higher in the southern United States compared to the north, attributed to the greater social acceptability of such prejudice in the southern region.
- Rogers and Frantz (1962) conducted research on immigrants to Rhodesia (now Zimbabwe) and discovered that the longer individuals resided in the country, the more they conformed to the prevailing cultural norm of prejudice against the black population.
Evaluation: Understanding the Role of Conformity
Conformity to social norms offers an explanation for prejudice in certain contexts. However, it is crucial to acknowledge that norms evolve over time, limiting the explanatory power of conformity alone in understanding prejudice and discrimination. Other factors, such as individual beliefs, personal experiences, and systemic influences, contribute to the complex nature of prejudice.
Examples of Discrimination
The table below provides examples of different forms of discrimination: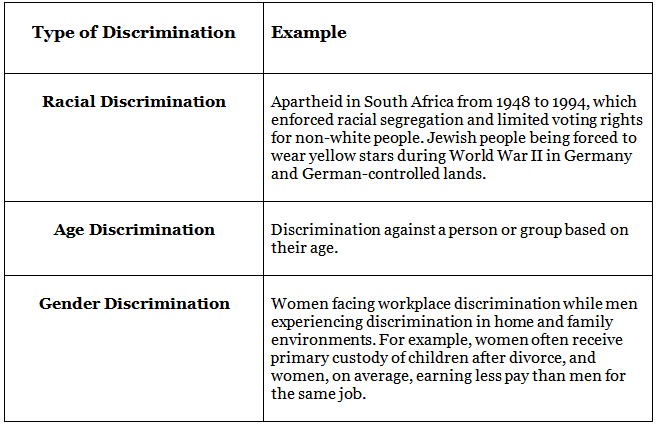
The document Prejudice and Discrimination in Psychology | Psychology for UPSC Optional (Notes) is a part of the UPSC Course Psychology for UPSC Optional (Notes).
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
160 videos|215 docs
|
Related Searches
















