UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Psychology for UPSC Optional (Notes) > Rapid Technological Growth and Environmental Degradation
Rapid Technological Growth and Environmental Degradation | Psychology for UPSC Optional (Notes) PDF Download
Introduction
In today's rapidly advancing world, technological advancements have played a vital role in helping nations overcome economic challenges. These advancements have the potential to create new markets and opportunities, provided that countries possess the necessary skills and competencies. However, it is crucial to address the environmental consequences that accompany rapid technological growth. This article explores the intersection of technological progress and its impact on the environment, highlighting the need for sustainable practices and responsible consumer behavior.
The Impact of Technological Advancements
As technology continues to advance at an unprecedented pace, its influence permeates various aspects of business, society, and culture. Cutting-edge technologies such as big data, the Internet of Things, artificial intelligence, and renewable energy systems have the potential to contribute significantly to achieving the Sustainable Development Goals and the 2030 Agenda. While these advancements offer promising prospects, they also pose challenges for policymakers. The disruptive nature of new technologies can reshape labor markets, exacerbate societal disparities, and raise ethical concerns that require careful governance.

Environmental Consequences of Technological Gadgets
Our modern lives are heavily intertwined with technology, especially portable electronic devices like smartphones, tablets, and laptops. While these devices have undoubtedly improved our quality of life, they have also had a profound impact on the environment. The production, consumption, and disposal of these gadgets contribute to resource depletion, energy consumption, carbon emissions, and waste generation. It is essential to recognize the full extent of their environmental footprint and take necessary measures to address these concerns.
Loss of Biodiversity
The adverse effects of technological progress extend beyond gadgets to include broader ecological consequences. Deforestation, water pollution, and the release of untreated sewage into natural water bodies have detrimental effects on aquatic ecosystems, leading to the loss of biodiversity. Diseases, eutrophication, and disruptions in the food chain further compound the negative outcomes associated with environmental degradation.
Digging Down for Resources
The production of electronic gadgets heavily relies on the extraction of natural resources and precious metals. Mining activities associated with these resources contribute to deforestation, landscape deterioration, water pollution, and significant carbon dioxide emissions. Greenhouse gases, particularly carbon dioxide, play a pivotal role in global warming, emphasizing the need for sustainable practices in resource extraction.
- The Mineral Intensity of Technology: Plastic and various metals play a vital role in the production of technological devices. However, the manufacturing processes required for these materials often involve high-emission production methods, leading to environmental issues. Additionally, the extraction of metals such as iron, aluminum, copper, lead, zinc, tin, nickel, and barium contributes to resource depletion and ecological damage.
- Significant Energy Consumption and Carbon Footprint: Transforming raw materials into sophisticated technological goods requires vast amounts of energy, resulting in a significant carbon footprint. Moreover, the global shipping of these products contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution. It is essential to address the energy consumption associated with technology and explore sustainable alternatives.
- E-Waste (Electronic Waste): The disposal of electronic waste, commonly known as e-waste, poses a significant challenge. Only a small fraction of obsolete electronics undergoes proper recycling, with most ending up in landfills or incinerated. The improper management of e-waste negatively impacts both human health and the natural environment. It is crucial for technology companies to adopt circular economy principles and encourage recycling and reuse to mitigate the environmental impact.
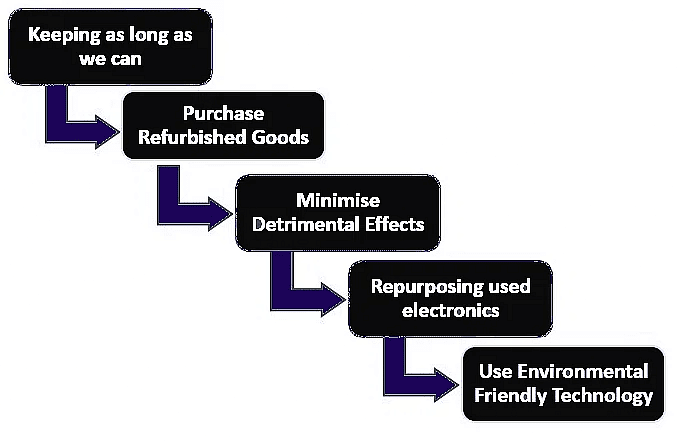
Responsible Consumer Actions
While the responsibility lies with technology companies to implement sustainable practices, individual consumers can also contribute to minimizing environmental damage. Actions such as prolonging the use of existing devices, opting for used or refurbished products, seeking sustainable and ethical solutions, and creatively repurposing old electronics can significantly reduce environmental footprints. By advocating for responsible technology recycling practices and urging governments and technology companies to prioritize environmental responsibility, consumers can play a crucial role in promoting a more sustainable future.
Conclusion
As consumers, we hold considerable power to drive environmental sustainability through our choices and demands. The rapid growth of technology must be accompanied by responsible practices that mitigate its environmental impact. By embracing sustainable alternatives, supporting circular economy principles, and demanding accountability from technology companies, we can contribute to a more harmonious and sustainable future for our planet.
The document Rapid Technological Growth and Environmental Degradation | Psychology for UPSC Optional (Notes) is a part of the UPSC Course Psychology for UPSC Optional (Notes).
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
160 videos|215 docs
|
Related Searches















