Motivation Theories | Psychology for UPSC Optional (Notes) PDF Download
Introduction
Motivation is a powerful force that fuels human actions, driving individuals to work with enthusiasm and commitment to achieve their goals. It plays a crucial role in personal and professional success, and understanding the various motivational theories can provide valuable insights into human behavior. In this article, we explore five famous motivation theories that shed light on what motivates individuals and how their needs and expectations influence their behavior. From Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs to McGregor's Theory X and Theory Y, these theories offer a comprehensive framework for understanding and harnessing motivation in different contexts.
Maslow's Theory of Hierarchical Needs
Abraham Maslow's Theory of Hierarchical Needs posits that individuals are motivated by a progression of needs that must be fulfilled in a specific order. Maslow presented these needs in a pyramid, emphasizing that higher-level needs cannot be pursued until lower-level needs are satisfied. The hierarchy includes:
- Physiological needs: Basic requirements for survival, such as air, sleep, food, water, clothing, sex, and shelter.
- Safety needs: Protection from threats, deprivation, and other dangers, encompassing health, secure employment, and property.
- Social (belongingness and love) needs: The need for association, affiliation, friendship, and social connections.
- Self-esteem needs: The need for respect, recognition, and a positive self-image.
- Self-actualization needs: The opportunity for personal development, learning, and engaging in challenging and fulfilling work.
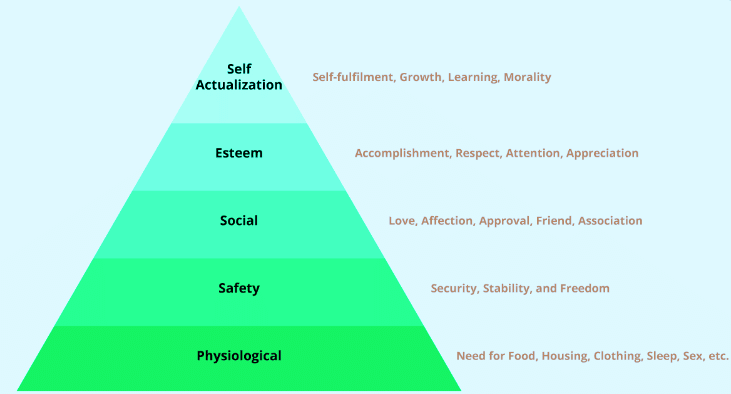
Understanding where individuals stand in this hierarchy can help leaders tailor their approach to motivate and support their team members effectively. By addressing specific needs, leaders can foster a conducive environment for growth and performance, thereby enhancing overall project management outcomes.
Herzberg's Two-Factor Theory
- Frederick Herzberg's Two-Factor Theory categorizes motivating factors into two broad groups: hygiene factors and motivating factors. Hygiene factors, such as working conditions, coworker relations, policies and rules, and supervisor quality, primarily serve to prevent dissatisfaction. While improving these factors can mitigate dissatisfaction, it does not necessarily motivate individuals. On the other hand, motivating factors, including achievements, recognition, responsibility, and the nature of the work itself, have a positive influence on job satisfaction and motivation.
- Herzberg's theory emphasizes that addressing hygiene factors alone is insufficient for long-term motivation. To cultivate a motivated workforce, organizations must focus on enhancing motivating factors and providing opportunities for personal and professional growth.
McClelland's Theory of Needs
McClelland's Theory of Needs asserts that individuals have three dominant motivating drivers: achievement, affiliation, and power. These drivers are not dependent on factors like gender or age but are shaped by an individual's life experiences. The three motivators are:
- Achievement: The need to accomplish goals and demonstrate personal competence, often preferring tasks that provide autonomy, personal responsibility, and acknowledgment of progress.
- Affiliation: The need for love, belonging, and social acceptance, driven by a desire to be liked and accepted by others, participating in social gatherings, and avoiding conflict.
- Power: The need for control over one's work or the work of others, aspiring for positions of status and authority, and seeking influence over others.
By understanding an individual's dominant driver, leaders can create an environment that aligns with their motivational needs, leading to higher engagement, productivity, and job satisfaction.
Vroom's Theory of Expectancy
Vroom's Expectancy Theory of Motivation posits that an individual's motivation is influenced by their expectations about the future. This theory highlights three key elements that impact motivation:
- Expectancy: The belief that increased effort will lead to improved performance, which can be influenced by factors such as available resources, management skills, and necessary support.
- Instrumentality: The belief that successful performance will result in desirable outcomes, depending on factors like clear performance-outcome relationships, trust in decision-makers, and transparency in the reward process.
- Valence: The importance an individual places on expected outcomes, considering personal preferences and priorities.
Vroom's theory emphasizes that individuals make choices based on these elements and the perceived value they attach to the expected outcomes. By aligning these factors effectively, leaders can enhance motivation and drive desired performance.
McGregor's Theory X and Theory Y
Douglas McGregor's Theory X and Theory Y offer contrasting management styles based on two assumptions about employee motivation and behavior. These theories can guide leaders in shaping their managerial approach:
- Theory X: Assumes that employees dislike work, lack motivation, require constant supervision, and avoid responsibility. Managers adhering to Theory X tend to adopt an authoritarian style, closely monitoring and controlling their team members' work.
- Theory Y: Assumes that employees are intrinsically motivated, take pride in their work, and seek challenges and growth. Managers following Theory Y employ a participative management style, allowing employees to take ownership of their work and exercise autonomy.
By adopting Theory Y principles, leaders can create a supportive and empowering environment that fosters employee motivation, initiative, and self-directed performance.
Alderfer's ERG Theory
Clayton Alderfer expanded on Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs, introducing his ERG (Existence, Relatedness, Growth) Theory. Alderfer's theory categorizes core needs into three groups:
- Existence needs: Basic material requirements for survival, including physiological needs (e.g., air, sleep, food, water) and safety-related needs (e.g., health, secure employment).
- Relatedness needs: The importance of maintaining interpersonal relationships, encompassing social needs (e.g., friendship, family) and esteem-related needs (e.g., gaining respect from others).
- Growth needs: Intrinsic desire for personal development, covering esteem-related needs (e.g., self-esteem, achievement) and self-actualization needs (e.g., creativity, problem-solving).
Alderfer's theory allows for more flexibility than Maslow's hierarchy, acknowledging that frustration or dissatisfaction in higher-level needs can lead individuals to focus on satisfying lower-level needs. Managers must recognize and address multiple needs simultaneously, taking into account the frustration-regression aspect of the ERG theory.
Conclusion
Motivation serves as the driving force behind human actions and behavior, shaping personal and professional outcomes. By understanding and applying the principles outlined in these five famous motivation theories, leaders can unlock the potential of their team members, foster engagement, and drive performance. From addressing hierarchy of needs to empowering employees and providing growth opportunities, an effective understanding of motivation can yield significant benefits in organizations.
|
160 videos|215 docs
|















