UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Psychology for UPSC Optional (Notes) > Psychology in Advertising
Psychology in Advertising | Psychology for UPSC Optional (Notes) PDF Download
Introduction
A basic advertisement involves a lot of strategy and thought, as well as more planning than one may assume. From the color scheme and visuals to the actual words used, each component of an ad is designed to appeal to the consumer in a unique way. Every aspect is specifically designed using basic principles of psychology to generate a desired reaction or response. While there are many potential psychological elements to incorporate, the use of emotions, persuasion and authority, memories, and colors are a few of the more common ones.
Emotions: Influencing Consumer Behavior
Advertising often plays to consumers' emotions. Fear, love, pleasure, or vanity can be powerful drivers of consumer desires and responses. Each of these emotions can be manipulated and used in a different way to affect behavior.
Fear: Motivating Action
Fear is a very powerful emotion and can be a robust motivator. Advertising can use fear tactics to create an uncomfortable position or situation, then provide a solution manifested through a given product or service. The approach of "the fear of missing out" is a common tactic, emphasizing urgency and scarcity to encourage immediate action.
Fun, Pleasure, and Love: Creating Desire
Advertisements utilizing fun and pleasure show consumers having a good time and enjoying themselves, all made possible by a given product or service. Love, as a primal emotion, can drive strong consumer behavior. Advertisements featuring love tap into the desire to provide the best for loved ones, positioning the advertised products as necessary to meet that need.
Vanity: Appealing to Self-Importance
Advertisements focused on vanity appeal to the consumer's sense of well-being, pride, importance, and relevance. By leveraging themes such as the latest trends and luxury, advertising drives awareness, interest, and action for the advertised brands. Appearance, status, and social validation play a significant role in these types of ads.
Persuasion and Authority: Building Trust and Credibility
One of the best ways to persuade someone to take action is to gain their trust or provide irrefutable logic. Advertising employs celebrity endorsements, as many consumers have implicit trust in celebrities. Celebrities can provide instant credibility for a product or service. Furthermore, persuasion and authority can be established through the power of experts or trusted peers, leveraging phrases such as "9-out-of-10 doctors recommend" or "3 out of 4 moms trust."
Memories: Crafting Positive Associations
Memories play a crucial role in advertising, as they are subject to alteration and malleability. Advertisers can leverage the malleability of memories to create affinity and intent. By creating positive and happy memories associated with their brand or product, companies can reinforce positive associations and potentially overshadow any negative experiences in consumers' minds.
Colors: Shaping Perception and Emotion
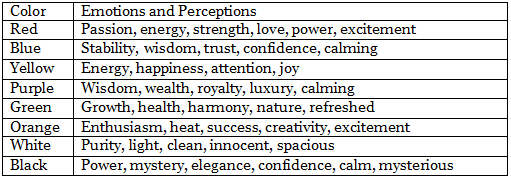
Colors evoke strong emotions and can influence how an advertisement is perceived. Each color serves a different purpose within an advertisement, controlling the emotional response and perception. Here are examples of how different colors can change the mood of an ad.
Table: Mood and Perception by Color
Psychology in Advertising: Driving Successful Campaigns
Psychology plays a significant role in the overall design and success of an advertising campaign. By incorporating basic psychological principles, ads can be created to generate desired emotions and reactions, ultimately driving desired consumer behaviors. Ads can be targeted to specific demographic or psychographic groups, enhancing brand recall, awareness, and overall brand affinity. Understanding the human mind and leveraging basic psychological principles are key to successful advertising and branding.
The document Psychology in Advertising | Psychology for UPSC Optional (Notes) is a part of the UPSC Course Psychology for UPSC Optional (Notes).
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
160 videos|215 docs
|
Related Searches
















