Ergonomics | Psychology for UPSC Optional (Notes) PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Ergonomics Process |

|
| Why is Ergonomics Important? |

|
| How does Ergonomics Work? |

|
| Benefits of Ergonomics |

|
Introduction
Ergonomics, the study of people in their workplace, is a scientific discipline that focuses on designing or rearranging workplaces, products, and systems to fit the individuals who use them. Its primary goal is to enhance workspaces and environments in order to reduce the risk of injuries. By understanding the interactions among humans and other elements of a system, ergonomics seeks to optimize human well-being and overall system performance. It is a multidisciplinary field that incorporates knowledge from anatomy and physiology, psychology, engineering, and statistics to create designs that align with the strengths and abilities of the users.
Ergonomics Process
The process of implementing ergonomics involves several key steps:
- Assess Risks: Identify potential hazards and risks associated with the workplace, taking into account factors such as awkward postures, extreme temperatures, and repetitive movements.
- Plan Improvements: Develop strategies and plans to modify or redesign the workspace, products, or systems to mitigate the identified risks and improve ergonomics.
- Measure Progress: Continuously evaluate the effectiveness of the implemented changes and monitor the impact on the well-being and performance of the individuals.
- Scale Solutions: Implement successful ergonomic solutions on a larger scale, considering the specific needs and requirements of the users.
Why is Ergonomics Important?
Ergonomics plays a crucial role in creating safe, comfortable, and productive workspaces. When the human body is subjected to awkward postures, extreme temperatures, or repetitive movements, the musculoskeletal system can be negatively affected, leading to various work-related injuries or illnesses. By incorporating ergonomic principles into workspace design, the risk of conditions such as computer vision syndrome, neck and back pain, and carpal tunnel syndrome can be significantly reduced. The primary reasons why ergonomics is important include:
- Ensuring Individual Fit: Designing workspaces that consider the body size, strength, skill, speed, sensory abilities, and attitudes of the individuals using them.
- Enhancing Comfort and Productivity: Creating work environments that promote comfort and increase productivity among employees.
How does Ergonomics Work?
Ergonomics relies on the collection of data and information from various disciplines to inform the design, modification, or rearrangement of equipment and systems. The following disciplines contribute to the field of ergonomics:
- Anthropometry: Study of body sizes, shapes, and variations among different populations.
- Biomechanics: Analysis of muscles, levers, forces, and strength in relation to human movement and tasks.
- Environmental Physics: Consideration of factors such as noise, light, heat, cold, radiation, and vibration in the design of workspaces.
- Body Systems: Understanding the impact of work environments on hearing, vision, and other sensory abilities.
- Applied Psychology: Incorporating knowledge of skill acquisition, learning processes, human errors, and individual differences in the design of systems.
- Social Psychology: Focusing on group dynamics, communication, learning, and behavioral aspects within the workplace.
- Mechanical and Industrial Engineering: Application of engineering principles to improve the design and functionality of workspaces and equipment.
- Industrial Design: Incorporating aesthetic and functional elements to create user-friendly and visually appealing products.
- Information Design: Designing information displays and interfaces that are intuitive and easy to understand.
- Kinesiology: Study of human movement and its relationship to physical activity, health, and well-being.
- Physiology: Understanding the physiological responses of the human body to different work environments and tasks.
Domains of Specialization in Ergonomics
Ergonomics encompasses three broad domains, each focusing on specific aspects of human interaction within the workplace:
- Physical Ergonomics: This domain primarily addresses workplace ergonomics, considering human anatomical, anthropometric, physiological, and biomechanical characteristics. It aims to design jobs and work environments that match the capabilities of individuals, resulting in better working experiences and reducing the risk of work-related musculoskeletal disorders.
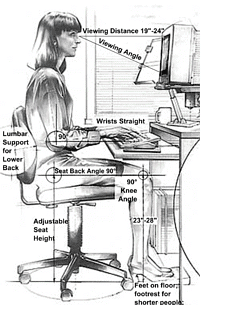
- Cognitive Ergonomics: Cognitive ergonomics explores mental processes such as perception, memory, reasoning, and motor response, and their impact on human interactions. It focuses on ensuring that the use of products aligns with users' cognitive capabilities, facilitating ease of use and enhancing overall usability.
- Organizational Ergonomics: Organizational ergonomics is concerned with optimizing social-technical systems, including organizational structures, policies, and processes. It takes into account factors such as teamwork, job shifts, work satisfaction, schedules, and ethical considerations, aiming to create work environments that enhance productivity, well-being, and job satisfaction.
Benefits of Ergonomics
Implementing ergonomic principles in the workplace offers numerous benefits, including:
- Reduced risk of work-related injuries and illnesses.
- Increased productivity among employees.
- Improved overall health and well-being.
- Enhanced mental clarity and insight.
- Better product quality.
- Decreased pain and discomfort.
- Happier and more engaged employees.
- Improved safety culture within the organization.
Conclusion
Ergonomics is a vital field that combines scientific knowledge from various disciplines to create workspaces, products, and systems that prioritize human well-being and performance. By understanding and addressing the needs and limitations of individuals, ergonomic design minimizes the risk of work-related injuries and enhances productivity. With its multidisciplinary approach, ergonomics continues to play a significant role in creating safer, more comfortable, and productive work environments.
|
160 videos|215 docs
|



















