UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Psychology for UPSC Optional (Notes) > Effective Strategies for Social Change
Effective Strategies for Social Change | Psychology for UPSC Optional (Notes) PDF Download
Introduction
Simple, selfless gestures like giving a stranger a kind smile or keeping the door open for them may have a profound effect on the world. Sometimes these spontaneous acts of goodwill can result in a ripple impact that stretches far beyond the initial performer. In this article, we will explore effective strategies for social change, highlighting the key roles and actions that individuals and groups can undertake to create meaningful transformations in society.
The Power of Small Acts: Magnitude of Effects
Meaningful social change begins with human interactions and connections. The effects of these shifts on society are cumulative and often far-reaching. Even seemingly insignificant acts of kindness can have a significant impact on the recipient's day and well-being. The magnitude of these effects, both for the recipient and the problem solver, can exceed expectations, demonstrating the power of small acts in creating positive change.
Key Roles for Effective Strategies in Social Change
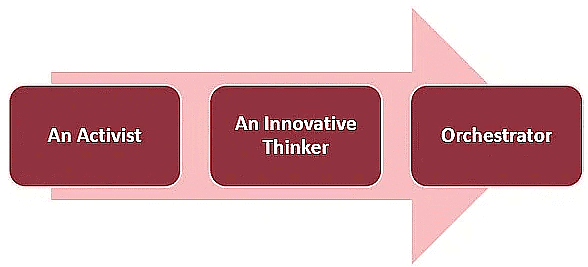
To effectively bring about social change, three key roles come into play: the Initiator, the Entrepreneur, and the Creative Force. Each role contributes uniquely to the process and is essential for any route seeking to affect meaningful social change.
- The Initiator: An initiator is an activist who raises awareness about the problems faced by a particular group or groups of people. They use a variety of appeals, including reason, justice, and passion, to increase the resonance of the issues. It is crucial for activists to understand and respect the diverse perspectives of all those involved.
- The Entrepreneur: An innovative thinker, the entrepreneur, is responsible for devising workable solutions to address the identified problems. They often draw upon their connections across various fields, allowing them to challenge established norms and develop novel solutions.
- The Creative Force: Acting as an orchestrator, the creative force organizes the efforts of multiple entities to bring the recommended solutions to a wider audience. By constructing venues for discourse and strategic alignment, they ensure effective coordination among different individuals, companies, and sectors, thereby maintaining momentum towards the desired change.
Collective Action for Effective Change
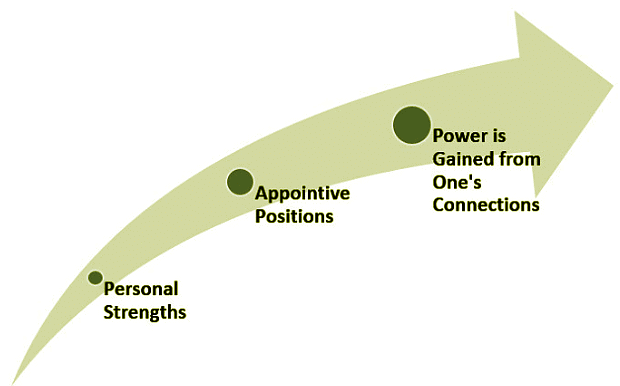
Creating effective social change requires mobilizing others to take collective action. This can be achieved by channeling various resources available to individuals and groups. Here are some potential sources of power:
- Personal Strengths: Personal attributes such as personality, hard work, experience, interests, and knowledge contribute to an individual's power to bring about change.
- Electoral and Appointive Positions: Holding legal positions of authority within institutions and societies grants individuals the power to implement change through policy and decision-making.
- Connections: Power can also be derived from one's connections with others, including family, friends, and coworkers. Leveraging these networks can facilitate cooperation and collaboration for social transformation.
Cooperation for the Most Effective Social Transformation
When individuals or groups assume the roles of agitators, innovators, or orchestrators, the tasks of communication, organization, and evaluation become paramount. Additionally, alternative energy sources are often required. To influence positive social change effectively, members of social movements should focus on the following three aspects:
- Communication: Leaders play a crucial role in fostering conversation and creating a consensus regarding the current gap, the desired end objective, and the best approach to bridge that gap. The power of storytelling can invoke empathy and motivate followers to take action.
- Organization: Organizing methods, techniques, and even formal organizational bodies are essential for coordinating collaborative action towards change. Participatory governance arrangements and advocacy organizations that foster public voice and collective identity can be instrumental in adapting to changing circumstances and achieving movement goals.
- Evaluation: Leaders must regularly assess the progress of the movement, especially when dealing with qualitative changes in people's actions, attitudes, and beliefs. Evaluating the acceptance of change over time helps the group maintain focus on its objectives and engage individuals despite setbacks. Evaluation can range from simple checkboxes early on to a more nuanced process that tracks outputs and potential effects.
Who Should Do What, and When?
As circumstances evolve, individuals must adapt to new responsibilities. When considering the roles of agitator, innovator, or orchestrator, leaders should ask themselves the following questions:
- Timing: When is it appropriate for a shift to occur? Assessing the right moment for change is crucial to maximize its impact.
- Alternative Solutions: Are there other solutions available that can be implemented? Exploring a range of possibilities helps identify the most effective approach.
- Implementation: Do we have plans in place to ensure the dissemination of existing solutions? Having strategies to promote and implement proven solutions is vital for achieving meaningful social change.
Conclusion
In a world where dissatisfaction with the status quo is widespread, identifying the roles of agitators, innovators, and orchestrators becomes increasingly important. From major political events like Brexit to grassroots movements like the Women's March, people from all walks of life are striving to create positive change. The challenge lies in organizing protests creatively while adhering to democratic norms, valuing diverse viewpoints, and fostering compromise. Local-level action provides an opportunity to experiment, learn, and demonstrate immediate victories, offering an alternative to the current status quo. By embracing effective strategies for social change, individuals and groups can work together to create a brighter future for all.
The document Effective Strategies for Social Change | Psychology for UPSC Optional (Notes) is a part of the UPSC Course Psychology for UPSC Optional (Notes).
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
160 videos|215 docs
|
Related Searches





















