Science and Technology: May 2023 UPSC Current Affairs | Science & Technology for UPSC CSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| ISRO's new NavIC Satellite NVS-01 |

|
| Fortification of Rice |

|
| XPoSat |

|
| PetaFLOP Supercomputers |

|
| Mitochondrial Replacement Therapy (MRT) |

|
| Aurora Borealis |

|
| Psychedelic Substances |

|
ISRO's new NavIC Satellite NVS-01
Why in News?
The NVS-01 satellite was successfully launched by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) using the GSLV-F12, and after a 19-minute flight, it was accurately placed into a Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit.
- GSLV-F12 is the 15th flight of India’s GSLV (Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle) and the 9th flight with indigenous cyro stage. This is the 6th operational flight of GSLV with indigenous cryogenic stage.
What is NVS-01?
- About:
- This satellite is the first of the second-generation satellites of ISRO’s NVS (Navigational Satellite) series of payloads.
- It weighs 2,232 kg, making it the heaviest in the constellation.
- The NVS-01 carried navigation payloads L1, L5 and S bands.
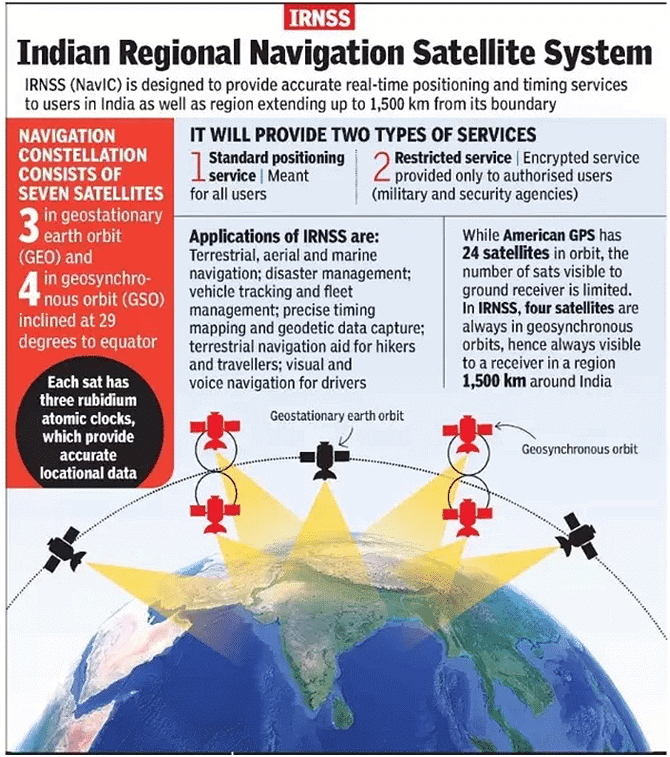
- Its purpose is to provide continuity for the NavIC (Navigation in Indian Constellation) services, which is an Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (similar to GPS) that offers accurate and real-time navigation within India and up to a 1,500 km region around the country.
- In the First generation, there are seven satellites in the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS) constellation, operationally named NavIC, weighing much less — around 1,425 kg — at liftoff.
- Atomic Clock:
- The satellite will have a Rubidium atomic clock onboard, a significant technology developed by India.
- Some of the existing satellites in the navigation constellation lost their ability to provide accurate location data due to failed atomic clocks. Satellite-based positioning systems rely on precise time measurements from atomic clocks to determine object locations. When the clocks fail, the satellites cannot provide accurate location information anymore.
- The satellite will have a Rubidium atomic clock onboard, a significant technology developed by India.
- L1 signals for better use in wearable devices:
- It will send signals in a third frequency, L1, besides the L5 and S frequency signals that the existing satellites provide, increasing interoperability with other satellite-based navigation systems.
- The L1 frequency is among the most commonly used in the Global Positioning System (GPS), and will increase the use of the regional navigation system in wearable devices and personal trackers that use low-power, single-frequency chips.
- It will send signals in a third frequency, L1, besides the L5 and S frequency signals that the existing satellites provide, increasing interoperability with other satellite-based navigation systems.
- Longer Mission Life:
- It will have a longer mission life of more than 12 years. The existing satellites have a mission life of 10 years.
What is NavIC?
- About:
- NavIC or the IRNSS is designed with a constellation of 7 satellites and a network of ground stations operating 24×7.
- There are a total of eight satellites however only seven remain active.
- Three satellites in geostationary orbit and four satellites in geosynchronous orbit.
- The constellations' first satellite (IRNSS-1A) was launched on 1st July 2013 and the eighth satellite IRNSS-1I was launched in April 2018.
- With the seventh launch of the constellation's satellite (IRNSS-1G), IRNSS was renamed NavIC by India’s Prime Minister in 2016.
- It was recognised by the International Maritime Organization (IMO) as a part of the World-Wide Radio Navigation System (WWRNS) for operation in the Indian Ocean Region in 2020.
- NavIC or the IRNSS is designed with a constellation of 7 satellites and a network of ground stations operating 24×7.
- Potential Uses:
- Terrestrial, aerial and marine navigation;
- Disaster management;
- Vehicle tracking and fleet management (especially for mining and transportation sector);
- Integration with mobile phones;
- Precise timing (as for ATMs and power grids);
- Mapping and geodetic data capture.
What is the Advantage of Having a Regional Navigation System?
- Regional Navigation System:
- NavIC is India's own regional navigation system developed by ISRO. It covers the Indian landmass and extends up to 1,500 km around it. The primary purpose of NavIC is to cater to the positioning and navigation needs of users in this specific region.
- Ground Stations:
- ISRO is working on setting up ground stations in countries like Japan, France, and Russia. These additional ground stations will enhance the accuracy and coverage of NavIC signals through better triangulation.
- Signal Reception:
- NavIC signals reach India at a 90-degree angle, making it easier for the signals to penetrate congested areas, dense forests, and mountainous terrain. In contrast, GPS signals arrive at an angle, which can sometimes pose challenges for reception in certain locations.
- Availability:
- NavIC signals are primarily designed to serve the Indian region. Therefore, users within the coverage area can expect reliable access to NavIC signals, even in remote or hard-to-reach areas.
Fortification of Rice
Why in News?
In a response to the recent wave of criticism surrounding the distribution of iron fortified rice, the Union Food Ministry has released an official statement dismissing the allegations levelled against the iron fortified rice.
What is Fortification of Rice?
- About:
- Fortification is the process of adding nutrients to food products that are not naturally present or are present in insufficient amounts.
- Fortification of rice can be done by coating the rice grains with a premix of micronutrients, or by producing extruded rice kernels that are enriched with micronutrients and then blended with regular rice.
- According to Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) norms, 1 kg fortified rice shall contain iron (28 mg-42.5 mg), folic acid (75-125 microgram) and Vitamin B-12 (0.75-1.25 microgram).
- Purpose:
- India has very high levels of malnutrition among women and children. According to the Food Ministry, every second woman in the country is anemic and every third child is stunted.
- Rice is a source of protein and contains various vitamins. Some nutrients, including vitamin E, magnesium, potassium, and manganese, are lost during milling and polishing (the process by which brown rice becomes white or polished rice).
- Rice is one of the most widely consumed staple foods in the world, especially in Asia and Africa.
- Per capita rice consumption in India is 6.8 kg per month. Therefore, fortifying rice with micronutrients is an option to supplement the diet of the poor.
- Iron deficiency also is a major public health problem that affects more than two billion people globally, causing anaemia, weakness, fatigue, impaired learning and increased risk of infections and maternal mortality.
- To address this problem, some countries have adopted the strategy of fortifying rice with iron and other micronutrients, such as folic acid and vitamin B12.
- Most of the iron we need comes from meat, which gets absorbed 50% by our body. Through vegetables, there is limited intake and only 3% absorption. This is the reason why iron deficiency is a major problem in India.
What are the Benefits of Iron Fortification of Rice?
- According to the World Health Organization (WHO), fortification of rice with micronutrients can be an effective, simple and inexpensive strategy to improve the nutritional status and health outcomes of populations that consume rice regularly. Some of the benefits of iron fortification of rice are:
- Improved Cognitive Development: Iron plays a crucial role in brain development and function.
- Adequate iron intake during early childhood is essential for optimal cognitive development and learning abilities.
- By fortifying rice with iron, particularly in regions where rice is a primary dietary staple, the potential for cognitive impairment due to iron deficiency can be reduced, leading to improved cognitive performance and better educational outcomes.
- Enhanced Maternal and Infant Health: Anemia is prevalent among pregnant women and can increase the risk of complications during pregnancy and childbirth.
- Iron fortification of rice can help improve the iron status of pregnant women, reducing the occurrence of maternal anemia and the associated risks. Additionally, adequate iron intake during pregnancy is essential for fetal development and can contribute to healthy birth outcomes.
What are the Risks Associated with Iron Fortification of Rice?
- Chances of Ineffectiveness:
- It may not be sufficient to meet the iron requirements of all individuals, especially those with high needs or low bioavailability of iron.
- Bioavailability of iron refers to the proportion of iron that is absorbed and utilised by the body, which depends on several factors such as the type and amount of iron compound used for fortification, the presence of enhancers or inhibitors of iron absorption in the diet, and the physiological status and genetic variation of the individual.
- Adverse Effects on Sensitive Individuals:
- It may cause adverse effects in some individuals who have excess iron intake or accumulation. Excess iron can be toxic to the body and cause oxidative stress, inflammation, organ damage and increased risk of infections and chronic diseases.
- Some groups that may be at risk of excess iron intake or accumulation are those with genetic disorders such as hemochromatosis or thalassemia, those with liver diseases or infections such as hepatitis or malaria, and those who consume other sources of fortified foods or supplements.
- Barriers Abound:
- It may face technical, regulatory or social barriers to implementation.
- Technical barriers include ensuring the quality, stability and safety of the fortified rice products;
- Regulatory barriers include establishing and enforcing standards, guidelines and monitoring systems for fortification;
- Social barriers include ensuring the acceptability, affordability and accessibility of the fortified rice products among consumers and stakeholders.
Way Forward
- Deploying Nanotechnology: There is a need to explore the use of nanotechnology to encapsulate iron particles and enhance their bioavailability.
- Nanoparticles can be engineered to increase iron absorption by improving solubility and preventing interactions with inhibitors present in rice.
- Blending Iron Fortification with Biofortification: There is a need to combine iron fortification with biofortification strategies.
- Biofortification involves breeding crops with higher nutrient content, including iron, through conventional breeding techniques.
- By integrating iron fortification and biofortification, we can develop rice varieties that are naturally enriched with iron.
- Public-Private Partnerships: There is a need to foster collaborations between governments, research institutions, private sector entities, and NGOs to promote and scale up iron fortification efforts.
- These partnerships can facilitate the development of innovative technologies, funding mechanisms, and distribution networks for iron-fortified rice.
- Continuous Research and Development: There is a need to encourage ongoing research and development to explore new technologies, formulation methods, and fortification techniques.
- Regularly assessing the efficacy and impact of iron fortification programs is required to identify areas for improvement and innovation.
XPoSat
Context
XPoSat is India’s first polarimetry mission, developed in collaboration between the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and the Raman Research Institute (RRI) (an autonomous research institute), to be launched later this year.
About XPoSat mission
Description | |
About | The X-ray Polarimeter Satellite (XPoSat) is an ISRO-planned space observatory to study the polarisation of cosmic X-rays |
What is Polarisation? | Polarization refers to the direction in which waves vibrate, particularly in the context of light. |
Explanation using an example | Imagine a rope being shaken up and down to create waves. If you hold the rope straight and shake it side to side, the waves will also move in that direction. This is similar to linear polarization. |
Significance of the Study | Studying how radiation is polarised gives away the nature of its source, including the strength and distribution of its magnetic fields, understanding the geometry and inner workings of the light source and the nature of other radiation around it. XPoSat will study the 50 brightest known sources in the universe, including pulsars, black hole X-ray binaries, active galactic nuclei, and non-thermal supernova remnants |
What are X-Rays? | X-rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation that has higher energy and shorter wavelengths than visible light. X-rays come from objects that are millions of degrees Celsius — such as pulsars, galactic supernova remnants, and black holes. |
Payload | POLIX (Polarimeter Instrument in X-rays): It will study 40 bright astronomical sources of different categories XSPECT (X-ray Spectroscopy and Timing): It will study X-ray pulsars, black hole binaries, low-magnetic field neutron stars, active galactic nuclei (AGNs), magnetars |
Orbit | The observatory will be placed in a circular low Earth orbit of 500–700 km |
Duration | A planned lifetime of about 5 years |
Goals | Understand emission mechanisms from complex physical processes; Provide valuable insights into the emission processes of X-ray sources |
Other such missions | XPoSat is India’s first, and only the world’s second polarimetry mission that is meant to study various dynamics of bright astronomical X-ray sources in extreme conditions. The other such major mission is NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) which was launched in 2021. |
PetaFLOP Supercomputers
Context
India will unveil its new 18 petaLOP supercomputer for weather forecasting institutes later this year, Union Earth Sciences Minister Kiren Rijiju said on May 24.
What is this new Supercomputer?
- The new supercomputer is expected to improve weather forecasts at the block level, help weather scientists give higher resolution ranges of the forecast, predict cyclones with more accuracy and better lead time (the difference between a phenomenon being forecast and actually occuring), and provide ocean state forecasts, including marine water quality forecasts.
- “Presently, we give forecasts with a 12-kilometre resolution. The new supercomputer will improve it to six-kilometre resolution. Our aim is to achieve one-kilometre resolution forecasts,” Ministry of Earth Sciences Secretary M Ravichandran said. Rijiju said that the supercomputer will cost Rs 900 crore.
What are FLOPs in computing?
- FLOPs, or Floating-Point Operations per Second, is a commonly used metric to measure the computational performance – processing power and efficiency – especially in the field of high-performance computing (HPC) and artificial intelligence (AI).
- Floating-point operations are a certain kind of mathematical calculation using real numbers with fractional parts.
How many FLOPs can a computer achieve?
- Modern computing systems, such as CPUs (Central Processing Units) and GPUs (Graphics Processing Units), are designed to perform multiple operations simultaneously, using parallel processing techniques.
- The parallelism significantly increases the number of FLOPs a system can achieve within a given time frame. Over the years, hardware has become more efficient, exponentially increasing computing power.
- For instance, in 1961, the IBM 7030 Stretch, costing a whopping $ 7.8 million at the time, performed one floating-point multiplication every 2.4 microseconds, roughly performing 417,000 FLOPs. A PlayStation 5 today is listed to have a peak performance of 10.28 TFLOP, i.e. 10.28 trillion FLOPs.
What is a petaFLOP?
- Due to the immense computing power of today’s computers, the FLOPs metric is most often represented in terms of billions (giga), trillions (tera), or even quadrillions (peta) of operations per second (GFLOPs, TFLOPs, PFLOPs, respectively).
- A petaflop is thus equal to a thousand TFLOPs or 1015 FLOPs.
- 2008 was the first year when a supercomputer was able to break what was then called “the petaFLOPS barrier,” when the IBM Roadrunner shocked the world with an astounding peak performance of 1.105 petaFLOPS. Currently, the world’s fastest computer in terms of PFLOPs is the Hewlett Packard Enterprise Frontier, or OLCF-5 with the capability to touch a peak performance of 1,685.65.
Are FLOPs the only metric to judge a computer’s performance?
No. FLOPs is not the only factor determining the performance of a computing system. Memory bandwidth, latency, and other architectural features also play significant roles. Nonetheless, FLOPs provide a valuable baseline for comparing the computational capabilities of different systems, especially in tasks where floating-point calculations dominate.
Is India already using petaFLOPs computers for weather forecasting?
The NCMRWF houses ‘Mihir’, a 2.8 petaflop supercomputer, while the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM), Pune, is home to ‘Pratyush’, a 4.0 petaflop supercomputer, as per PTI. These were launched in 2018 and will be decommissioned once the new supercomputer is unveiled
Conclusion
As India makes advances in Science and Tech, Supercomputers will play a prominent role in fields like weather forecasting, climate modeling, AI, chemical simulation, drug discovery and other high computational fields.
Mitochondrial Replacement Therapy (MRT)
Why in News?
The recent news of a baby born in the UK with three parents' DNA has sparked curiosity and discussions about the scientific breakthrough behind this remarkable achievement.
- This revolutionary technique, known as mitochondrial replacement therapy (MRT) or three-parent IVF, aims to prevent the inheritance of mitochondrial diseases.
What is Mitochondria?
About:
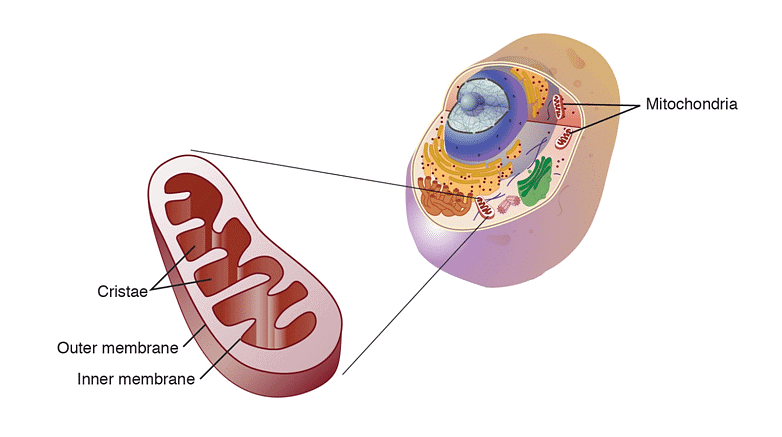
- Mitochondria are membrane-bound organelles found in the cells of most eukaryotic organisms.
- They are often referred to as the "powerhouses" of cells because they generate the majority of the cell's energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
- Functions:
- Mitochondria carry out cellular respiration, a process that converts nutrients into ATP.
- Mitochondria convert energy from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into a usable form for the cell.
- They metabolize glucose to produce ATP, which powers various cellular processes.
- Mitochondria participate in cell signaling pathways, influencing processes like cell growth, differentiation, and apoptosis.
- Inheritance:
- Mitochondria have their own DNA, known as mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA), which encodes a small number of essential proteins.
- In most animals, mtDNA is inherited solely from the mother.
- Mutations in mtDNA can lead to mitochondrial disorders and various health conditions.
- Mitochondrial Diseases:
- Certain mutations in mitochondria can lead to mitochondrial diseases, affecting energy production and impacting various organs, including the brain, nerves, muscles, kidneys, heart, and liver.
- These diseases can result in severe symptoms, such as organ failure, muscle wastage, and even brain damage. Unfortunately, there is no cure for mitochondrial diseases, but they can be managed to some extent.
- Few examples of mitochondrial diseases are Leigh Syndrome, Kearns-Sayre syndrome (KSS), Mitochondrial Myopathy and Mitochondrial DNA Depletion Syndrome.
What is Mitochondrial Donation Treatment (MDT)/MRT?
- About:
- To address the issue of mitochondrial diseases, scientists and researchers developed an advanced In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) technique called Mitochondrial Donation Treatment (MDT) or three-parent IVF.
- This technique involves a complex process to ensure that the baby inherits healthy mitochondria while carrying the genetic material from both biological parents.
- The Scientific Process:
- Identifying Suitable Candidates:
- The procedure is specifically intended for couples who wish to have their genetic child but do not want to use a donor egg.
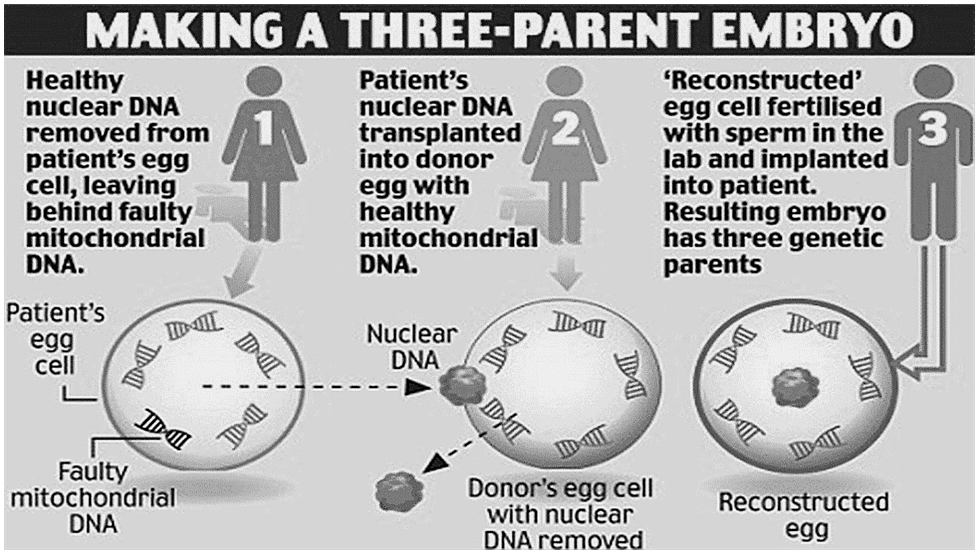
- Selection of Donor and Biological Parents:
- The biological mother, who has a mitochondrial disease, provides her eggs, which are fertilized by the biological father's sperm.
- Additionally, a separate female donor with healthy mitochondria is involved.
- Mitochondrial Replacement:
- The genetic material (DNA) from the donor's egg is extracted and replaced with the genetic material from the biological parents.
- This creates an embryo with the parents' DNA and the donor's mitochondria.
- Implantation and Pregnancy:
- The modified embryo is then implanted in the uterus and carried to full term, resulting in the birth of a baby free from the mother's mitochondrial disease.
- Potential Side Effects:
- While the procedure has shown promising results, it is not without minimal risks. In some cases, a small amount of faulty maternal mitochondria may be inadvertently passed on during the procedure.
- Further research and published data are needed to establish consensus and refine the technique for improved outcomes.
- Legislation and Approval:
- The UK government amended its law in 2015 to allow mitochondrial replacement therapy, and the Newcastle Fertility Centre became the first licensed center to perform the procedure in 2017.
- Mitochondrial Disease Statistics:
- Globally, an estimated 1 in 5,000 people have a genetic mitochondrial disease.
- Mitochondrial disorders affect approximately one in 6,500 babies in the UK, and around 12,000 people in the country live with such conditions.
- In the United States, an estimated 1,000 to 4,000 babies with mitochondrial disease are born each year.
Aurora Borealis
Why in News?
A significant geomagnetic storm is anticipated, triggered by strong solar storm. This occurrence has the potential to "supercharge" auroras, creating a spectacular visual display in the night sky.
What are Auroras?
- About:
- Auroras are luminous phenomena that occur near the North (Aurora Borealis) and South Poles (Aurora Australis).
- They are caused by the interaction of charged particles from the Sun with the Earth's magnetic field and atmosphere.

- Composition and Colors:
- Auroras consist of gases and particles, including oxygen and nitrogen.
- The collisions of these particles with the atmosphere release energy in the form of light.
- The colors observed in auroras depend on the type of gas and altitude of the collisions.
- Geomagnetic Storms and Auroras:
- Geomagnetic storms, triggered by solar events like coronal mass ejections (CMEs) and solar flares, enhance auroral activity.
- CMEs are eruptions of plasma and magnetic fields from the Sun, while solar flares are bursts of energy.
- CMEs often occur alongside solar flares, which are explosions on the Sun's surface, but they are also known to occur independently.
- Solar Storms and Aurora Intensity:
- Strong solar storms result in increased solar activity, leading to more pronounced auroral displays.
- The number of charged particles reaching the Earth's atmosphere during these storms intensifies the auroras.
- The strength of the solar storm and the alignment of the Earth's magnetic field affect the visibility and vibrancy of the auroras.
- Cultural and Scientific Significance:
- Auroras hold cultural and spiritual significance in various indigenous communities around the world.
- Scientific research on auroras helps us understand the Earth's magnetosphere, solar-terrestrial interactions, and space weather.
Psychedelic Substances
In News
- Psychedelic drugs are emerging in research as promising ways to treat treatment-resistant depression and post-traumatic stress disorder.
What are Psychedelics ?
- Psychedelics are a group of drugs that alter perception, mood, and thought-processing while a person is still clearly conscious. Usually, the person’s insight also remains unimpaired.
- They are non-addictive, non-toxic and compared to illicit drugs, they are less harmful to the end user.
- In India, the Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act 1985 prohibits the use of psychedelic substances. Ketamine, a dissociative anaesthetic with psychedelic properties, is used under strict medical supervision, for anaesthesia and treatment-resistant depression.
History of psychedelics?
- A psychiatrist named Humphrey Osmond first used the term ‘psychedelic’ in 1957. The word is derived from the Greek words psyche, meaning ‘mind’, and deloun, meaning ‘to manifest’.
- Between 1947 and 1967, LSD was widely used as a therapeutic catalyst in psychotherapy. Around this time, medical concerns and the Vietnam War prompted the criminalisation of the use of psychedelics and other psychoactive drugs.
- Media campaigns in the 1960s and 1970s further stigmatised the use of all psychoactive drugs.
How does it work?
- Users of psychedelic substances report changes in perception, somatic experience, mood, thought-processing, and entheogenic experiences. An intriguing phenomenon called synaesthesia may occur, where the sensory modalities cross and the user may ‘hear colour’ or ‘see sounds’.
- Modern neuroimaging suggests that psychedelics are neither stimulants nor depressants of brain activity. Instead, they increase the cross-talk between different brain networks, and this correlates with the subjective effects of psychedelics.
Can such substances cause harm?
- Death due to direct toxicity of LSD, psilocybin or mescaline has not been reported despite 50-plus years of recreational use. An overdose requires cardiac monitoring and supportive management.
- The psychological effects of psychedelics depend on the interaction between the drug and the user’s mindset (together called a set), and the environmental setting.
- People with a personal or family history of psychosis are strongly discouraged from experimenting with psychedelics.
Way Ahead
- Although recent findings are encouraging, there remains uncertainty about where the psychedelic renaissance will take us.
- Psychedelic substances provide an intriguing avenue through which one can probe the broader constructs of creativity, spirituality, and consciousness, aside from their therapeutic effects.
|
90 videos|488 docs|209 tests
|















