Types of Forces: Concepts, Sub-types, & Examples | AP Physics 1 - Grade 9 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Types of Force |

|
| Contact Forces |

|
| Non-Contact Forces |

|
| Conclusion |

|
| Solved Example |

|
Types of Force
In the realm of physics, the concept of force reigns supreme, governing the behavior of objects and shaping the very fabric of our physical world. From the gentle push of a breeze to the mighty gravitational pull of celestial bodies, forces are the driving agents behind all interactions and motions. Understanding the fundamentals of force is not only essential for scientists and engineers but also empowers us to comprehend the everyday phenomena that surround us.
There are two broad categories of forces: contact forces, which occur when objects are in physical contact with each other, and non-contact forces, which act even when objects are not in direct contact.
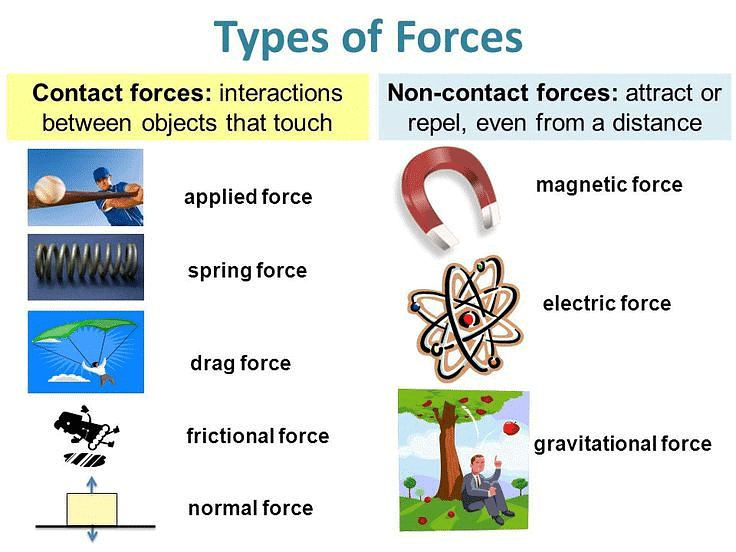 Types of Forces
Types of Forces
Contact Forces
Contact forces encompass any forces that require physical contact with another object. These forces play a crucial role in mechanical interactions. Let's explore the sub-types of contact forces in more detail:
Muscular Forces
- Muscles function as the source of a resulting force known as muscular force. This force is exerted only when an object is in direct contact with the muscles. From everyday activities like breathing, digestion, and lifting objects to pushing and pulling, muscular force simplifies our daily tasks.
 Example of Muscular Forces
Example of Muscular Forces
Frictional Forces
- When an object changes motion, frictional force comes into play. This force acts as a resistance when an object is moved or tries to move across a surface. Examples of frictional forces include lighting a matchstick or stopping a moving ball. Frictional forces arise from the contact between two surfaces.
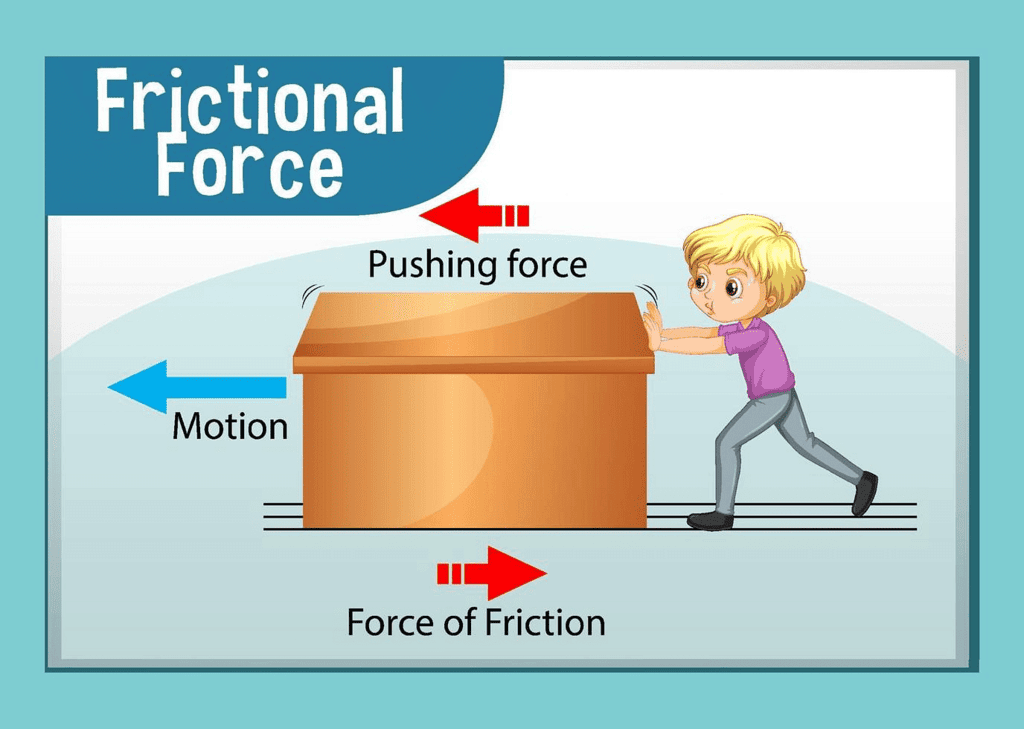 Example of Frictional Force
Example of Frictional Force
Normal Force
- Even when an object appears stationary, it experiences an opposing force due to gravity, called the normal force. For instance, when a book rests on a table, the normal force counteracts the gravitational force pulling it towards the Earth. Understanding the normal force helps us comprehend the equilibrium of objects on surfaces.
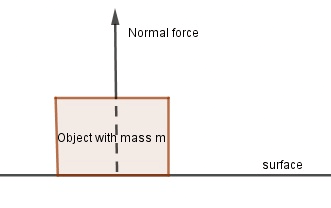 Representation of Normal Force
Representation of Normal Force
Applied Force
- When you push or pull an object in contact with another, you apply an external force known as applied force. This force comes into play during activities like moving a table across a room. Understanding applied forces helps us analyze the interactions between objects in motion.
Tension Force
- A fully stretched cable or wire anchored to an object exerts tension force. This force pulls equally in both directions, exerting equal pressure. Tension forces can be observed in scenarios involving cables, ropes, or wires.
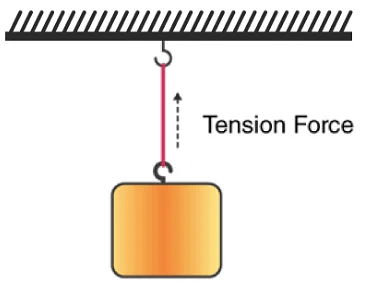 Representation of Tension Force
Representation of Tension Force
Spring Force
- A compressed or stretched spring exerts a force known as the spring force. Depending on how the spring is attached, this force can either push or pull. Understanding spring forces is crucial in various applications, such as mechanical systems and engineering.
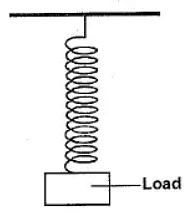 Spring Force
Spring Force
Air Resisting Force
- When objects move through the air, they experience air-resisting forces. These forces are resistive, creating frictional resistance against the motion of objects. Understanding air-resisting forces is vital in fields like aerodynamics and fluid dynamics.

Non-Contact Forces
Non-Contact Forces
In contrast to contact forces, non-contact forces can be exerted without any physical contact between objects. Let's explore the sub-types of non-contact forces:
Gravitational Force
- Gravitational force is an attractive force governed by Newton's law of gravity. It states that the gravitational force between two bodies is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. This force plays a fundamental role in interactions between large bodies, such as planets and stars. Examples of gravitational force include water droplets falling due to the Earth's gravitational pull.
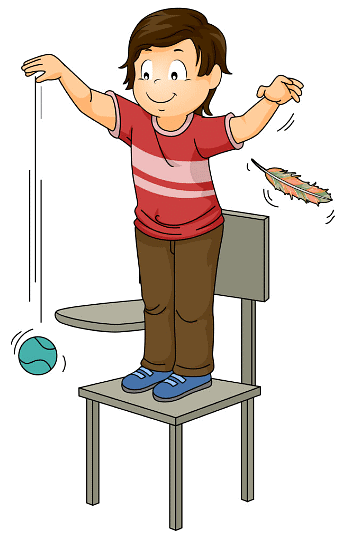 Example of Gravitational Force
Example of Gravitational Force
Magnetic Force
- Magnetic forces are exerted by magnets on magnetic objects. Unlike contact forces, magnetic forces can act without any physical contact between the two objects. These forces play a significant role in various applications, including magnetic levitation, electrical motors, and data storage.
 Example of Magnetic Force
Example of Magnetic Force
Electrostatic Force
- Electrostatic forces arise from the interaction between electrically charged bodies. These forces can be both attractive and repulsive, depending on the charges of the bodies involved. Understanding electrostatic forces helps us comprehend phenomena such as static electricity, lightning, and the behavior of charged particles.
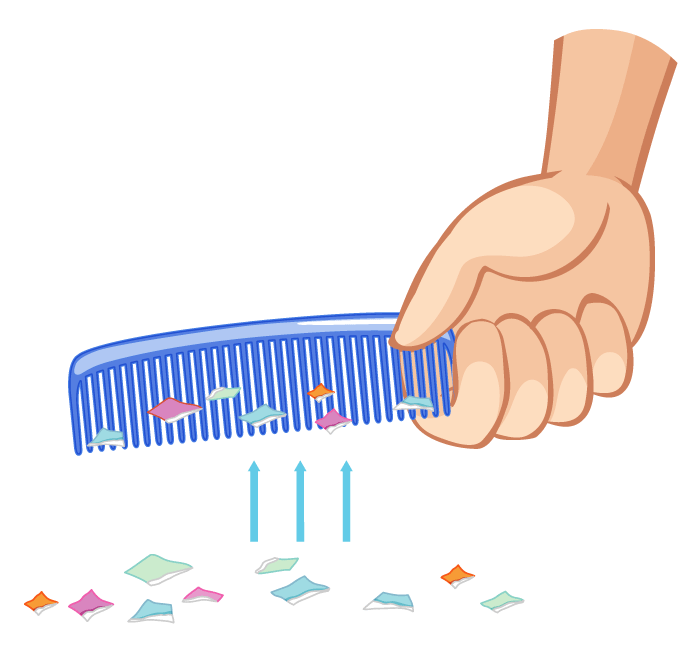 Electrostatic Forces
Electrostatic Forces
Conclusion
- Forces are omnipresent in our lives, shaping our interactions with the physical world. By exploring the diverse types of forces, categorized into contact forces and non-contact forces, we gain a deeper understanding of the mechanics that govern our surroundings.
- Through real-life examples, we have delved into the concepts behind each force, highlighting their relevance in various fields of science and engineering. So, the next time you sit in your room or push an object across a table, remember the forces at play and how they contribute to the intricate dynamics of our world.
Solved Example
Q. Which of the following provides evidence for the existence of a force acting on Earth and directed towards the Sun?
(a) The apparent motion of the sun around the earth
(b) The phenomenon of day and night
(c) Revolution of Earth around the Sun
(d) Deviation of the falling body towards Earth
Ans: C
Solution:
The fact that Earth revolves around the Sun prompts us to ponder the force responsible for maintaining this orbital motion. For Earth to continuously move in a circular path, a centripetal force is required to provide the necessary centripetal acceleration. This vital force of attraction between Earth and the Sun is none other than gravitational force.
Q. Which force causes a charged balloon to attract another balloon?
Ans: Electrostatic force
Solution: The force that makes a charged balloon pull towards another balloon is called electrostatic force. This happens because the balloons acquire an electric charge when rubbed against a material, creating an attraction between them due to the opposite charges they acquire.
|
48 videos|69 docs|30 tests
|
FAQs on Types of Forces: Concepts, Sub-types, & Examples - AP Physics 1 - Grade 9
| 1. What are contact forces? |  |
| 2. What are non-contact forces? |  |
| 3. Can contact forces exist without non-contact forces? |  |
| 4. Give an example of a contact force. |  |
| 5. Give an example of a non-contact force. |  |















