Types of Problems in Friction | Physics Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Motion on a Rough-Inclined Plane |

|
| Two Blocks on an Inclined Plane |

|
| Pulley Block System Involving Friction |

|
| Two Block System |

|
Motion on a Rough-Inclined Plane
Suppose a motion up the plane takes place under the action of pull P acting parallel to the plane
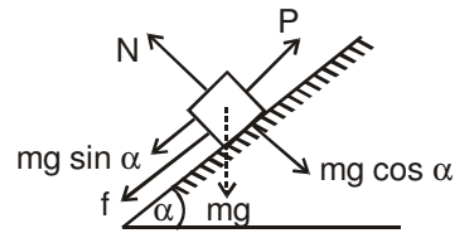 Motion on Rough Inclined Plane
Motion on Rough Inclined Plane
- The frictional force acting down the plane F = μN = μ mg cos α (N= μ mg cos α)
Appling Newton's second law for motion up the plane
P - (mg sin α + f) = ma
P - mg sin α - μ mg cos α = ma - If P = 0 the block may slide downwards with an acceleration a.
The frictional force would then act up the plane
mg sin α - F = ma
mg sin α - μ mg cos α = ma
Example. A 20 kg box is gently placed on a rough inclined plane of inclination 30° with horizontal. The coefficient of sliding friction between the box and the plane is 0.4. Find the acceleration of the box down the incline.
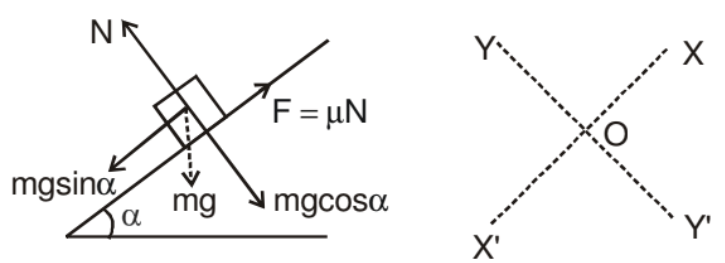
Solution. In solving inclined plane problems, the X and Y directions along which the forces are to be considered may be taken as shown. The components of the weight of the box are
(i) mg sin α acting down the plane and
(ii) mg cos α acting perpendicular to the plane.
N = mg cos α
mg sin α - μ N = ma ⇒ mg sin α - μ mg cos α = ma
a = g sin α - μg cos α
a = g (sin α - μ cos α)
a =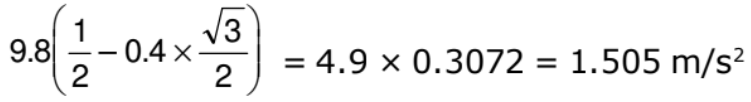
The box accelerates down the plane at 1.505 m/s2.
Example: A force of 400 N acting horizontally pushes up a 20 kg block placed on a rough inclined plane which makes an angle of 45° with the horizontal. The acceleration experienced by the block is 0.6 m/s2. Find the coefficient of sliding friction between the box and the incline.
Solution: The horizontally directed force of 400 N and the weight of 20 kg of the block are resolved into two mutually perpendicular components, parallel and perpendicular to the plane as shown.
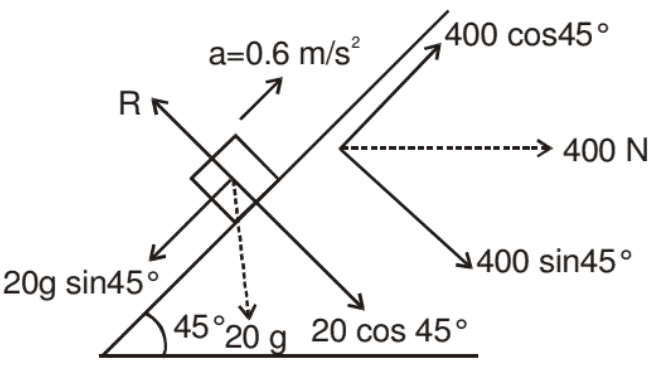
N = 20 g cos 45° + 400 sin 45° = 421.4 N
The frictional force experienced by the block
F = μN = μ x 421.4 = 421.4 μN.
As the accelerated motion is taking place up the plane.
400 cos 45° - 20 g sin 45° - f = 20a
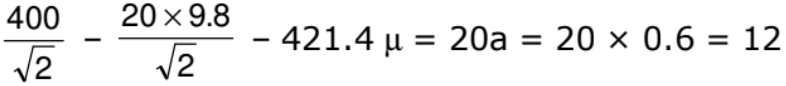
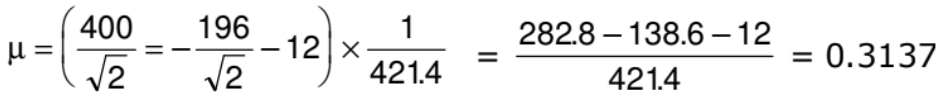
The coefficient of sliding friction between the block and the incline = 0.3137
Two Blocks on an Inclined Plane
Consider two blocks having masses m1 & m2 placed on a rough inclined plane. μ1 & μ2 are the friction coefficient for m1 & m2 respectively. If N is the normal force between the contact surface of m1 & m2
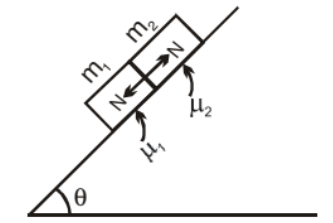 Two Blocks on an Inclined Plane
Two Blocks on an Inclined Plane
Now three condition arises:
(i) If μ1 = μ2= μ then
N = 0 because Both the blocks are in contact but do not press each other.
a1 = a2 = g sin θ - μ mg cos θ
(a1, a2 are acceleration of block μ1 & μ2 respectively)
(ii) If μ1 < μ2 then
N = 0 because there is no contact between the blocks.
a1 = g sin θ - μ1 g cos θ
a2 = g sin θ - μ2 cos θ
⇒ a1 > a2
(iii) If μ1 > μ2 then N ≠ 0
a1 = a2
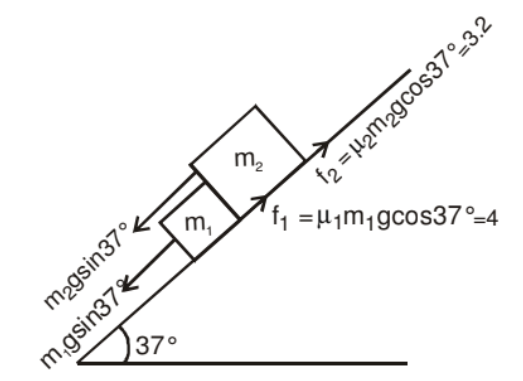
Example: Mass m1 & m2 are placed on a rough inclined plane as shown in the figure. Find out the acceleration of the blocks and contact force in between these surfaces.
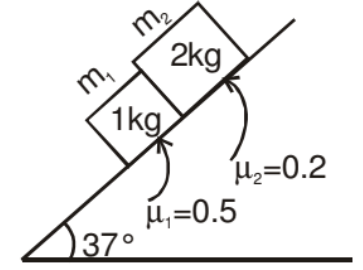
Solution: As we know if μ1 > μ2, both blocks will travel together so
a1 = a2 = a
F.B.D
which is equivalent to
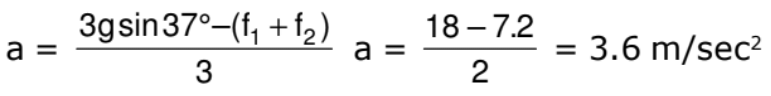
Now F.B.D of 1 kg block is
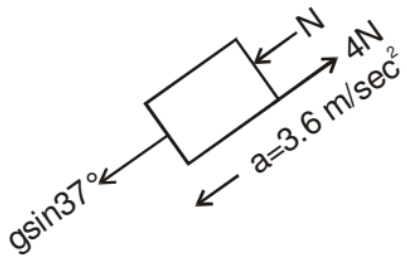 FBD of 3 kg block is
FBD of 3 kg block is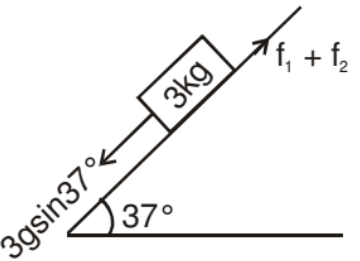
gsin37° + N - 4 = (1) a
N = 3.6 + 4 - 6 = 1.6 Newton
Pulley Block System Involving Friction
If friction force is acting and the value of the acceleration of a particle is negative, then it means the direction of friction force is opposite to that of what we assumed and acceleration would have a different numerical value.
Example: Two blocks of masses 5 kg and 10 kg are attached with the help of a light string and placed on a rough incline as shown in the figure. Coefficients of friction are as marked in the figure. The system is released from rest. Determine the acceleration of the two blocks.
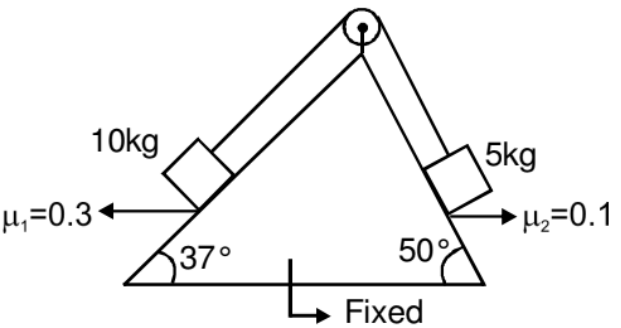 Solution: Let 10 kg block is sliding down, then the acceleration of both the blocks is given by,
Solution: Let 10 kg block is sliding down, then the acceleration of both the blocks is given by,
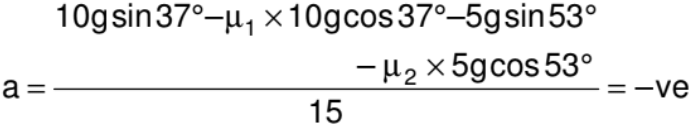
It means our assumed direction of motion is wrong and the 5 kg block is going to slide down, if this is the case, the direction of friction force will reverse and the acceleration of blocks would be given by :
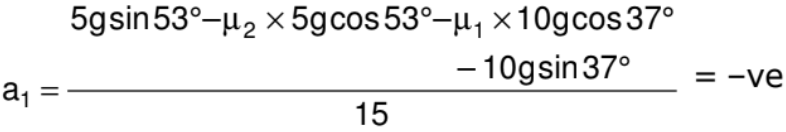
It means in this direction also there is no motion. So we can conclude that the system remains at rest and friction force is static in nature.
Two Block System
Example: Find out the maximum value of F for which both the blocks will move together.
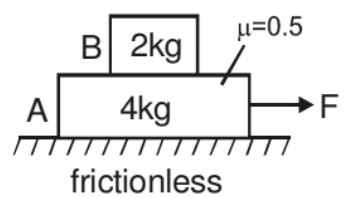
Solution: In the given situation 2kg block will move only due to the friction force exerted by the 4 kg block
F.B.D.
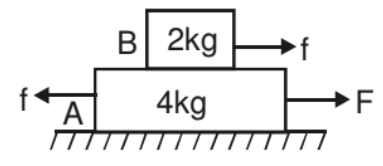
The maximum friction force exerted on the block B is
fmax = μN
fmax = (0.5) (20) = 10 N
So the maximum acceleration of a 2 kg block is
a2max = 10/2 = 5 m/s2
amax is the maximum acceleration for which both blocks will move together. i.e., for a £ 5 ms-2 acceleration, both blocks will be the same and we can take both blocks as a system.
F.B.D
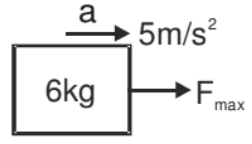
Fmax = 6 × 5 = 30 N
for 0 < F < 30
Both the blocks move together.
Example. In the above question find the acceleration of both the block when
(i) F = 18 N
(ii) F = 36 N
Solution. (i) Since F < 30 both the blocks will move together
F.B.D.
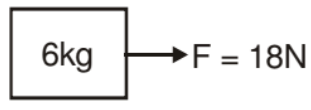
(ii) When F = 36 N
When F > 30 both the blocks will move separately so we treat each block independently
F.B.D of 2 kg block
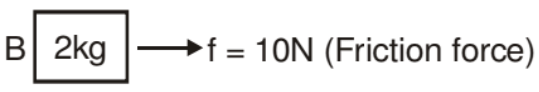
aB = 5 m/s2
F.B.D of 4 kg block
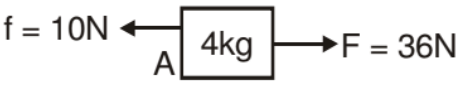
Example. Find out the range of force in which both the blocks move together.
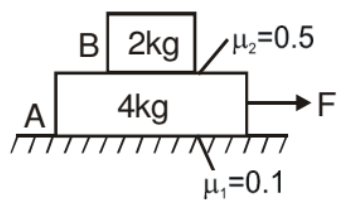
Solution. If f1 is the friction force between block A & lower surface and f2 is the friction force between both the block's surfaces.
F.B.D.
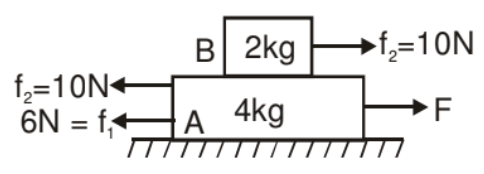
f1 max = m1N1 = (0.1) (60) = 6 N
f2 max = m2N2 = (0.5) (20) = 10 N
The upper 2kg block is moved only due to friction force so the maximum acceleration of that block is
amax = 10/2 = 5m/s2
This is the maximum acceleration for which both the blocks will move together.
Therefore for a ≤ 5ms-2 we can take both the blocks as one system.
F.B.D.
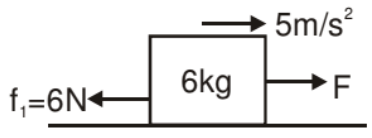
For F < 6 N. Blocks will not move at all.
Now the value of Fmax for which both the blocks will move together.
Fmax - 6 = 6 × 5
Fmax = 36 N
Conclusion if
0N < F < 6N No blocks will move
6N < F < 36 N Both blocks will move together
F > 36 N Both move separately.
Example: What is the minimum acceleration with which bar A should be shifted horizontally to keep bodies 1 and 2 stationary relative to the bar? The masses of the bodies are equal and the coefficient of friction between the bar and the bodies is equal to m. The masses of the pulley and the threads are negligible while the friction in the pulley is absent. See Fig.
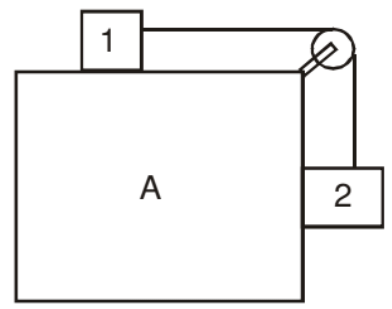
Solution: Let us place the observer on A.
Since we have a non-inertial frame we have pseudo forces.
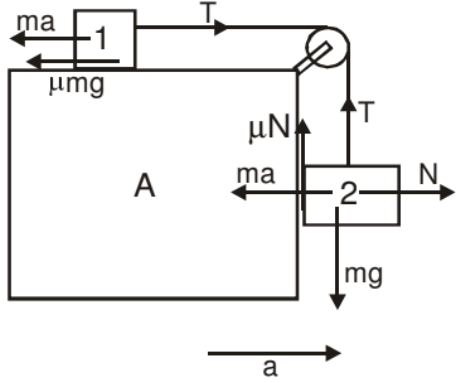
For body '1' we have,
T = ma + μmg ....(1)
For body '2' we have,
N = ma
mg - T - μma = 0
mg = T + μmg ....(2)
From (1) and (2)
Example: Mass m2 placed on a plank of mass m1 lying on a smooth horizontal plane. A horizontal force F = a0t (a0 is a constant) is applied to a bar. If the acceleration of the plank and bar are a1 and a2 respectively and the coefficient of friction between m1 and m2 is m. Then find acceleration a with time t.
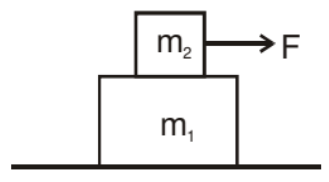
Solution: If F < mm2g then both blocks move with common acceleration, i.e., a1 = a2
When F > μm2g, then
The equation for a block of mass m
F - μm2g = m2a2 ...(1)
μm2g = m1a1 ...(2)
From equation (1)
αοt - μm2g = m2a2
i.e., acceleration a2 varies with time linearly, its slope positive and intercept negative.
From equation (2) a1 is independent of time.
So, the graph between a & t is as follows.
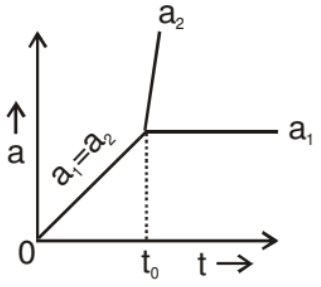
|
96 videos|367 docs|98 tests
|
FAQs on Types of Problems in Friction - Physics Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is the effect of friction on motion on a rough-inclined plane? |  |
| 2. How does the presence of friction affect the motion of two blocks on an inclined plane? |  |
| 3. What role does friction play in a pulley block system involving friction? |  |
| 4. How does the presence of friction impact a two-block system? |  |
| 5. What are some common types of problems related to friction? |  |




















