Difference & Relation Between Force and Power | AP Physics 1 - Grade 9 PDF Download
What is a Force?
Force refers to the interaction between two objects or the push or pull experienced by an object when subjected to an external force. Another way to describe force is as the determining factor for whether an object remains in a state of rest or motion until influenced by an external force. The unit of force is expressed in newtons.
This concept is elucidated in Newton's first law of motion.
Newton's First Law: If an object is not subjected to any force, it will remain at rest or continue moving in a straight line at a constant speed.
Force can be exerted through either direct contact or without physical contact.
Examples of forces exerted through direct contact include pushing a box or kicking a ball, while examples of forces without physical contact include gravitational force and electrostatic force.
The equation for force is given by Force = Mass × Acceleration.
What is Power?
Power is the measure of the amount of energy consumed or the rate at which work is performed within a specific time frame. It can be defined as the energy expended or work accomplished per unit of time.
The formula for power is given by Power = Work done/Time taken.
The unit of power is the watt.
Example: Let's consider the scenario of a lift motor moving a fully laden lift a distance of 4m between floors within a time frame of 1.5s.
The lift has a mass of 1850 kg (ignoring friction).
a) Calculate the weight of the fully laden lift.
Weight (W) = mass (m) × acceleration due to gravity (g) = 1850 kg × 10 m/s² = 18500 N.
b) What is the upward force in the cable when the lift is moving at a constant speed?
When the lift is moving at a constant speed, the forces must be balanced. Therefore, the upward force is equal to the downward force (weight). Hence, the upward force is 18500 N.
c) What is the work done by the motor?
Work done (W) = force (F) × distance (d) = 18500 N × 4 m. Therefore, the work done is 74000 J (joules).
d) What is the minimum power of the motor to raise the lift at a steady speed?
Steady speed implies balanced forces.
Power = work done/time = 74000 J / 1.5 s.
Therefore, the minimum power of the motor required to raise the lift at a steady speed is 49333 W (watts).
Difference Between Force and Power
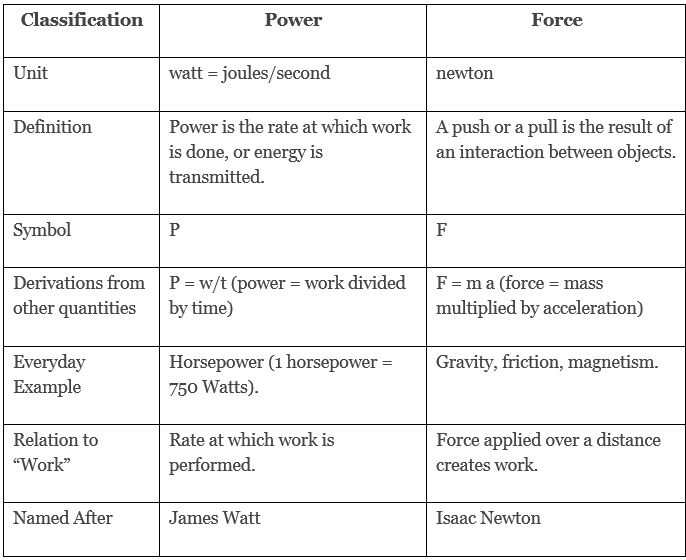
The Relation Between Force and Power
Also, power and force are related to each other.
We know that power is work done per unit time and it is expressed as:
P = W/ΔT
Work can be said as the force which is applied to make the object move, and it is expressed as:
W = FΔx
Therefore, the relation between force and power is given as:
P = FΔx/ΔT
|
48 videos|69 docs|30 tests
|




















