JAMB Economics Previous Year Questions: 2022 PDF Download
Q1: Marginal cost is?
(a) the lowest cost of producing goods
(b) the cost of production of the most efficient firm in an industry
(c) the cost of production of the most inefficient firm in an industry
(d) the cost of production of the last or extra unit of goods produced by a firm
Ans: (d)
The additional cost incurred in producing an additional unit of a good or service is known as the marginal cost.
Q2: The price mechanism
(a) regulates supply and demand
(b) rations the consumers
(c) rewards the producers
(d) allocates scarce resources
Ans: (d)
The price mechanism allocates scarce resources by using market prices to signal the relative scarcity of goods and services. When a good is scarce, the price tends to rise, signaling producers to increase supply and consumers to reduce demand. This process helps to ensure that resources are allocated efficiently to their most valuable uses.
Q3: In a free market economy, the rationing of scarce goods is done principally by?
(a) the government
(b) business organizations
(c) the price mechanism
(d) consumers
Ans: (c)
In a free market economy, the price mechanism is used to ration scarce goods. When a good becomes scarce, its price rises, encouraging consumers to buy less and producers to supply more, which helps allocate the limited resources to their most valued uses.
Q4: Scale of preference shows
(a) incomes of consumers in order of size
(b) utilities enjoyed by consumers
(c) opportunity cost of goods consumed
(d) consumer's wants in order of priority
Ans: (d)
A scale of preference is a table that displays an individual needs and wants in either chronological order or according to priority.
Q5: There is unemployment of resources when production is
(a) within the production possibility curve
(b) outside the production possibility curve
(c) along the production possibility curve
(d) adequate to meet market demand
Ans: (a)
Inefficient use of resources, widespread unemployment, or resources not being fully employed are indicated by points inside the production possibility curve.
Q6: A major characteristic of natural resources is they
(a) are unlimited in supply
(b) have high cost of production
(c) are free gifts of nature
(d) do not command any price
Ans: (c)
Unlike man-made resources, which are produced by humans, natural resources exist naturally. Natural resources are products of nature and cannot be attributed to human activity.
Q7: A major disadvantage of a capitalist economy is that it
(a) leads to low production of goods and services
(b) requires large number of officials to operate
(c) considers individual consumers' satisfaction
(d) worsens income inequality among the citizens
Ans: (d)
The concentration of wealth and power over the means of production in the hands of a small number of people is one of the disadvantages of capitalism. The wealthy families always have control over society's wealth.
Q8: The mining sector of an economy contributes 60% to the Gross Domestic Product(GDP). If the GDP is $540, what is the contribution of the mining sector?
(a) $ 90.00
(b) $ 180.00
(c) $ 324.00
(d) $ 350.00
Ans: (c)
The contribution of the mining sector = 60% x 540 = 324
Q9: The increase in the demand for a commodity may lead to a decrease in the demand for another if both are
(a) in complementary demand
(b) of the same quality
(c) in composite demand
(d) in competitive demand
Ans: (d)
Competitive demand, also referred to as substituted demand. There are substitute commodities that have comparable utility and can satisfy similar wants. When the demand for one increases, the desire for the other decreases.
Q10: The demand curve for goods of ostentation is usually
(a) negatively sloped
(b) positively sloped
(c) vertical
(d) horizontal
Ans: (b)
Ostentation goods are expensive items like jewellery, gold watches, etc. The quantity demanded increases as the price rises. As a result, there is a positive relationship between price and quantity demanded.
Q11: PN equals average revenue or marginal revenue cure of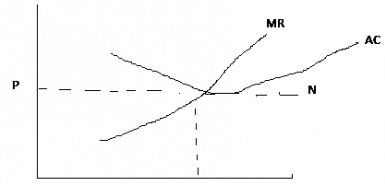 (a) An imperfect competitive firm
(a) An imperfect competitive firm
(b) a monopoly
(c) a perfectly competitive firm
(d) a monopolistic competitive firm
Ans: (c)
The average revenue or marginal revenue of a perfect market or perfectly competitive firm is represented by the figure PN in the diagram.
Q12: If the quantity demanded of a commodity increases from 20 units to 30 units when there is an increase in price from $4.00 to $5.00, the elasticity of demand is
(a) 0.50
(b) 0.65
(c) 2.00
(d) 2.50
Ans: (c)
e = ΔQd/ΔP x P/Qd
= 30 - 20/ 5 - 4 x 4/ 20
= 10/1 x 4/20
= 2
Q13: The supply curve of a locally-produced good may shift to the right if
(a) there is an increase in taxes on inputs
(b) government increases subsidies
(c) rural-urban migration is encouraged
(d) the price of the commodity increases
Ans: (d)
Because of positive relationship, as the price increases, so do the quantity demanded rises as well which is one of the laws of supply. As a result, an increase in price will cause the the supply curve to move to the right.
Q14: In perfectly elastic supply, the supply curve
(a) is vertical
(b) is horizontal
(c) slopes upward
(d) slopes downward
Ans: (b)
When the supply curve is precisely horizontal, a perfect elastic supply curve is present. It is a theoretical curve, and one like it doesn't really exist in reality.
Q15: A country's budget allocation to various sectors of the economy is shown in the pie chart above...
Use it to answer this question.
If the budget of the country was $7,200, how much is allocated to Education?
(a) $2,400.00
(b) $2,000.00
(c) $1,200.00
(d) $1,000.00
Ans: (a)
120 /360 x 7200 = 2400
Q16: A country's budget allocation to various sectors of the economy is shown in the pie chart above...
Use it to answer this question
Q. What is the ratio of expenditure on health to Agriculture?
(a) 2: 3
(b) 3:4
(c) 4:3
(d) 5:4
Ans: (b)
Health = 60/360 x 7200
= 1200
Agriculture = 80/360 x 7200
= 1600
The ratio of expenditure on health to agriculture = 1200/1600
= 3:4
Q17: A consumer of a single commodity is in equilibrium when
(a) he can equate his demand with price
(b) he equates marginal utility and price
(c) he can equate his marginal and total utilities
(d) his marginal utility is equal to zero
Ans: (b)
A consumer is in equilibrium when the marginal utility equal to the price of the commodity i.e MUx = Px.
Where : X = the commodity
MU = Marginal utility
P = price of the commodity
Therefore, a consumer who consume a single commodity such as apple will be at equilibrium when MUa = Pa
Q18: If the government imposes a minimum price on a commodity
(a) market surplus occurs
(b) the market will be cleared in the short-run
(c) excess demand occurs
(d) government regulation is no longer needed
Ans: (a)
The government often sets a minimum price, also known as a price floor, to protect the producer or seller. This minimum price is established above the equilibrium price, resulting in a surplus of goods as the supply exceeds the demand.
Q19: A minimum price legislation is also called
(a) price ceiling
(b) price floor
(c) price control
(d) price mechanism
Ans: (b)
Minimum price legislation is also commonly referred to as a "price floor" is a government-imposed price floor that sets a legal minimum price for a particular good or service. It is designed to protect producers or sellers from being paid prices that are too low, but can result in an excess supply of the good and a potential surplus.
Q20: Which of the following factors is not a cause of diminishing returns?
(a) Increase in variable inputs
(b) Land fragmentation
(c) Constant technology
(d) Technological innovations
Ans: (d)
The law of diminishing returns, which is also known as the law of variable proportion, applies to the analysis of production in the short run. The causes of diminishing returns, including fixed costs, limited demand, no change in technology, and scarce factors, can all be attributed to this law.
Q21: In manufacturing, division of labour may be hindered by
(a) excessive demand for the product
(b) low level of technology
(c) excess supply of labour
(d) increase in the export of goods
Ans: (b)
Factors such as the size of the market, production method/technology, nature of commodities, non-availability of capital, non-availability of required skilled labour, and low level of technology can all limit the application of division of labour.
Q22: The production cost that varies inversely with output is the
(a) total fixed cost
(b) marginal cost
(c) average fixed cost
(d) average cost
Ans: (d)
When the number of goods increases, the average cost of goods decreases because average cost is directly proportional to the total cost of goods and inversely proportional to the number of goods.
Q23: A firm that closes down will still incur
(a) variable cost
(b) fixed cost
(c) total cost
(d) marginal cost
Ans: (b)
If a firm shuts down, it will not generate any revenue, and its variable production cost will be zero. This means that the firm's total cost of production is equivalent to its fixed cost. Nevertheless, the firm will still have to bear the fixed cost.
Q24: The sufficient condition for a firm to be in equilibrium is that the
(a) firm must show that it is profitable
(b) marginal cost must be equal to average revenue
(c) marginal revenue curve is above the average revenue curve
(d) marginal cost curve cuts the marginal revenue curve from below
Ans: (d)
For a firm to be in equilibrium, it must fulfill the following conditions:
- It should earn maximum profit
- Marginal revenue must be equal to marginal cost
- Marginal cost must intersect marginal revenue from below
Q25: Cooperative societies are formed mainly to
(a) assist producers to maximize their profits
(b) encourage thrift and credit among members
(c) promote and maintain the welfare of members
(d) break the monopolies of private companies
Ans: (c)
The purpose of cooperative societies is to benefit their members. It is frequently a voluntarily formed group of people who gather together to cooperate and further their economic interests.
Q26: A disadvantage of a jont-stock company is
(a) unlimited liability
(b) limited liability
(c) lack of continuity when a shareholder dies
(d) limited control in management by shareholders
Ans: (d)
Shareholders, who own the business, have limited or no influence on its affairs, while those who are in charge of running the business but do not own it may not do their jobs well.
Q27: The middlemen is responsible for
(a) providing research facilities
(b) purchasing raw materials
(c) designing the product
(d) breaking the bulk
Ans: (d)
In a chain of distribution or transactions, the middleman serves as an intermediary, promoting communication between the participants. The middlemen are the wholesalers and retailers who specialise in carrying out tasks related to the acquisition and sale of goods as they move from the manufacturer to the final consumers.
Q28: A major function of the retailer is to
(a) grant credit to the wholesaler
(b) break bulk and sell products in small units
(c) reduce cost of distribution
(d) generate demand for products through advertisement
Ans: (b)
A retailer's main duty is to sell products in small quantities to consumers. Additionally, they carry out various marketing activities, including promoting sales, advertising, and displaying goods at the point of purchase.
Q29: A positive effect of a rapid population increase is
(a) an excessive budget deficit
(b) a reduction in standard of living
(c) a wider market for goods and services
(d) a higher dependency ratio
Ans: (c)
A large population has three positive effects:
- It boosts the abundance of inexpensive labor.
- It generates a significant market since investors prefer to invest in countries with large populations.
- It encourages innovation among individuals.
Q30: Which of the following factors may not affect the efficiency of labour?
(a) Education and training
(b) Provision of welfare service
(c) Race and colour of workforce
(d) Quality of other factor inputs
Ans: (c)
Several factors influence labor efficiency, including:
- Technological advancements
- Competitive wages
- Favorable working conditions
- Job security
- Education and training opportunities
- Promotion
Q31: The type of unemployment found among workers who leave their jobs in search of other jobs is termed
(a) seasonal unemployment
(b) structural unemployment
(c) frictional unemployment
(d) cyclical unemployment
Ans: (c)
A person experiences frictional unemployment when they are between jobs. It is also a form of unemployment when job searchers look for employment while employers look for staff or workers.
Q32: The main objective of marketing boards is to
(a) accumulate revenue for government
(b) educate farmers on pricing of cash crops
(c) stabilize the incomes of cash crop farmers
(d) provide warehousing facilities
Ans: (c)
Most marketing boards are established with the primary goal of stabilizing producer prices, especially for products intended for export markets that experience extreme price volatility.
Q33: The point x inside the PPC indicate?
(a) resources are fully utilized
(b) the country is poor
(c) some resources are idle
(d) resources are not available
Ans: (c)
If point X lies within the PPC, it means that resources are not being fully utilized and are, in fact, either idle or underemployed.
Q34: Which of the following industries will add more value to primary products?
(a) Service industry
(b) Construction industry
(c) Mining industry
(d) Processing industry
Ans: (c)
Industries that involve the extraction or cultivation of raw materials, such as agriculture, fishing, mining, and forestry, produce primary products. These goods do not undergo any manufacturing process and include commodities like oil, water, fish, fruit, crops, and wood.
Q35: Gross National Product (GNP) less the provision for the wear and tear of assets is the
(a) net present value
(b) net national product
(c) net factor income
(d) net indirect taxes
Ans: (b)
To calculate Net National Product, subtract depreciation, also known as capital consumption allowance, from Gross National Product. In other words, NNP = GNP - Depreciation.
Q36: An example of transfer payments in national income accounting is
(a) money transferred to another country
(b) unemployment allowance paid to the citizens
(c) the amount paid to a worker on transfer
(d) transfer of funds from one bank to another
Ans: (b)
Transfer payments refer to receipts that do not stem from participation in productive activities within the economy, but instead represent transfers of funds from one party to another. Examples of transfer payments include pensions, bursaries, awards, gifts, and unemployment benefits. When computing or estimating national income, transfer payments are not included.
Q37: Increasing national income without effective control of population size in a country can lead to
(a) higher per capita income
(b) increase in poverty
(c) increased outflow of aid
(d) underutilization of resources
Ans: (d)
If a country experiences a rise in national income but fails to effectively manage population growth, it may result in underutilization of resources within that country.
Q38: An example of commodity money is
(a) currency note
(b) mobile money
(c) cheques
(d) silver
Ans: (d)
Commodity money refers to money that possesses value both as currency and as a commodity, examples of which include gold, silver coins, diamonds, cattle, beads, and other similar items.
Q39: If inflation is anticipated, people may
(a) save more money
(b) spend more money
(c) give out more loans
(d) spend less money
Ans: (b)
Anticipated inflation arises when individuals are aware that inflation is imminent and take steps to prepare for it, such as by increasing interest rates.
Q40: If the Central Bank increases its bank rate
(a) many banks will shut down their operations
(b) customers will borrow more from banks
(c) the supply of money may be reduced
(d) interest charges by banks will fall
Ans: (c)
An increase in the bank rate will cause commercial banks to raise their interest charges, leading to a reduction in borrowing by the general public and a decrease in the money supply due to the high interest rate.














