Basic Geometrical Ideas Class 6 Worksheet Maths Chapter 4
Q1: What do the following things in our surroundings represent: (use the words given in the box).
| A point | A ray | A line segment |
| A plane | Parallel lines | Intersecting lines |
Tip of pencil A point (example)
(a) Edge of a ruler __________
(b) Corner of a book __________
(c) Light coming out of torch __________
(d) Flat surface of a table __________
(e) Opposite edges of a ruler __________
(f) Adjacent edges of a ruler __________
Q2: In relation to the adjoining figures, write the names of:

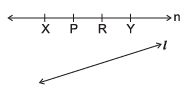
(a) 6 line segments
(b) 6 rays
(c) Two intersecting lines
(d) Two parallel lines
(e) How many points have been marked and named on the line 'n'?
(f) How many lines does a point have?
Q3: What is the name of the angle shown in this figure? Name the points.
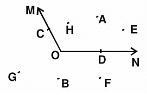 (a) In the interior of angle
(a) In the interior of angle
(b) On the angle
(c) In the exterior of angle.
Q4: State whether the following statements are true or false:
(a) Line segment is a definite part of a line.
(b) Through a given point, only one line can be drawn.
(c) A line is also a curve.
(d) Interior of an angle is a restricted area.
(e) Line is a part of a ray.
(f) Two lines in a plane can intersect each other at two points.
Q5: Which of the following are polygons:-
(a) 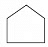
(b)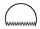
(c)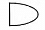
(d)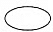
(e)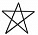
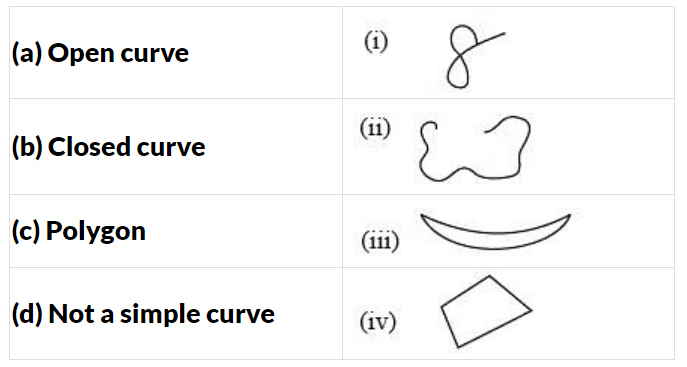
Q6: Match the following:
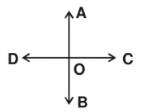
Q7: Name the rays in this figure. How many angles are being formed?
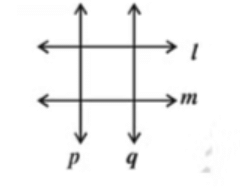
Q8: Identify and name the pairs of parallel lines.
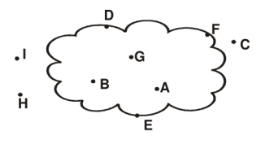
Q9: Identify the points which are:
(a) In the exterior of the curve
(b) On the curve
(c) In the interior of the curve
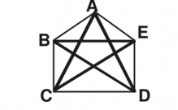
Q10:
(a) Name the 5 vertices forming this figure.
(b) Name any 2 adjacent sides.
(c) Name any 2 opposite sides.
(d) Name the diagonals.
You can access the solutions to this worksheet here.
FAQs on Basic Geometrical Ideas Class 6 Worksheet Maths Chapter 4
| 1. What are the basic geometrical shapes and their properties? |  |
| 2. How do you calculate the area of different shapes? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between perimeter and area? |  |
| 4. How can I use a protractor to measure angles? |  |
| 5. What are complementary and supplementary angles? |  |

















