Important Diagrams: Cell - The Unit of Life - Part 1 | Crash Course for NEET PDF Download
A cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life. It is the smallest unit of an organism that can carry out all the processes necessary for life. Cells are often called the "building blocks of life" because all living organisms, whether they are single-celled or multicellular, are composed of cells.
Some of the different types of cells based on various criteria are given below that can you in your NEET exam.
1: Types of Cell
Cells can vary in size, shape, and function, but they all share certain fundamental characteristics.
(a) Eukaryotic Cell
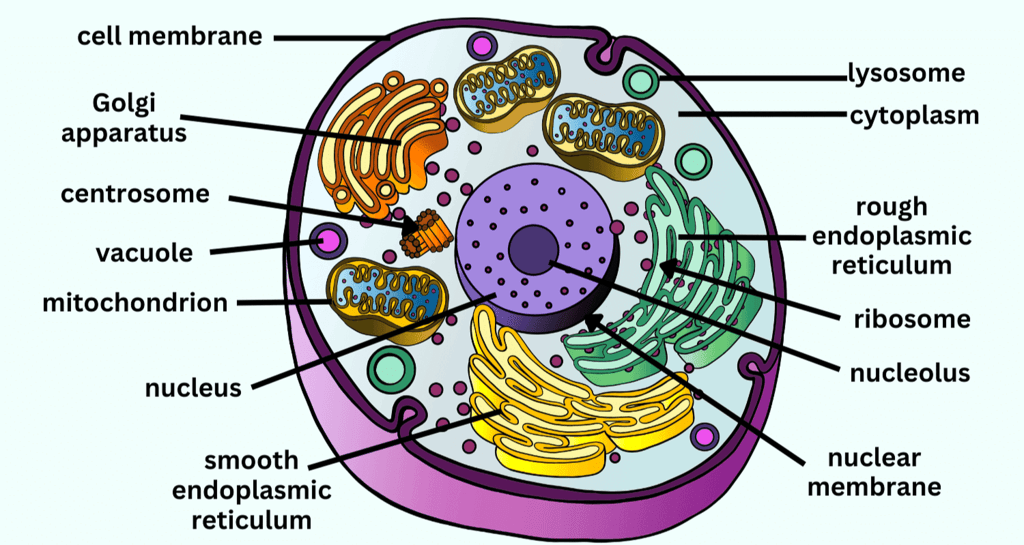
Eukaryotic cells are complex cells with a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
- They are the building blocks of multicellular organisms and are characterized by their organized internal structure, including the nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, and other organelles.
- Eukaryotic cells are involved in various cellular processes and are found in plants, animals, fungi, and some single-celled organisms.
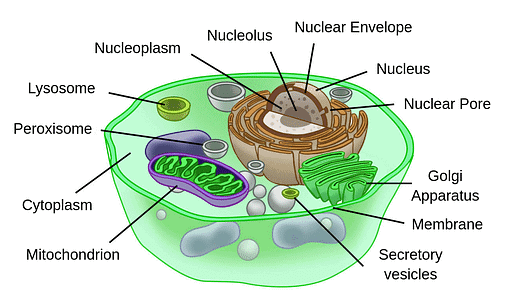 Eukaryotic Cell
Eukaryotic Cell
(b) Prokaryotic Cell
Prokaryotic cells are simpler in structure compared to eukaryotic cells, and they lack a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
- Prokaryotic cells are found in organisms such as bacteria and archaea.
- They are generally smaller and less complex than eukaryotic cells but are highly adaptable and have evolved to thrive in a wide range of environments
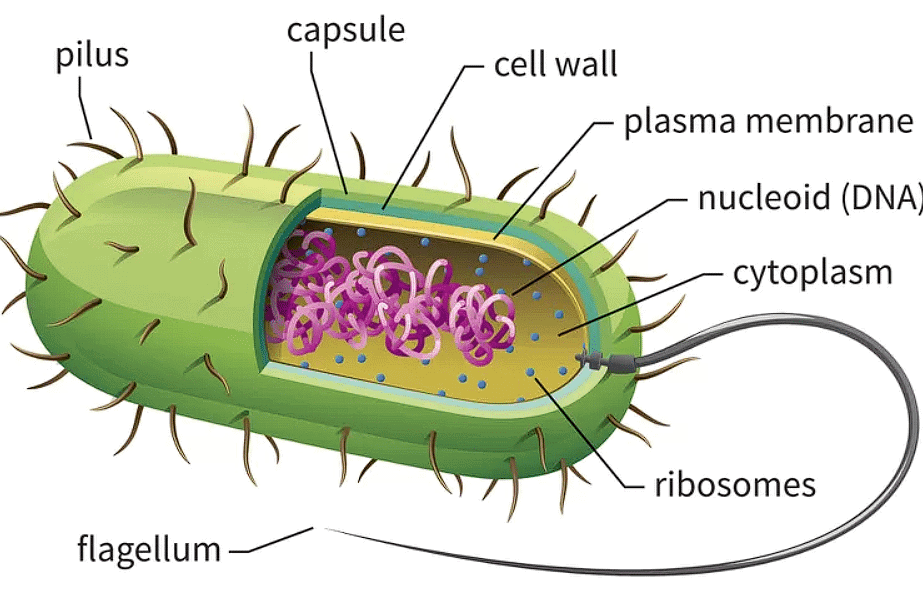 Prokaryotic Cell
Prokaryotic Cell
(c) Plant Cell
Plant cells are fundamental to the structure and function of plants. They possess unique organelles like chloroplasts and a central vacuole that are not found in animal cells.
- These features enable them to perform photosynthesis, store water and nutrients, and provide structural support, all of which are essential for plant growth and survival.
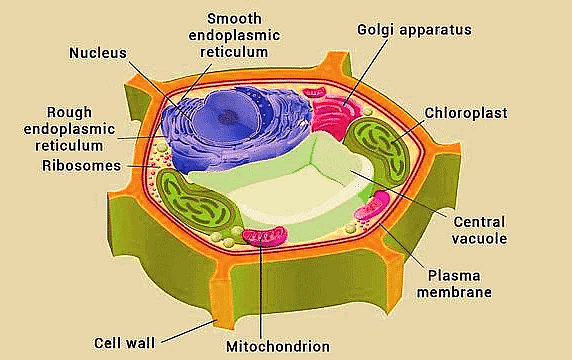 Plant Cell
Plant Cell
(d) Animal Cell
An animal cell is the fundamental structural and functional unit of animal organisms. It is a microscopic, membrane-bound structure that serves as the basic building block of animal tissues and organs.
- An animal cell is typically small and has a complex internal structure.
- It is surrounded by a semi-permeable cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, which encloses the cell's contents and separates it from the extracellular environment.
 Animal Cell
Animal Cell
2: Different Shapes of Cells
Cells can vary in shape and structure depending on their functions and the organisms they belong to. While the basic structural components of cells are similar, there can be variations.
- Spherical Cells: These cells have a round or spherical shape. Examples include many animal cells, such as blood cells (erythrocytes) and some bacterial cells.
- Cuboidal Cells: Cuboidal cells are cube-shaped, with all sides approximately equal in length. These cells are often found in epithelial tissues, such as those lining the kidney tubules.
- Columnar Cells: Columnar cells are elongated and have a tall, rectangular shape. They are commonly found in the lining of the intestines, where they aid in absorption.
- Squamous Cells: Squamous cells are flat and thin, resembling scales or fried eggs. They are found in tissues where a thin structure is needed, like the lining of blood vessels and the skin's outermost layer.
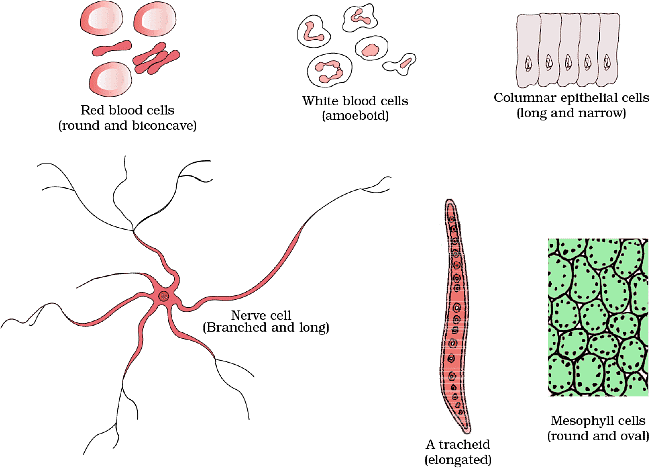 Shapes of Cell
Shapes of Cell
3: Types of Chromosomes
Chromosomes are thread-like structures found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. They are composed of DNA and associated proteins, and they carry genetic information in the form of genes. In humans and many other organisms, there are several types of chromosomes.
Some of the key types of chromosomes:
- Metacentric Chromosomes: Metacentric chromosomes have a centrally located centromere, resulting in two equal arms of the chromosome.
- Submetacentric Chromosomes: Submetacentric chromosomes have a centromere that is slightly off-center, resulting in one longer arm (q-arm) and one shorter arm (p-arm).
- Acrocentric Chromosomes: Acrocentric chromosomes have a centromere that is located closer to one end of the chromosome. They have a very short p-arm and a long q-arm.
- Telocentric Chromosomes: Telocentric chromosomes have a centromere located at one end of the chromosome, resulting in a long single arm.
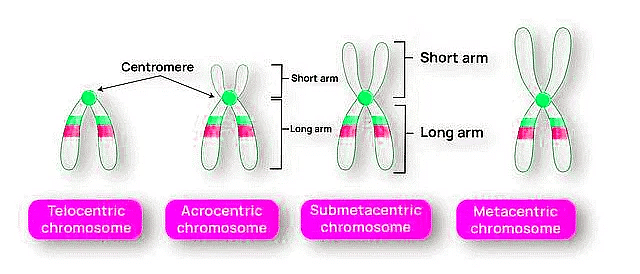 Types of Chromosmes
Types of Chromosmes
Diagram Based Previous Questions- NEET
Q1: Match List -I with list -II. (2022)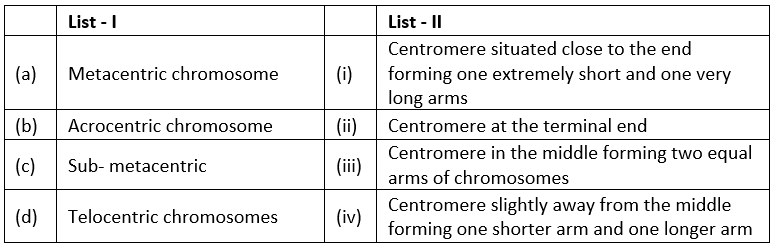 Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(A) (a)-(i), (b)-(iii), (c)-(ii), (d)-(iv)
B) (a)-(ii), (b)-(iii), (c)-(iv), (d)-(i)
C) (a)-(i), (b)-(ii), (c)-(iii), (d)-(iv)
(D) (a)-(iii), (b)-(i), (c)-(iv), (d)-(ii)
Ans. (d)
Solution. 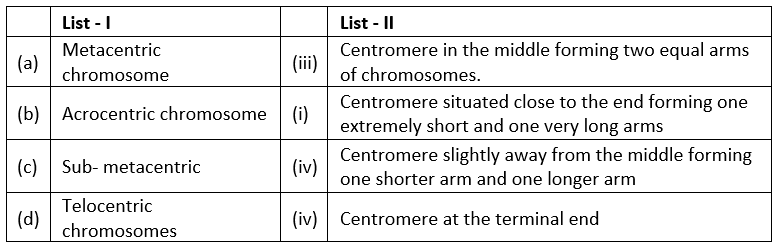
Q2: Select the wrong statement.
(a) Bacterial cell wall is made up of peptidoglycan.
(b) Pili and fimbriae are mainly involved in motility of bacterial cells.
(c) Cyanobacteria lack flagellated cells.
(d) Mycoplasma is a wall-less microorganism.
Ans. (b)
Solution.
 Prokaryotic Cell
Prokaryotic Cell
Pili and fimbriae are bacterial appendages which arc not involved in locomotion. Actually, pili are long, fewer and thick tubular outgrowths which develop in response to F+ or fertility factor in Gram negative bacteria.
- Being long they are helpful in attaching to recipient cell and forming conjugation tube. Fimbriae are small bristle-like fibres sprouting from cell surface in large number.
- There are 300-400 of them per cell. They are involved in attaching bacteria to solid surfaces.
Some Important Terms
An Overview of Cell
Organelles: The eukaryotic cells have other membrane bound distinct structures called organelles like the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), the golgi complex, lysosomes, mitochondria, microbodies and vacuoles.
Eukaryotic cells & Prokaryotic cells: Eukaryotic cells that have membrane bound nuclei are called eukaryotic whereas cells that lack a membrane bound nucleus are prokaryotic.
Centrosome: Animal cells contain another non-membrane bound organelle called centrosome which helps in cell division.
Prokaryotic Cells
- Plasmids: Many bacteria have small circular DNA outside the genomic DNA. These smaller DNA are called plasmids.
- Gram positive & Gram negative bacteria: Bacteria can be classified into two groups on the basis of the differences in the cell envelopes and the manner in which they respond to the staining procedure developed by Gram viz., those that take up the gram stain are Gram positive and the others that do not are called Gram negative bacteria.
- Slime layer & Capsule: Glycocalyx differs in composition and thickness among different bacteria. It could be a loose sheath called the slime layer in some, while in others it may be thick and tough, called the capsule.
- Mesosome: A special membranous structure is the mesosome which is formed by the extensions of plasma membrane into the cell. These extensions are in the form of vesicles, tubules and lamellae.
- Pili & Fimbriae: Besides flagella, Pili and Fimbriae are also surface structures of the bacteria but do not play a role in motility. The pili are elongated tubular structures made of a special protein. The fimbriae are small bristle like fibres sprouting out of the cell.
- Inclusion bodies: Reserve material in prokaryotic cells are stored in the cytoplasm in the form of inclusion bodies.
|
115 videos|67 docs
|
FAQs on Important Diagrams: Cell - The Unit of Life - Part 1 - Crash Course for NEET
| 1. What are the different types of cells? |  |
| 2. What are the different shapes of cells? |  |
| 3. What are the types of chromosomes? |  |
| 4. What are some important terms related to cells? |  |
| 5. What are some important diagrams related to the cell? |  |
















