UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 16th July 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Siachen Glacier |

|
| What is the Rubber Board? |

|
| About Rubber Board |

|
| Declare Floods as National Calamity |

|
| Vector-borne Disease |

|
| India Mobile Congress 2023 |

|
| About Parkinson’s Disease |

|
GS-I
Siachen Glacier

Why in News?
NJ 9842 is the known boundary between India and Pakistan, but fewer know about 5Q 131 05 084, the number assigned to the Siachen Glacier by the Geological Survey of India (GSI), a disputed area between the two countries since 1984.
- The point NJ 9842 as it is the last mutually demarcated point between India and Pakistan as per the Karachi ceasefire agreement of 1949 and also the point where the Line of Control of the Simla Agreement ends.
What is the First GSI Survey of Siachen Glacier?
- GSI Survey:
- The first GSI survey of the Siachen Glacier was conducted in June 1958 by an Assistant Geologist V. K. Raina, with the GSI. The survey aimed to study the Himalayan glacier systems as part of the International Geophysical Year activities.
- The GSI team spent nearly three months camping at the base of the glacier, conducting various studies and establishing survey points.
- Significance for India:
- The survey holds significance for India as it marks the official Indian exploration of the Siachen Glacier, an area that would later become a bone of contention between India and Pakistan.
- The peaceful environs surveyed in 1958 turned into a conflict zone when India launched Operation Meghdoot in 1984 to secure its presence in the region.
- The GSI survey provides historical evidence of India's early knowledge and scientific engagement with the glacier, countering any claims of Pakistani control since the beginning.
- Pakistan’s Claims:
- Initially, during the GSI survey in 1958, Pakistan did not raise any protests or objections to the Indian presence on the glacier. This could be attributed to both countries abiding by the terms of the Karachi ceasefire agreement of 1949, which had delineated the ceasefire line up to the glaciers and called for mutual demarcation.
- However, Pakistan's lack of interest in scientific visits and explorations in the region might have also played a role.
- It was only 25 years later, in August 1983, that Pakistan unilaterally extended the Line of Control (LOC) from NJ 9842 till the Karakoram Pass in its protest notes, challenging the status quo.
- This moves raised concerns in India, leading to the pre-emptive occupation of the strategic Saltoro Heights by Indian forces in April 1984.
- Pakistan's claims and actions since then have been based on differing interpretations of historical agreements, such as the Karachi ceasefire agreement and the Simla Agreement.
What is Siachen Glacier?
- The Siachen Glacier is located in the Eastern Karakoram range in the Himalayas, just northeast of Point NJ9842 where the LOC between India and Pakistan ends.
- The entire Siachen Glacier, with all major passes, has been under the administration of India since 1984 (Operation Meghdoot).
- The Siachen Glacier is positioned from northwest to southeast. It originates at the base of the Indira Col West, a col (low point) on the Indira Ridge, at an altitude of 6,115 metres, and it descends to an altitude of 3,570 metres.
- It is the Second-Longest glacier in the World's Non-Polar areas after Fedchenko Glacier in Tajikistan.
- The Siachen Glacier lies immediately south of the great drainage divide that separates the Eurasian Plate from the Indian subcontinent in the extensively glaciated portion of the Karakoram sometimes called the "Third Pole".
- Nubra river originates from Siachen Glacier.
- The Siachen Glacier is the world's highest battlefield.
Source: PIB
What is the Rubber Board?

Why in News?
The Central Government has dismissed concerns over a new Rubber Bill and existence of the Rubber Board.
About Rubber Board
- It is a statutory organization constituted under the Rubber Act, 1947.
- It functions under the administrative control of the Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
Functions of Rubber Board
- The Board is responsible for the development of the rubber industry in the country by assisting and encouraging research, development, extension and training activities related to rubber.
- It also maintains statistical data of rubber, takes steps to promote marketing of rubber and undertake labor welfare activities.
- A crucial function of the Rubber Board is issuing licenses to rubber producers, manufacturers, and exporters/traders. This license, known as the "Rubber Board license/registration," is mandatory for anyone involved in rubber manufacturing and export
Structure of Rubber Board
- The Board is headed by a Chairman appointed by the Central Government.
- It has 28 members representing various interests of the natural rubber industry.
- Headquarters: Kottayam, Kerala.
- The activities of the Board are exercised through Five Departments viz. General Services, Extension & Advisory Services, Research Services (rubber Research Institute of India), Training (Rubber Training Institute) & Finance.
Source: The Hindu
Declare Floods as National Calamity

Why in News?
The Samyukt Kisan Morcha (SKM) urged the Union government to declare the floods and landslides in north Indian States as a national calamity.
Implications of Declaration
- When a calamity is declared to be of “rare severity”/”severe nature”, support to the state government is provided at the national level.
- The Centre also considers additional assistance from the NDRF.
- A Calamity Relief Fund (CRF) is set up, with the corpus shared 3:1 between Centre and state.
- When resources in the CRF are inadequate, additional assistance is considered from the National Calamity Contingency Fund (NCCF), funded 100% by the Centre.
- Relief in repayment of loans or for grant of fresh loans to the persons affected on concessional terms, too, are considered once a calamity is declared “severe”.
Provisions to Classify a National Calamity
- There is no provision, executive or legal, to declare a natural calamity as a national calamity.
- The existing guidelines of the State Disaster Response Fund (SDRF)/ National Disaster Response Fund (NDRF), do not contemplate declaring a disaster as a ‘National Calamity.”
- The 10th Finance Commission (1995-2000) examined a proposal that a disaster is termed “a national calamity of rarest severity” if it affects one-third of the population of a state.
- The panel did not define a “calamity of rare severity” but stated that a calamity of rare severity would necessarily have to be adjudged on a case-to-case basis taking into account.
- The intensity and magnitude of the calamity
- Level of assistance needed
- The capacity of the state to tackle the problem
- The alternatives and flexibility were available within the plans to provide succour and relief, etc.
- In 2001, the National Committee on Disaster Management under the chairmanship of the then Prime Minister was mandated to look into the parameters that should define a national calamity.
What are Floods?
- Floods are the most frequent type of natural disaster and occur when an overflow of water submerges land that is usually dry.
Types of Floods
- Flash floods are caused by rapid and excessive rainfall that raises water heights quickly, and rivers, streams, channels or roads may be overtaken.
- River floods are caused when consistent rain or snow melt forces a river to exceed capacity.
- Coastal floods are caused by storm surges associated with tropical cyclones and tsunamis.
- Urban flooding occurs as a result of land development. Permeable soil layers are being replaced by impermeable paved surfaces, through which water cannot infiltrate.
- This leads to greater runoff being generated, which can make rivers out of roadways and ponds out of car parks.
What Causes Floods?
- Natural Causes:
- Prolonged rainfall: When rain falls for a prolonged period of time, the soil can become saturated. When water is unable to infiltrate into the saturated soil, it is forced to flow over the soil, thus increasing surface runoff.
- Intense/Heavy rainfall: When rain falls heavily; the raindrops hit the ground with a force. This can cause the rain drops to bounce off the soil instead of infiltrating into the soil. The water from the rain is then forced to flow over the surface instead, thus increasing the surface runoff.
- Relief refers to the difference in height between the highest point and the lowest point on land. When rain falls, the surface runoff can move very quickly from mountainous or hilly areas to low lying areas making these low lying areas more prone to flooding.
- Anthropogenic Causes
- Deforestation: The lack of vegetation encourages water to flow over the surface rather than infiltrate into the soil thus increasing surface runoff.
- Poor land use practices: Slash and burn agriculture, over-cultivation and overgrazing eventually cause the soil to become infertile and unable to sustain vegetative growth. Consequently, the lack of green cover encourages water to flow over the surface rather than infiltrate into the soil thus increasing surface runoff.
- Urbanization leads to the replacement of permeable soil with that of an impervious layer of pitch and concrete, through which water cannot infiltrate.
- Improper waste disposal: Oftentimes, garbage that is not properly disposed enters into drainage systems and clogs drains.
- Quarrying is the clearing of land for the removal of aggregates (mainly sand and gravel) which is to be utilized in the construction industry. The action of quarrying leaves land bare and devoid of any trees and shrubs hence increasing surface runoff produced.
- Collapsed Dams: If the dams begin to collapse, they will discharge more water downstream, resulting in flooding.
- Climate change: Uncontrolled human activities can contribute to climatic changes, which are responsible for flooding in most regions.
Implications
- Drowning accounts for 75% of deaths in flood disasters. Flood disasters are becoming more frequent and this trend is expected to continue.
- Drowning risks increase with floods particularly in low- and middle-income countries where people live in flood prone areas and the ability to warn, evacuate, or protect communities from floods is weak or only just developing.
- Deaths also result from physical trauma, heart attacks, electrocution, carbon monoxide poisoning or fire associated with flooding. Often, only immediate traumatic deaths from flooding are recorded.
- Floods can also have medium- and long-term health impacts, including:
- water- and vector-borne diseases, such as cholera, typhoid or malaria
- injuries, such as lacerations or punctures from evacuations and disaster cleanup chemical hazards,
- mental health effects associated with emergency situations,
- disrupted health systems, facilities and services, leaving communities without access to health care,
- damaged basic infrastructure, such as food and water supplies, and safe shelter.
- Economic losses to the State and individuals are also major concerns of the flooding.
Prevention
- Drainage Improvement: Ensure that there is proper drainage or expand on existing drainage systems whenever there’s new settlements or structures being constructed.
- Diversion of Flood Water: Diverting all or a part of the discharge into a natural or artificially constructed channel, lying within or in some cases outside the flood plains is a useful means of lowering water levels in the river.
- Catchment Area Treatment/Afforestation: Watershed management measures such as developing the vegetative cover i.e. afforestation and conservation of soil cover in conjunction with structural works like check dams, detention basins etc. serve as an effective measure in reducing flood peaks and controlling the suddenness of the runoff.
- Anti-erosion Works: Bank erosion can be minimized by adopting measures that aim at deflecting the current away from the river bank or which aim at reducing the current along the bank of the river and induce silt.
- Sea Walls/Coastal Protection Works: Sea walls/coastal protection works in the form of groins etc. are constructed to prevent flooding erosion in coastal areas by sea water.
- Inspection, Rehabilitation and Maintenance: Structural works require a periodic and systematic inspection, rehabilitation and maintenance programme to ensure that the design capabilities are maintained.
Source: TH
GS-II
Vector-borne Disease
Why in News?
The Union health ministry has sounded the alarm on a vector-borne disease outbreak with record rainfall in North India creating a favourable breeding ground for disease-carrying mosquitoes.
Vector-borne diseases
- They are human illnesses caused by parasites, viruses and bacteria that are transmitted by vectors.
- They are of six types (Malaria, Dengue, Chikungunya, Japanese Encephalitis, Lymphatic Filariasis, Kala-Azar). They are seasonal and outbreak prone with all except lymphatic Filariasis showing outbreak during monsoon and post-monsoon period generally.
Emerging Challenges
- Changing climatic conditions, particularly temperature and moisture variations following events such as extreme rainfall in some places and drought in others, will lead to a surge in the spread of vector-borne and infectious diseases across India, say scientists.
- As concerns mount over the recent increase in respiratory viral infections, including H2N3, adenoviruses and swine flu, in many parts of India
- The prospect of climate change leading to an increased burden with the spread of diseases such as dengue, chikungunya and malaria looms large
WHO response
- The "Global Vector Control Response (GVCR) 2017–2030" was approved by the World Health Assembly in 2017.
- It provides strategic guidance to countries and development partners for urgent strengthening of vector control as a fundamental approach to preventing disease and responding to outbreaks.
India’s Efforts
- Government is providing technical support through guidelines, advisories, epidemiological reports on outbreak preparedness, financial support through budget under NHM, monitoring and supervision, awareness through IEC campaigns, additional support through Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria (GFTAM).
- The Government of India is dedicated to curb these diseases and has the target of eliminating Malaria by 2030, Lymphatic Filariasis by 2030 and Kala-Azar by 2023.
- Government is putting out advisories to states and Union Territories (UTs) to collaborate with the respective civic agencies and take prompt action.
Way out
- Modelling future scenarios using state-of-the-art techniques that allow predictive future disease patterns or hotspots can be a useful tool to aid decision-makers in planning suitable and timely interventions
Source: LM
India Mobile Congress 2023

Why in News?
Recently, the 7th edition of India Mobile Congress (IMC) 2023 was inaugurated by the Ministery for Communications and Cellular Operators Association of India (COAI).
- The theme of IMC 2023 is "Global Digital Innovation," seeks to establish India as a leading technology developer, telecom manufacturer and exporter.
What is India Mobile Congress (IMC) 2023?
- India Mobile Congress (IMC) 2023 is a prominent annual event that showcases the latest advancements and innovations in the mobile and digital technology sector.
- It serves as a platform for industry leaders, policymakers, technology enthusiasts, and stakeholders to come together and discuss the future of the digital landscape.
How IMC is Promoting Technology and Societal Welfare?
- India has witnessed remarkable progress in several aspects of the telecom sector, such as the Atma Nirbhar Bharat initiative, the rollout of 5G technology, and the development of a roadmap for 6G.
- Fostering Innovation and Indigenous Technology:
- IMC 2023 focuses on nurturing an innovative ecosystem by facilitating collaborations between industry leaders, startups, and academia.
- The involvement of at least 100 universities and the inclusion of students in the event provide a platform for knowledge-sharing and encourages young minds to contribute to digital transformation.
- The event emphasizes the development of indigenous technologies, including telecom and semiconductor manufacturing, to support the vision of an Atmanirbhar Bharat (Self-Reliant India).
- IMC's Impact on India's Technological Advancement:
- IMC has played a pivotal role in India's technological transformation, contributing to the country's rapid 5G rollout, Atmanirbhar Bharat initiative, and the roadmap for 6G technology.
- Expanding Horizons:
- IMC has evolved beyond its initial focus on telecom, encompassing various industries such as drone technology, power electronics, AI innovations, deep tech, satcom, mobile manufacturing, cybersecurity, data center innovation, and more.
- By broadening its scope, IMC fosters collaboration across sectors, facilitating technological advancements that benefit agriculture, education, logistics, transportation, and animal husbandry.
- Ensuring Cybersecurity:
- Recognizing the importance of cybersecurity, IMC 2023 dedicates a section to address consumer-facing cyber threats, aiming to enhance organizational and public safety from cyber frauds.
- By creating awareness and discussing effective cybersecurity measures, the event contributes to safeguarding digital infrastructure and privacy.
- Virtual Exhibition and Outreach:
- To ensure broader accessibility and participation, IMC 2023 introduces the concept of a virtual exhibition, enabling individuals from different parts of the country to engage with the event remotely.
- This expansion reflects the event's commitment to reaching diverse audiences and promoting digital innovation on a national scale.
- Aspire: Igniting Future Entrepreneurship:
- It introduces Aspire, a dedicated start-up event aimed at fostering entrepreneurship among young innovators in the telecom and digital domains.
- With sections like an Investor zone, pitching zone, workshop zone, and networking zone, Aspire aims to create an unparalleled experience and accelerate the growth of aspiring entrepreneurs.
Conclusion:
- India Mobile Congress 2023 signifies the crucial role played by India in the worldwide digital revolution. With its emphasis on global digital innovation, the development of indigenous technology, and cross-industry collaboration, IMC acts as a catalyst for India's technological progress.
- By fostering innovation, broadening its scope, ensuring cybersecurity, promoting global collaboration, and nurturing entrepreneurship, IMC reinforces India's leadership in the technology sector and propels the nation towards a future empowered by digital advancements.
Source: The Hindu
GS-III
About Parkinson’s Disease
Why in News?
Neuroscientists recently found that intensive exercise could slow the course of Parkinson's disease.
About Parkinson’s Disease
- It is a progressive neurological disorder that affects the nervous system and the parts of the body controlled by the nerves.
- It is a condition in which a patient holds limited or no control over his movements and body balance.
- It occurs and progresses with ageing, but in rare cases, it is also witnessed among children and teenagers as well.
- It has no cure.
- Many studies have suggested that men are more likely to be affected by Parkinson’s than women.
Cause of Parkinson’s Disease
- It is caused by the degeneration of nerve cells in the part of the brain called the substantia nigra, which controls movement.
- These nerve cells die or become impaired, losing the ability to produce an important chemical called dopamine.
- Dopamine operates with other neurotransmitters to help coordinate the millions of nerve and muscle cells involved in the movement.
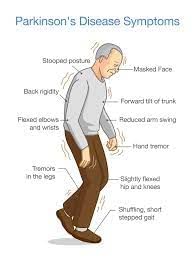
Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease
- Tremors (trembling in the hands, arms, legs, and jaw); rigidity (stiffness of the limbs); slowness of movement; and impaired balance and coordination.
- Parkinson’s patients may also experience other symptoms such as difficulty in swallowing, chewing, and speaking, urinary problems, constipation, skin problems, depression, emotional changes, and sleep disruption.
- Currently, no blood laboratory or radiological tests are available to diagnose Parkinson’s disease.
Source: DTE
|
38 videos|5293 docs|1118 tests
|















