NEET Exam > NEET Notes > Biology Class 11 > Mnemonics: Plant Growth & Development
Mnemonics: Plant Growth & Development | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| 1. Phases of Growth |

|
| 2. Sequence of the Developmental Process in a Plant Cell |

|
| 3. Types of Growth Regulators |

|
| 4. Functions of Growth Regulators |

|
This document will help you remember important information about Plant Growth & Development in a fun and easy way. Inside, you'll find mnemonics—memory tricks—that will make it easier for you to remember key concepts, and examples related to Plant Growth & Development.
Whether you're studying for an exam, preparing for a quiz, or simply looking to enhance your understanding of Plant Growth & Development, these mnemonics will serve as valuable memory tools. Utilise them alongside your regular study routine to reinforce your knowledge and increase your recall ability.
Happy mnemonic learning!
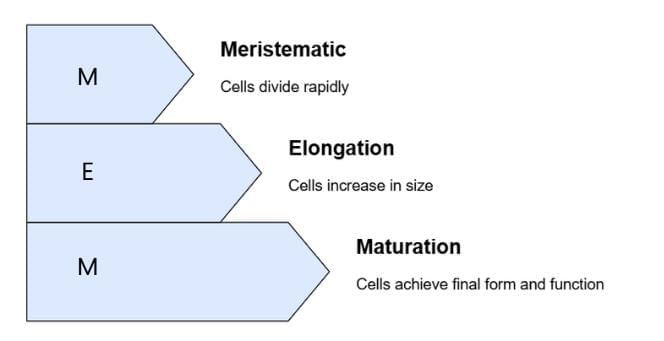
1. Phases of Growth
Mnemonic: "MEM": (Meristematic, Elongation, Maturation)
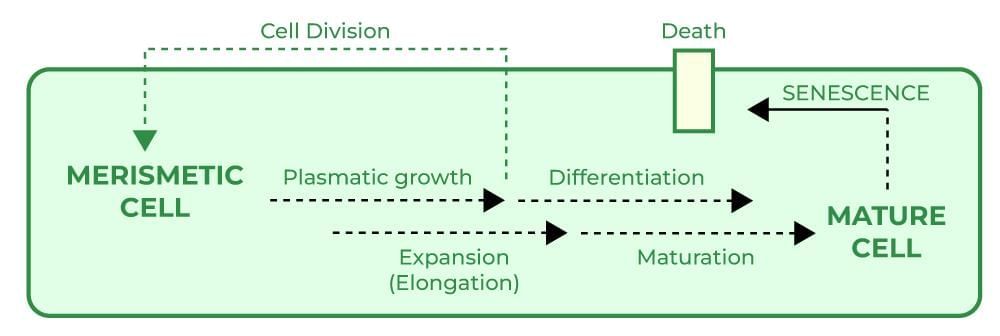
2. Sequence of the Developmental Process in a Plant Cell
Mnemonic: "Many Plants Expand Daily, Making Strong Cells"
- Many → Meristematic cells
- Plants → Plasmatic growth
- Expand → Expansion (Elongation)
- Daily → Differentiation
- Making → Maturation
- Strong → Senescence
- Cells → Cell Death
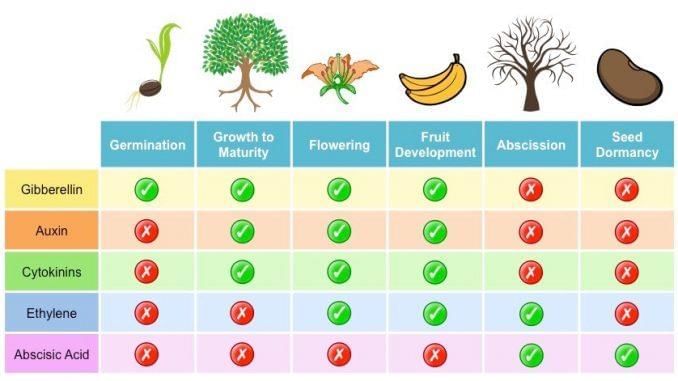
3. Types of Growth Regulators
(Auxins, Gibberellins, Cytokinins, Ethylene, Abscisic Acid):Mnemonic: "AGE CA"
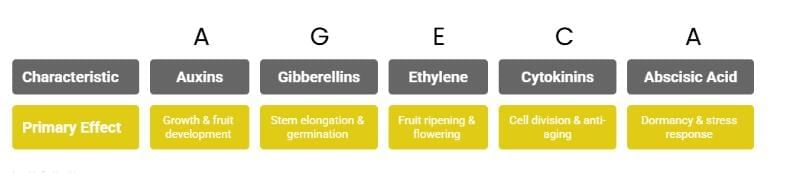 Mnemonic Explanation:
Mnemonic Explanation:
- A = Auxins: Promote growth and fruit development.
- G = Gibberellins: Stimulate stem elongation and seed germination.
- E = Ethylene: Influences fruit ripening and flower opening.
- C = Cytokinins: Promote cell division and delay ageing.
- A = Abscisic Acid: Induces seed dormancy and stress responses.
4. Functions of Growth Regulators
(a) Auxin
Mnemonic: "Rooty Flowers Avoid Lazy Cutting For Weedless Clean Xylem"
- Rooty → Root initiation (in stem cuttings)
- Flowers → Flowering promotion (e.g., in pineapples)
- Avoid → Abscission prevention (prevents early leaf/fruit drop)
- Lazy → Lateral bud inhibition (Apical dominance)
- Cutting → Cut shoot grows side branches (after decapitation)
- For → Fruit without seeds (Parthenocarpy in tomatoes)
- Weedless → Weed killer (2,4-D kills dicot weeds, not monocots)
- Clean → Cell division
- Xylem → Xylem differentiation
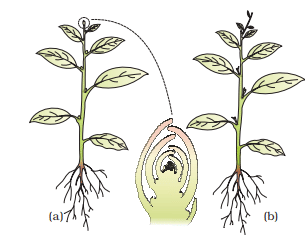 Apical dominance in plants : (a) A plant with apical bud intact (b) A plant with apical bud removed Note the growth of lateral buds into branches after decapitation.
Apical dominance in plants : (a) A plant with apical bud intact (b) A plant with apical bud removed Note the growth of lateral buds into branches after decapitation.
Mnemonic: "GROW FAST SEEDS"
G – Grape stalk elongation
(Gibberellins increase length of the grape stalk)R – Rosette bolting
(Bolting in beet, cabbage — sudden elongation before flowering)O – Overcome dwarfism
(Helps increase plant height in dwarf varieties)W – Wider apple shape
(Improves apple size and shape)F – Fruit stay longer
(Delays senescence — fruits remain on tree longer)A – Alcohol making
(Used in malting for brewing industry)S – Sugarcane yield
(Increases stem length — more sugar per acre)T – Tallness
(General stem elongation in various plants)S – Seed formation early
(Induces early maturity in juvenile conifers)
(c) Cytokinin
Mnemonic: "New Cute Leaves Grow Longer, Stay Young"
New → New cell formation (promotes cell division, especially cytokinesis)
Cute → Chloroplast development in leaves
Leaves → Leaf production (new leaf formation)
Grow → Growth of lateral shoots (overcomes apical dominance)
Longer → Lateral shoot formation (adventitious shoots)
Stay → Senescence delayed
Young → Youth maintained by nutrient mobilisation
Tip: Cytokinins = "Cell division & Staying young"
(d) Ethylene
Mnemonic: "Ripe Fruits Fall, Sleep Breaks, Roots Rise"
Ripe → Ripening of fruits (like bananas, apples, tomatoes)
Fruits → Fruit set & flowering (in pineapples, mango)
Fall → Abscission (leaves, flowers, and fruit drop)
Sleep → Seed/bud dormancy broken
Breaks → Bud sprouting & seed germination (e.g., in peanuts, potatoes)
Roots → Root growth and root hair formation
Rise → Shoot elongation in water (like in deep-water rice)
Bonus: Ethephon = Ethylene releaser (used in agriculture)
Tip: Ethylene = "Ripening & dropping hormone"
(e) Abscisic Acid (ABA)
Mnemonic: "Always Be Asleep During Stress"
Always → Abscission regulation (leaf/fruit fall)
Be → Bud dormancy
Asleep → Seed dormancy (inhibits germination)
During → Development of seeds (helps maturation)
Stress → Stress tolerance (closes stomata, fights desiccation)
Tip: ABA = "Sleepy & stress hormone" (antagonist to gibberellins)
The document Mnemonics: Plant Growth & Development | Biology Class 11 - NEET is a part of the NEET Course Biology Class 11.
All you need of NEET at this link: NEET
|
183 videos|524 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Mnemonics: Plant Growth & Development - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What are the primary functions of the plant hormone auxin? |  |
Ans. Auxin is primarily responsible for promoting cell elongation, regulating phototropism (growth towards light), and apical dominance (the inhibition of lateral bud growth). It also plays a vital role in root formation and development, as well as in the differentiation of vascular tissues.
| 2. How do cytokinins affect plant growth and development? |  |
Ans. Cytokinins promote cell division and are crucial for shoot development and growth. They help delay senescence (aging) in leaves, promote nutrient mobilization, and work in conjunction with auxins to regulate various aspects of plant growth, including root and shoot development.
| 3. What are the different stages of plant growth? |  |
Ans. The stages of plant growth include germination, vegetative growth, flowering, and fruiting. Germination is the process of seed sprouting, vegetative growth involves the development of leaves and stems, flowering is the stage where reproductive structures form, and fruiting is the stage where seeds develop within fruits.
| 4. How can mnemonics help in remembering plant growth and development concepts for NEET? |  |
Ans. Mnemonics are memory aids that can simplify complex information. For plant growth and development, using acronyms or phrases can help students recall the stages of growth or the functions of hormones like auxins and cytokinins, making it easier to memorize important details for exams like NEET.
| 5. Why is understanding plant hormones essential for NEET preparation? |  |
Ans. Understanding plant hormones is crucial for NEET preparation because they play significant roles in plant physiology and development. Hormones like auxins and cytokinins are often part of questions related to plant biology, and knowing their functions can help students answer questions accurately and enhance their overall understanding of plant systems.
Related Searches





















