Nuclear chemistry: Basics | Science & Technology for UPSC CSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Atomic Number (Z) |

|
| Mass Number (A) |

|
| Isotopes |

|
| Isobars |

|
| Allotropes |

|
| Radioactivity |

|
| Alpha Radiation: |

|
| Beta Radiation |

|
| Gamma Radiation |

|
| Nuclear Reactions |

|
| Nuclear Fission |

|
| Nuclear Fusion |

|
Atomic Number (Z)
The atomic number of an atom is the number of protons or electrons it contains. In a neutral atom, the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons, defining the element's identity.
Example: Nitrogen (N) has an atomic number of 7, Calcium (Ca) has an atomic number of 20, and Oxygen (O) has an atomic number of 8.Mass Number (A)
The mass number of an atom is the sum of protons and neutrons present in its nucleus. It helps determine the atom's mass and is denoted by the symbol "A."
Example: Nitrogen (N) has a mass number of 14, Calcium (Ca) has a mass number of 40, and Oxygen (O) has a mass number of 16.
Isotopes
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have the same atomic number (number of protons) but different mass numbers (different number of neutrons). Consequently, isotopes have different atomic masses.
Example: Protium, Deuterium, and Tritium are isotopes of hydrogen. They all have one proton (Z = 1) but different numbers of neutrons, giving them distinct mass numbers.
Isobars
Isobars are atoms or elements that have the same mass number (total number of protons and neutrons) but different atomic numbers (different number of protons). This means they belong to different elements but have the same mass.
Example: 40S (Sulfur-40), 40Cl (Chlorine-40), 40Ar (Argon-40), 40K (Potassium-40), and 40Ca (Calcium-40) are isobars. They all have a mass number of 40 but different atomic numbers.
Allotropes
Allotropes are different forms or structural arrangements of the same element, presenting distinct physical and chemical properties.
Example: Diamond and graphite are allotropes of carbon. Both are composed of carbon atoms, but they have different crystal structures, resulting in contrasting properties.
Radioactivity
Unstable atomic nuclei spontaneously decompose to form nuclei with higher stability, and this process is known as radioactivity.
Energy and particles released during the decomposition process are called radiation.
Three Types of Natural Radioactivity
Alpha Radiation:
Alpha radiation involves the emission of alpha particles from a radioactive nucleus.
An alpha particle consists of 2 protons and 2 neutrons, which is equivalent to a helium nucleus.
Example: 23892U → 42He + 23490Th
Beta Radiation
Beta radiation occurs when a radioactive nucleus emits beta particles.
A beta particle is an electron (0-1e) or a positron (0+1e).
Example: 23490Pa → 0-1e + 23491U
Gamma Radiation
Gamma radiation consists of high-energy photons with very short wavelengths. Unlike alpha and beta radiation, gamma emission does not alter the atomic number or atomic mass of the nucleus.
Nuclear Reactions
Nuclear reactions involve changes in atomic nuclei and can be classified into two types:
Nuclear Fission
Nuclear fission occurs when an atomic nucleus splits into two or more smaller nuclei.
The smaller nuclei produced are called fission products, and particles like neutrons, photons, or alpha particles may also be released.
Example: 23592U + 10n → 9038Sr + 14354Xe + 310n
Nuclear Fusion
Nuclear fusion is a process where atomic nuclei fuse together to form heavier nuclei.
This process releases large amounts of energy.
- 11H + 21H → 32He
- 32He + 32He → 42He + 211H
- 11H + 11H → 21H + 0 +1β
Comparison of Alpha, Beta, and Gamma Radiation: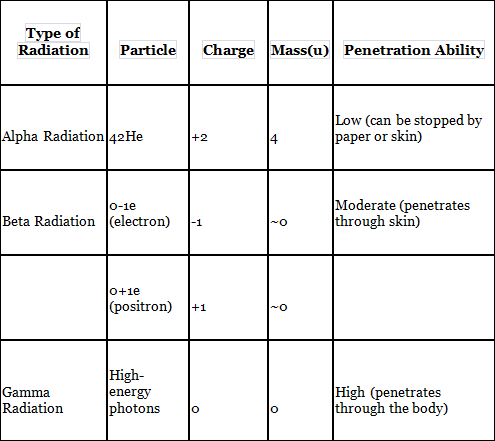
|
90 videos|490 docs|209 tests
|




















