Worksheet Solutions: Cube - 1 - Class 7 PDF Download
Q1: Which of the following numbers is a perfect cube?
(a) 256
(b) 243
(c) 1331
(d) 250
Ans: (c)
Here 256 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 243 = 3 × 3× 3 × 3 × 3
1331 = 11 × 11 × 11
250 = 2 × 5 × 5 × 5
Clearly 1331 is a perfect cube.
Q2: What will be the volume of a cube having edge length 12m? (in m3)
(a) 1728
(b) 1628
(c) 2248
(d) 1848
Ans: (a)
Volume of cube = (12)3 = 1728 m3
Q3: What is the smallest number by which 576 is divided that quotient is a perfect cube?
(a) 8
(b) 9
(c) 4
(d) 72
Ans: (b)
We have
576 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 3
∴ 576 should be divided by 9, to get a prefect cube.
Q4: If, 13 + 23 + 33 = (1 + 2 + 3)2, 13 + 23 + 33 + 43 = (1 + 2 + 3 + 4)2, then, 13 + 23 + 33 + 43 + 53 + 63 + 73
(a) 900
(b) 441
(c) 784
(d) 484
Ans: (c)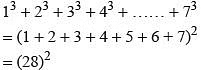
= 784
Q5: Observing the pattern 13 + 23 + 33 = (1 + 2 + 3)2, 13 + 23 + 33 + 43 = (1 + 2 + 3 + 4)2 , Find the sum: 13 + 33 + 53 + 73 + 93
(a) 1225
(b) 2025
(c) 825
(d) 1625
Ans: (a)
13 + 23 + 33 + …… + 93 = (1 + 2 + 3 …… + 9)2
⇒ (13 + 33 + 53 + 73 + 93) + 23 (13 + 23 + 33 + 43)
= (45)2 = 2025
⇒ x + 23 (1 + 2 + 3 + 4)2 = 2025
⇒ x = 2025 – 8 × 100 = 1225
Q6: Simplify : 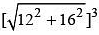
(a) 400
(b) 8000
(c) 64000
(d) 512000
Ans: (b)
Here 122 + 162 = 400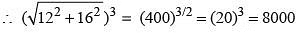
Q7: Simplify: (64/125)2/3
(a) 4/5
(b) 8/25
(c) 16/25
(d) 4/25
Ans: (c)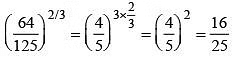
Q8: A natural number is of the form (3n + 2). Its cube will be of the form :
(a) 3n
(b) 3n + 1
(c) 3n + 2
(d) None of these
Ans: (c)
(3n + 2)3 = 27n3 + 8 + 3 × 3n × 2(3n + 2)
= 27n3 + 8 + 18n (3n + 2)
= 27n3 + 54n2 + 36n + 8
= 3 (9n3 + 18n2 + 12n + 2) + 2
= 3n + 2
Q9: A rational number, p < 1, then,
(a) p3 > 1
(b) p3 < 0
(c) p3 < p
(d) p3 > p
Ans: (c)
If, 0 < p < 1,
then, p3 < p.
Q10: A real number ‘p’ is such that p > 1, then
(a) p3 < 1
(b) p3 > p
(c) p3 < p
(d) p3 < 0
Ans: (b)
If, p > 1
then, p – 1 > 0
∴ p3 > p
Q.11: Find the cube of 3.5.
Sol: 3.53 = 3.5 x 3.5 x 3.5
= 12.25 x 3.5
= 42.875
Q.12: Find the smallest number by which 128 must be divided to obtain a perfect cube.
Sol: The prime factorisation of 128 gives:
128 = 2×2×2×2×2×2×2
Now, if we group the factors in triplets of equal factors,
128 = (2×2×2)×(2×2×2)×2
Here, 2 cannot be grouped into triples of equal factors.
Therefore, we will divide 128 by 2 to get a perfect cube
Q.13: Find the cube root of 13824 by prime factorisation method.
Sol: First let us prime factorise 13824:
13824 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 3 × 3
= 23 × 23 × 23 × 33
3√13824 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 = 24
Q.14: Is 392 a perfect cube? If not, find the smallest natural number by which 392 should be multiplied so that the product is a perfect cube.
Sol: The prime factorisation of 392 gives:
392 = 2 x 2 x 2 x 7 x 7
Since, we can see, number 7 cannot be paired in a group of three. Therefore, 392 is not a perfect cube.
To make it a perfect cube, we have to multiply the 7 by the original number.
Thus,
2 x 2 x 2 x 7 x 7 x 7 = 2744, which is a perfect cube, such as 23 x 73 or 143.
Hence, the smallest natural number which should be multiplied to 392 to make a perfect cube is 7.
Q.15: Parikshit makes a cuboid of plasticine of sides 5 cm, 2 cm, 5 cm. How many such cuboids will he need to form a cube?
Sol: Given, side of the cube is 5 cm, 2 cm and 5 cm.
Therefore, volume of cube = 5×2×5 = 50
The prime factorisation of 50 = 2×5×5
Here, 2, 5 and 5 cannot be grouped into triples of equal factors.
Therefore, we will multiply 50 by 2×2×5 = 20 to get perfect square.
Hence, 20 cuboid is needed.


















