Class 7 Maths Chapter 6 Practice Question Answers - The Triangle and Its Properties
Q1. The construction of a triangle ABC, given that BC = 3 cm is possible when difference of AB and AC is equal to :
A.3.2 cm
B.3.1 cm
C.3 cm
D.2.8 cm
Ans: (d)
Sol: Let the length of AB be x and AC be y
A triangle can be formed if the sum of any two sides is greater then the third
⇒ BC + AC > AB
⇒ 3 + AC > AB
⇒ 3 > AB − AC
⇒ AB − AC < 3
So only option Dis correct.
Q2. In a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is x times the sum of the squares of the other two sides. The value of x is:
A.2
B.1
C.1/2
D.1/4
Ans: (b)
Sol: In a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
Its a standard pythagoras theorem for right angle triangles.
Hyp2 = Perpendicular2 + Base2
According to question we have
Hyp2 = x(Perpendicular2 + Base2 )
So on comparing the above two equations,
We get, x = 1.
Q3. In ΔABC, if AB = BC then :
A.∠B>∠C
B.∠A=∠C
C.∠A=∠B
D.∠A<∠C
Ans: (b)
Sol: In △ABC , AB=AC
∴ the triangle is isoceles.
In an isoceles triangle the angles opposite to equal sides are equal.
∴ ∠A=∠C
Q4. The exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of two
A.Exterior angles
B.Interior angles
C.Interior opposite angles
D.Alternate angles
Ans: (c)
Sol: The exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of two interior opposite angles.
Q5. The △ formed by BC =7.2 cm , AC =6 cm and ∠C = 120o is:
A.An acute angle △
B.An obtuse angled △
C.A right angled △
D.None of these
Ans: (b)
Sol: Given ∠C=120∘
Here one of the angles of the triangle is greater than 90∘ . So the △ is obtuse angled triangle.
Therefore option B is correct.
Q6. If two angles in a triangle are 40∘ and 60∘ , then the third angle is:
A.90∘
B.80∘
C.70∘
D.60∘
Ans: (b)
Sol: Let the third angle be x
We know, by angle sum property, the sum of all angles of a triangles is 180∘ .
40∘ + 60∘ + x = 180∘
100∘ + x = 180∘
⇒ x = 80∘
Q7. Number of interior angles formed in a triangle are:
A.1
B.2
C.3
D.4
Ans: (c)
Sol: Number of interior angles formed in a triangle are 3.
Here, m∠A,m∠B and m∠C stand for measure of angle A,B and C.
Q8. In the given figure, XYZ is a/an________ triangle.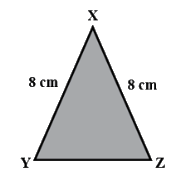
A.isosceles
B.equilateral
C.scalene
D.none of these
Ans: (a)
Sol: In the given △XYZ,
XY = XZ = 8 cm
Since two sides are equal of the given triangle.
∴ △XYZ is an isosceles triangle.
Option A is correct.
Q9. A triangle with the sides measuring 4 cm, 5 cm and 5 cm is called
A.an equilateral triangle
B.an isosceles triangle
C.a scalene triangle
D.none of the above
Ans: (b)
Sol: Given, the sides of the triangle are 4 cm, 5 cm and 5 cm
A triangle having two equal sides is called an isosceles triangle.
Here, two sides of the triangle are 5 cm and 5 cm. So, it is an isosceles triangle.
So, option B is correct.
Q10. A triangle with one right angle and two acute angles is called
A.right angled triangle
B.acute angled triangle
C.equilateral triangle
D.none of these
Ans: (a)
Sol: A triangle with a right angle and two acute angles is called right angled triangle.
Q11. The triangle formed by BC=5 cm,AC=3 cm,AB=5.8 cm is:
A.a right angled Δ
B.an isosceles Δ
C.an equilateral Δ
D.a scalene Δ
Ans: (d)
Sol: Given three lengths of sides are different.
Also, the sides do not follow Pythagora's theorem.
So, it is a scalene triangle.
Option D is correct.
Q12. A triangle can have :
A.one right angle
B.two right angles
C.three obtuse angles
D.none of these
Ans: (a)
Sol: Right angled triangle is a type of a triangle where one angle is right angle.
By angle sum property, sum of angles of a triangle =180o
If two angles are right angles in a triangle, then according to angle sum property, third angle =0o
This is not possible for a triangle.
So, other two angles have to be acute angle.
A is the answer.
Q13. A triangle with the sides measuring 5 cm, 6 cm and 4 cm is called:
A.an equilateral triangle
B.an isosceles triangle
C.a scalene triangle
D.none of the above
Ans: (c)
Sol: A triangle with three unequal sides is called scalene triangle.
So, option C is correct.
Q14. In a right angled triangle, the other two angles are:
A.acute
B.obtuse
C.right
D.none of these
Ans: (a)
Sol: An acute angle is an angle smaller than a right angle (90o is called a right angle). Hence, in a right angled triangle the other two angles are acute.
Q15. A triangle with all 3 equal sides is called
A.isosceles
B.equilateral
C.scalene
D.none of these
Ans: (b)
Sol: An equilateral triangle is one in which all three sides and angles are equal.
So, B is correct.
Q16. The length of the hypotenuse of a right-angle triangle whose measure of two sides are 12 cm and 0.35 m is:
A.37 cm
B.3.72 cm
C.0.372 cm
D.37 m
Ans: (d)
Sol: 0.35m = 0.35 × 100cm = 35cm
For a right angle triangle using Pythagorus theorem we get,
(Hypotenuse)2 =(side)2 + (side)2
= (12)2 +(35)2
= 144+1225
= 1369
Hypotenuse = 1369 = 37cm
Q17. A triangle with one obtuse and two acute angles is called
A.right angled triangle
B.acute angled triangle
C.obtuse angled triangle
D.none
Ans: (c)
Sol: An obtuse triangle (or obtuse-angled triangle) is a triangle with one obtuse angle (greater than 90°) and two acute angles.
The sum of angles in a triangle must be 180° and no triangle can have more than one obtuse angle.
So option C is the correct answer.
Q18. The triangle formed by BC=8.2cm, AC=7cm and ∠C=120∘ is-
A.An obtuse angled triangle
B.An acute angle triangle
C.A right angled triangle
D.None of these
Ans: (a)
Sol: In△ABC,
BC = 8.2cm,AC = 7cm and ∠C = 120∘
Here, we can see triangle contain one obtuse angle.
So,△ABC, is an obtuse angled triangle
Option A is the correct answer.
Q19. Sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle is always ____ than the length of the third side.
A.less than
B.equal to
C.greater than
D.None of these
Ans: (c)
Sol: It is a property of a triangle that:
Sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle is always greater than the length of the third side.
Q20. A quadrilateral is having _____.
A.one diagonal
B.two diagonals
C.three diagonals
D.four diagonals
Ans: (b)
Sol: A quadrilateral is a four-sided polygon.
Here, ABCD is a quadrilateral having four sides AB,BC,CD and AD
Diagonal is a line segment that goes from one corner to another.
The diagonals of quadrilateral ABCD are AC and BD.
∴ A quadrilateral is having two diagonals.
Q21. The interior of a triangle is
A.the intersection of three lines
B.the union of three line segments
C.the set of the intersection of interiors of the angles of triangle
D.none of these
Ans: (c)
Sol: The interior of a triangle is the set of the intersection of interiors of the angles of triangle.
Q22. Can the three sides of length 6cm,5cm, and 3cm form a triangle?
A.Yes
B.No
C.Sometimes
D.None
Ans: (a)
Sol: Taking two sides at a time to check the inequality property of a triangle that is the sum of two sides of a triangle is always greater than the third side.
(1) (6+5)=11>3 {Satisfying}
(2) (5+3)=8>6 {Satisfying}
(3) (3+6)=9>5 {Satisfying}
Hence, they can form a triangle.
Q23. If one angle of a triangle is equal to half the sum of the other two equal angles, then the triangle is
A.Isosceles
B.Scalene
C.Equilateral
D.Right-angled
Ans: (d)
Sol: ∠A = 1/2 (∠B + ∠C)
∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 1/2 (∠B + ∠A)
or∠B + ∠C = 90∘or∠A = 90∘
Q24. All equilateral triangles have ___ sides and ____ angles equal.
A.two, two
B.three, three
C.three , two
D.two, three
Ans: (b)
Sol: A triangle with all sides equal and all the three angles equal to 60∘ is called an Equilateral triangle.
Thus, option B is correct.
Q25. We use ______ formula to find the lengths of the right angled triangles.
A.Pythagoras theorem
B.Postulate theorem
C.Thales theorem
D.None of the above
Ans: (a)
Sol: a2 + b2 = c2 is the formula used to find the lengths of the right angled triangles. This formula was named after the mathematician named Pythagoras called Pythagoras theorem .
Therefore, A is the correct answer.
Q26. Angles opposite to ____ sides of an isosceles triangles are equal.
A.equal
B.unequal
C.any two
D.none of these
Ans: (a)
Sol: Angles opposite to equal sides of an isosceles triangles are equal.
Q27. In Pythagoras theorem in right angled triangle the longest side is called the
A.Hypotenuse
B.Height
C.Perpendicula
D.Bisector
Ans: (a)
Sol: Longest side is called Hypotenuse and its is opposite to the right angle.
In the attached figure AC is Hypotenuse.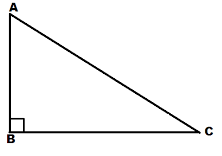
Q28. A triangle whose _____ angle(s) is 90o is called a right angled triangle.
A.0
B.3
C.2
D.1
Ans: (d)
Sol: A triangle whose one angle is 90o is called a right angled triangle.
Q29. What is the name of the closed figure with four sides?
A.Hexagon
B.Triangle
C.Pentagon
D.Quadrilateral
Ans: (d)
Sol: A quadrilateral is a closed figure having four sides.
Therefore, D is the correct answer.
Q30. Define Pythagoras theorem.
A.In a right angled triangle , square of a hypotenuse is not equal to the sum of the squares of two sides.
B.In a right-angled triangle, the square of a hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
C.In a right angled triangle , hypotenuse is equal to the sum of two sides.
D.In a triangle , square of a side is equal to the square of another side.
Ans: (b)
Sol: In a right angled triangle ,square of hypotenuse (longest side) is equal to the sum of squares of other two sides.
In △ABC
(AC)2 =(AB)2 +(BC)2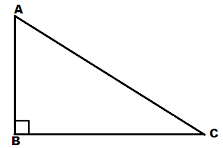
Q31. In the given diagrams, find the value of x in each case.
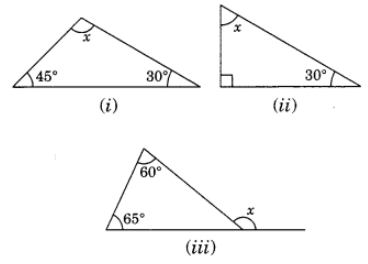 Sol:
Sol:
(i) x + 45° + 30° = 180° (Angle sum property of a triangle)
⇒ x + 75° – 180°
⇒ x = 180° – 75°
x = 105°
(ii) Here, the given triangle is right angled triangle.
x + 30° = 90°
⇒ x = 90° – 30° = 60°
(iii) x = 60° + 65° (Exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of interior opposite angles)
⇒ x = 125°
Q32. In the given figure, find x.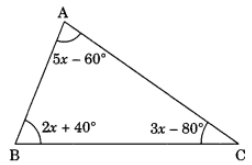 Sol:
Sol:
In ∆ABC, we have
5x – 60° + 2x + 40° + 3x – 80° = 180° (Angle sum property of a triangle)
⇒ 5x + 2x + 3x – 60° + 40° – 80° = 180°
⇒ 10x – 100° = 180°
⇒ 10x = 180° + 100°
⇒ 10x = 280°
⇒ x = 28°
Thus, x = 28°
Q33. One of the equal angles of an isosceles triangle is 50°. Find all the angles of this triangle.
Sol: Let the third angle be x°.
x + 50° + 50° = 180°
⇒ x° + 100° = 180°
⇒ x° = 180° – 100° = 80°
Thus ∠x = 80°
Q34. In ΔABC, AC = BC and ∠C = 110°. Find ∠A and ∠B.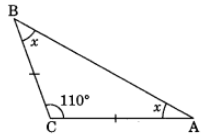 Sol: In given ΔABC, ∠C = 110°Let ∠A = ∠B = x° (Angle opposite to equal sides of a triangle are equal)
Sol: In given ΔABC, ∠C = 110°Let ∠A = ∠B = x° (Angle opposite to equal sides of a triangle are equal)
x + x + 110° = 180°
⇒ 2x + 110° = 180°
⇒ 2x = 180° – 110°
⇒ 2x = 70°
⇒ x = 35°
Thus, ∠A = ∠B = 35°
Q35. In the given right-angled triangle ABC, ∠B = 90°. Find the value of x.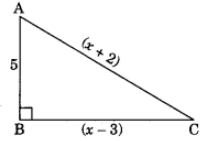 Sol:
Sol:
In ΔABC, ∠B = 90°
AB2 + BC2 = AC2 (By Pythagoras property)
(5)2 + (x – 3)2 = (x + 2)2
⇒ 25 + x2 + 9 – 6x = x2 + 4 + 4x
⇒ -6x – 4x = 4 – 9 – 25
⇒ -10x = -30
⇒ x = 3
Hence, the required value of x = 3
Q36. In figure (i) and (ii), Find the values of a, b and c
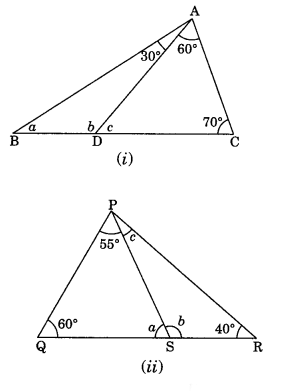 Sol:
Sol:
(i) In ∆ADC, we have
∠c + 60° + 70° = 180° (Angle sum property)
⇒ ∠c + 130° = 180°
⇒ ∠c = 180° – 130° = 50°
∠c + ∠b = 180° (Linear pair)
⇒ 50° + ∠b = 180°
⇒ ∠ b = 180° – 50° = 130°
In ∆ABD, we have
∠a + ∠b + 30° = 180° (Angle sum property)
⇒ ∠a + ∠130° + 30° = 180°
⇒ ∠a + 160° = 180°
⇒ ∠a = 180° – 160° = 20°
Hence, the required values are a = 20°, b = 130° and c = 50°
(ii) In ∆PQS, we have
∠a + 60° + 55° = 180°(Angle sum property)
⇒ ∠a + 115° = 180°
⇒ ∠a = 180° – 115°
⇒ ∠a = 65°
∠a + ∠b = 180° (Linear pair)
⇒ 65° + ∠b = 180°
⇒ ∠b = 180° – 65° = 115°
In ∆PSR, we have
∠b + ∠c + 40° = 180° (Angle sum property)
⇒ 115° + ∠c + 40° = 180°
⇒ ∠c + 155° = 180°
⇒ ∠c = 180° – 155° = 25°
Hence, the required angles are a = 65°, b = 115° and c = 25°
|
76 videos|386 docs|39 tests
|
FAQs on Class 7 Maths Chapter 6 Practice Question Answers - The Triangle and Its Properties
| 1. What are the different types of triangles based on their sides? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of triangles based on their angles? |  |
| 3. How can you find the area of a triangle? |  |
| 4. What is the Pythagorean theorem and how does it relate to triangles? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of the triangle inequality theorem? |  |
















