Class 8 Maths - Comparing Quantities CBSE Worksheets Solutions
Multiple Choice Questions
Q1: The ratio of 50cm to 2.5m is
(a) 10 : 1
(b) 5 : 1
(c) 1 : 5
(d) None of these
Ans: (c)
We know that, 1m = 100cm
2.5m = 2.5 × 100 = 250cm
Ratio of 50cm to 2.5m = 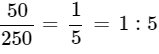
Q2: The number of unelectrified villages in India decreased from 18,000 to 12,000 in last 6 years. What is the percentage of decrease?
(a) 30%
(b) 50%
(c) 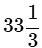
(d) None of these.
Ans: (c)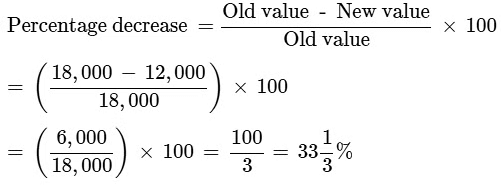
Q3: Cost of an item is Rs. 50. It was sold with a profit of 12%. Find the selling price
(a) Rs.56
(b) Rs. 60
(c) Rs.70
(d) None of these.
Ans: (a)
We know that
Cost Price = Rs. 50
and, Profit % = 12
Therefore, Profit = 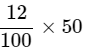
⇒ Profit = 6
⇒ S.P. = C.P. + Profit
⇒ S.P. = 50 + 6
⇒ S.P. = Rs 56
Q4: The simple interest on Rs.6000 for 1 year at 4% per annum is
(a) Rs.126.50
(b) Rs.240
(c) Rs.43
(d) None of these
Ans: (b)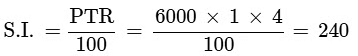
Q5: The fraction form of 45% is
(a) 3/20
(b) 9/20
(c) 11/20
(d) 13/2
Ans: (b)
45% = 45/100 = 9/20
Q6: The fraction form of 60% is
(a) 3/5
(b) 4/5
(c) 3/10
(d) 7/10
Ans: (a)
60% = 60/100 = 6/10 = 3/5
Q7: The percent form of 3.05 is
(a) 61/20%
(b) 61/50%
(c) 305%
(d) 350%
Ans: (c)
3.05 x 100% = 305/100 x 100 = 305%
Q8: The Decimal form of 21% is
(a) 0.21
(b) 2.1
(c) 21
(d) 210
Ans: (a)
21% = 21/100 = 0.21
Q9: The decimal form of 300% is
(a) 0.3
(b) 0.03
(c) 3.0
(d) 30.0
Ans: (c)
300% = 300/100 = 3.0
Q10: 35% of 1 kg is equal to
(a) 3.5 GM
(b) 35 GM
(c) 350 GM
(d) 3.5 KG
Ans: (c)
35% x 1000gm
35/100 x 1000gm = 350gm
Answer the following Questions
Q1: A school trip is being planned in a school for class VIII. Girls are 60% of the total strength and are 18 in number. Find the ratio of number of boys to number of girls.
Ans: Let ‘x’ be the total number of students.
Thus, number of girls = 60% of x = 18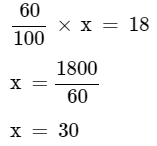
Number of boys = (Total number of students) - (Total number of girls)
= 30 – 18
= 12.
Hence ratio of number of boys to girls is
= 12 : 18
= 2 : 3.
Q2: In a constituency there are 120 voters 90 of them voted Yes. What percent voted Yes?
Ans: Given:
Number of voters = 120
Number of voters who voted Yes = 90
Q3: If Rs. 250 is divided among Rakshith, Ravi and Raju. So that Rakshith gets 3 parts, Ravi gets 2 parts and Raju gets 5 parts. How much money will each get in percentages?
Ans: Given: total amount = 250
Total number of parts = 10
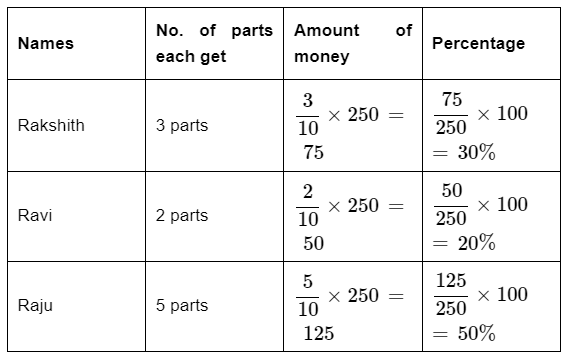
Q4: My grandmother says in her childhood milk was at Rs.2 per litre. It was Rs.36 per litre today. By what percentage has the price gone up?
Ans: Given:
Old value = Rs. 2 per litre
New price = Rs. 36 per litre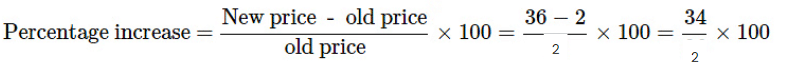
=1700%.
Q5: The cost of a toy car is Rs. 140. If the shopkeeper sells it at a loss of 10%. Find the price at which it is sold.
Ans: Given:
C.P. of toy car = Rs. 140
Loss% = 10%
S.P. = ?
We know that,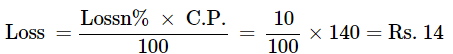
Loss = C.P. – S.P.
S.P. = C.P. – Loss
S.P. = 140 – 14
S.P. = Rs.126
Q6: Rashida purchased an air-conditioner for Rs. 3400 including a tax of 10%. Find the actual price of the air conditioner before VAT was added.
Ans: Let ‘x’ be the cost before adding VAT.
VAT = 10% of x = 0.1x
Cost after adding VAT = x + 0.1x = 1.1x
Given: cost = Rs.3,400
1.1x = Rs. 3400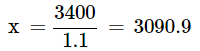
Thus, the price of an air-conditioner = Rs. 3090.9.
Q7: At what rate of simple interest will the sum double itself in 2 years?
Ans: We know that,
A = S.I. + P
Where,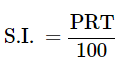
Given: A = 2 × principle = 2P
Time = t = 2 years
R = ?
Formula becomes 2P = S.I. + P
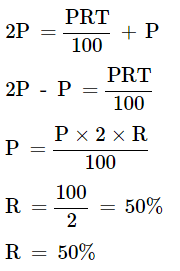
Therefore, at the rate of 50%, the sum will double.
Q8: In what time will Rs. 1600 amount to Rs. 1768 at 6% per annum simple interest?
Ans: Given:
Principle = Rs. 1600
Amount = Rs. 1768
Rate = 6% per year
Time = ?
A = S.I. + P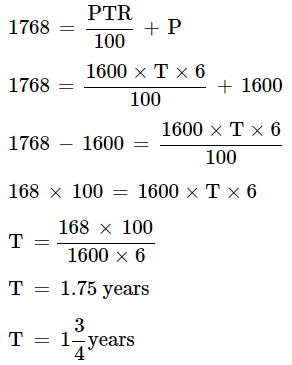
Q9: What amount Harish has to pay at the end of 2 years of Rs. 40,000 at an interest of 16% compounded annually?
Ans: We know that, formula for compound interest,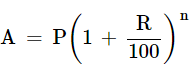
Where, P = principle
N = no. of years
P = Rs. 40,000, R = 16%, n = 2.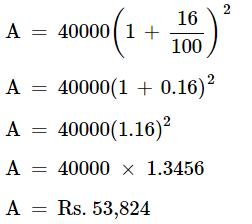
Amount paid by Harish at the end of 2 years is Rs. 53,824.
Q10: Mahesh sells two tables for Rs. 3000 each. He gains 20% on one table and on the other he loses 20%. Find his gain or loss percent on whole transaction.
Ans: For the first table: given:
S.P. = Rs. 3000
Gain% = 20% = 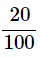
Gain percent implies increased percent on cost price.
For Rs.100 cost price, the gain = Rs.20
S.P. = C.P. + gain
S.P. = 100 + 20 = Rs.120
Thus, S.P. is Rs. 120 when C.P. is Rs.100
Therefore, for S.P. of Rs. 3000, the cost price will be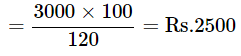
For second table,
S.P. = Rs.300
Loss percent = 20% =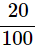
Loss percent decreases percent on cost price.
For Rs.100 of C.P., loss = Rs.20
S.P. = C.P. – loss = 100 – 20 = Rs.80.
Thus, S.P. is Rs.80 when C.P. is Rs.100
For S.P. of Rs.3000, the cost price is given by
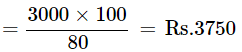
Total cost price = 2500 + 3750 = 6250
Total S.P. = 2500 + 3750 = 6000
Here, S.P. < C.P., Hence loss is Occured
Loss = C.P. – S.P. = 6250 – 6000 = 250
Loss percent =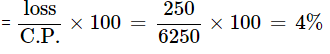
Therefore, there is a loss of 4% on whole transaction.
Q11: Prateeksha went to a shopping mall to purchase a saree. Marked price of the saree is Rs.1000. Shop owner gave a discount of 20% and then 5%.Find the single discount equivalent to these 2 successive discounts.
Ans: 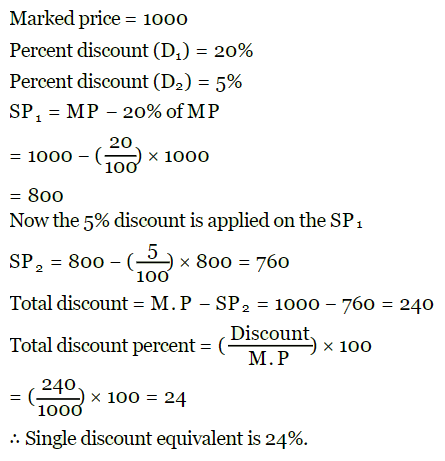
Q12: Rajanna purchased 25 dozen bananas for RS. 625. He spent Rs. 125 for transportation. He could not sell 5 dozen bananas as they were spoiled. He sold the remaining banana’s at Rs. 30 for each dozen. Find loss and profit percent.
Ans: Total cost price = Cost price of bananas + transportation charge
=Rs. 625 + Rs. 125 = Rs. 750
Number of dozens of bananas sold = No. of purchased – No. of spoiled
= 25 – 5
= 20
Given: 1 dozen = Rs.30
Therefore, S.P. = 20×30=Rs.600
Since, S.P. < C.P., it is a loss
Loss = C.P. – S.P. = 750 – 600 = 150
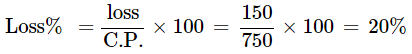
|
81 videos|423 docs|31 tests
|
FAQs on Class 8 Maths - Comparing Quantities CBSE Worksheets Solutions
| 1. What is the concept of comparing quantities in Class 8 mathematics? |  |
| 2. How can I compare two quantities using ratios and proportions? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of understanding profit and loss in comparing quantities? |  |
| 4. How can I calculate simple interest to compare quantities? |  |
| 5. How can I apply the concept of comparing quantities in real-life situations? |  |

















