Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Question Answers - Nutrition in Plants
Q1. List some harmful effect of fungi.
Ans: Fungi, although beneficial in numerous ways, also have several harmful effects. One of the significant impacts of fungi is on agriculture as they cause diseases in crops, leading to reduced yield and quality.
- They infect various crops and cause diseases like rice blast, corn smut, and potato blight. Besides, fungi also cause diseases in animals and humans, such as athlete's foot, ringworm, and more severe conditions like histoplasmosis and cryptococcosis.
- Furthermore, fungi are responsible for the spoilage of fruits, vegetables, and all kinds of foodstuff, leading to significant economic losses in the food industry. The deterioration of foodstuff by fungi is due to their ability to grow and reproduce rapidly under favorable conditions.
- They also spoil leather items and clothes, causing economic loss, especially in the leather and textile industries.
Thus, the harmful effects of fungi are diverse and significant, affecting various aspects of human life and the economy.
Q2. From where do the plants obtain nitrogen?
Ans: Plants obtain nitrogen, a vital nutrient for their growth and development, primarily from the soil.
- The soil contains specific bacteria, such as Rhizobium and Azotobacter, which have the unique ability to convert gaseous nitrogen from the atmosphere into a soluble form through a process called nitrogen fixation.
- These bacteria release the converted nitrogen into the soil, making it available for plants. The plants absorb these soluble forms of nitrogen along with water through their roots.
- In addition to natural sources, plants also obtain nitrogen from artificial sources like fertilizers, which farmers add to the soil to enhance its nutrient content. These fertilizers contain nitrogen in a readily absorbable form, aiding in the plant's growth and productivity.
Q3. Explain the symbiotic relationship between Rhizobium bacteria and leguminous plants.
Ans: The symbiotic relationship between Rhizobium bacteria and leguminous plants is of great ecological significance and has substantial agricultural benefits.
- This mutualistic relationship involves a unique exchange of nutrients between the two organisms. Nitrogen gas, which constitutes about 78% of the earth's atmosphere, is plentiful but not directly usable by plants. Plants require nitrogen in a soluble form that can be absorbed and utilized for growth and development.
- Rhizobium bacteria, living in the root nodules of leguminous plants, have the unique ability to convert this atmospheric nitrogen into a soluble form, a process known as nitrogen fixation.
- However, these bacteria cannot synthesize their own food and thus rely on the plant for sustenance. The leguminous plants provide the Rhizobium bacteria with food and shelter, and in return, the bacteria provide the plant with a usable form of nitrogen, thereby benefiting both.
Q4. Differentiate between parasitism and symbiosis.
Ans: Parasitism
- It is a relationship between two organisms which is beneficial to one and harmful to the other.
- One of the partner which draws food is called parasite and the other which provide nutrients is called host.
- Example: Cuscuta
Symbiosis:
- It is a relationship in which two organisms live together in a manner benefited.
- Each partner of the relationship is called a symbiont.
- Example: Lichen
Q5. How does a pitcher plant trap insects?
Ans: The pitcher plant is a carnivorous plant that has a unique and fascinating mechanism to trap insects. Its leaf is modified into a pitcher-like structure with a lid at the apex, which can open and close.
- The inside of the pitcher is lined with downward-directed hairs and contains a digestive juice. When an insect lands on the pitcher, the lid closes, trapping the insect inside.
- The trapped insect, unable to escape due to the downward-pointing hairs, is eventually digested by the digestive juice present inside the pitcher.
- This adaptation allows the pitcher plant to supplement its nutrient intake, particularly nitrogen, in nutrient-poor soils.
Q6. Explain the symbiotic relationship in lichens.
Ans: The symbiotic relationship in lichens is a classic example of mutualism, where both organisms benefit from the association.
- In lichens, a chlorophyll-containing partner, typically a green alga or cyanobacterium, lives together with a fungus.
- The alga, capable of photosynthesis, provides the fungus with organic nutrients. In return, the fungus provides the alga with shelter, water, and essential minerals.
- This symbiotic relationship enables lichens to survive in harsh environmental conditions where neither partner could survive alone.
Q7. Differentiate between autotrophic and heterotrophic modes of nutrition.
Ans:
Autotrophic:
- This type of nutrition is found in green plants.
- Autotrophic organism can prepare their own food.
- In this mode of nutrition, carbon dioxide is utilized to prepare food in presence of sunlight.
Heterotrophic:
- This type of nutrition is found in some plants and all animals.
- Heterotrophic organisms cannot prepare their own food.
- They cannot use carbon dioxide to prepare food in presence of sunlight.
Q8. What is saprotrophic nutrition? Define the term saprotrophs.
Ans: Saprotrophic nutrition is a mode of nutrition in which organisms obtain their nutrients from dead and decaying matter.
- Saprotrophs, the organisms that employ this mode of nutrition, secrete digestive juices onto the dead and decaying matter. These digestive juices break down the complex organic matter into simpler substances, which are then absorbed by the organism.
- This type of nutrition is commonly found in fungi and some types of bacteria. These saprotrophs play a crucial role in the ecosystem as they help in the breakdown and recycling of organic matter, thereby contributing to the nutrient cycle.
Q9. Describe the function of stomata.
Ans: The leaves take in carbon dioxide from the air through the small openings present on the surface of leaf called stomata (singular: stoma). Each stoma is bound by two crescent-shaped guard cells.
These cells draw water from the neighboring cells and swell up allowing the stomata to open. This allows carbon dioxide to enter the cells of the leaf through the stomata.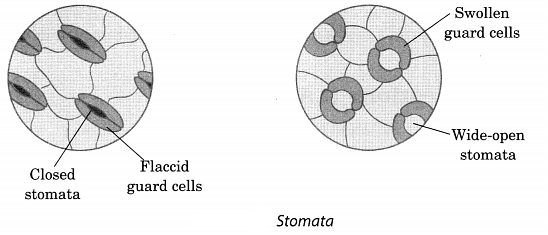
Q10. What is photosynthesis? Draw a schematic diagram to show photosynthesis.
Ans: The process by which green plants containing chlorophyll prepare their own food with the help of sunlight, water and carbon dioxide is called photosynthesis.
Carbon dioxide from air is taken in through the tiny pores present on the surface of leaves. Water and minerals absorbed by the roots are transported to the leaves by the vessels which run throughout the plant.
The process can be represented as:
During the process of photosynthesis oxygen is released.
The carbohydrate so formed in the above process is ultimately converted into starch.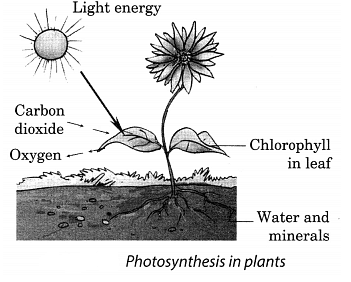
Q11. Explain with the help of a labelled diagram ‘structure of a cell’.
Ans: The body of a living organisms are made of tiny units called cells.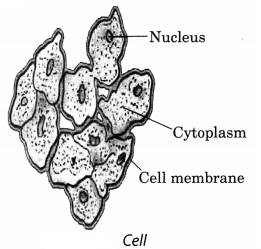
Cells can be seen only under the microscope. Some organisms are made of only one cell. The cell is enclosed by a thin outer boundary, called the cell membrane. Most cells have a distinct, centrally located spherical structure called the nucleus. The nucleus is surrounded by a jelly-like substance called cytoplasm.
Q12. With the help of an experiment show that chlorophyll is necessary for photosynthesis.
Ans: Take a variegated leaf like that of garden corton or Coleus. Boil the leaf in a test tube containing water and then alcohol in a water bath. Take out the leaf and wash it with warm water. Keep the leaf in a Petri plate and add 4-5 drops of iodine solution on it.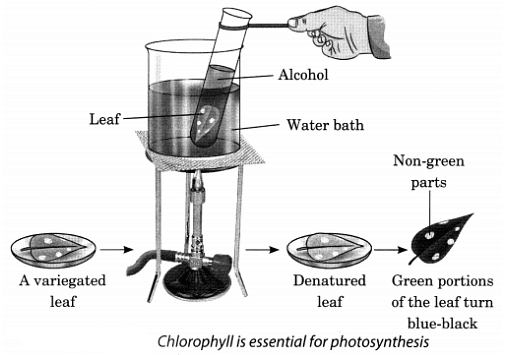
Take a variegated leaf like that of garden corton or Coleus. Boil the leaf in a test tube containing water and then alcohol in a water bath. Take out the leaf and wash it with warm water. Keep the leaf in a Petri plate and add 4-5 drops of iodine solution on it.
You will observe that only those portions of the leaf will turn blue-black which were green. The non-green part did not show any colour change. This shows chlorophyll is necessary for photosynthesis.
Q13. Different modes of nutrition has been observed in plants. What are they? Give example of each.
Ans: Plants show two major modes of nutrition, i.e.
(i) Autotrophs are those which can synthesise their own food.
(ii) Heterotrophs are those which are dependent on other plants and animals for their food. They are of following types:
(a) Parasites, e.g. Cuscuta
(b) Saprotrophs, e.g. fungi.
Q14. If plant has a requirement for nitrogen, then from where will they obtain it?
Ans: Soil contains nitrogen in the form that is not usable by plants. Bacteria like Rhizobium converts nitrogen into soluble form that can be easily used by plants. So, if plant has a requirement for nitrogen, then it will obtain that which the help of bacteria.
Q15. Autotrophs and heterotrophs are two different organisms with distinct modes of nutrition state. How are they different from each other?
Ans: The difference between autotrophs and heterotrophs are as follows: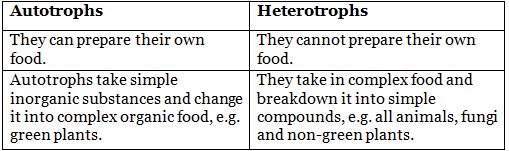
Q16. What are the various raw materials for photosynthesis?
Ans: Plants utilise carbon dioxide from air and water and minerals are derived from soil (through roots) as raw material for photosynthesis. Besides these chlorophyll present in green leaf is necessary for the process and sunlight is the source of energy which is converted into chemical energy during the process of photosynthesis.
Q17. Observe the given figure and label the following terms given in the box. Stomatal opening, guard cell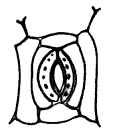
Ans:
Labelled figure is given below: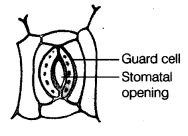
|
112 videos|286 docs|28 tests
|






















