Class 7 Science Chapter 7 Question Answers - Transportation in Animals and Plants
Q1. Arrange the following statements in the correct order in which they occur during the formation and removal of urine in human beings.
(a) Ureters carry urine to the urinary bladder.
(b) Wastes dissolved in water is filtered out as urine in the kidneys.
(c) Urine stored in urinary bladder is passed out through the urinary opening at the end of the urethra.
(d) Blood containing useful and harmful substances reaches the kidneys for filtration.
(e) Useful substances are absorbed back into the blood.
Ans:
The correct order of the formation and removal of urine in human beings is
(d) Blood containing useful and harmful substances reaches the kidneys for filtration.
(e) Useful substances are absorbed back into the blood.
(b) Wastes dissolved in water is filtered out as urine in the kidneys.
(a) Ureters carry urine to the urinary bladder.
(c) Urine stored in urinary bladder is passed out through the urinary opening at the end of the urethra.
Q2. Look at figure and draw another figure of the same set up as would be observed after a few hours.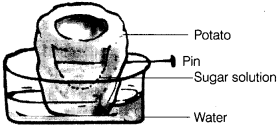
Ans: After the few hours, the figure will be shown as follows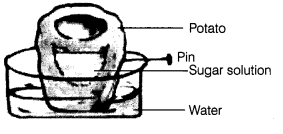 This figure shows that there will be an increase in the level of sugar solution in the potato piece. This increase in the level of sugar solution rises due to water that passes throgh the wall of potato and goes inside it.
This figure shows that there will be an increase in the level of sugar solution in the potato piece. This increase in the level of sugar solution rises due to water that passes throgh the wall of potato and goes inside it.
Q3. Make a table depicting the function of all chambers of the human heart.
Ans: The human heart is divided into four chambers, i. e. upper two atrium and lower two ventricles. The functions of these chambers can be tabulated as follows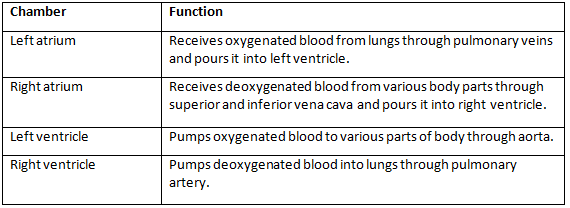
Q4. Observe the given diagram of human heart and label all the parts from A to H.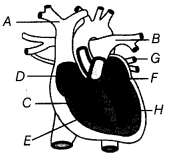
Ans: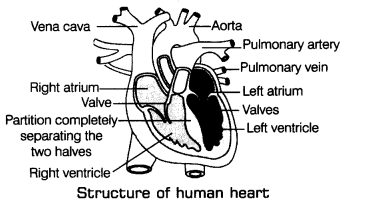
Q5. The internal structure of heart has four chambers.
(a) Name the upper chambers of heart.
(b) Name the lower chambers of heart.
Ans:
The vertical section of heart shows that heart is divided into four compartments called as chambers.
(a) The upper two chambers of heart are called atria or atrium.
(b) The lower two chambers of heart are called ventricles.
Q6. Name the tissues of a plant which carries
(a) water and minerals from roots to the leaves.
(b) food from the leaves to the other parts of the plant.
Ans:
The tissue which carries
(a) water and minerals from roots to leaves is xylem.
(b) food from the leaves to the other parts of the plant is phloem.
Q7. Give one function of each of the following organs,
(a) Blood vessels
(b) Kidney
(c) Blood platelets
(d) Heart
Ans:
The main function of the following organs are as follows:
(a) Blood vessels These run between the heart and the rest of the body. It helps in the transport of blood between heart and various organs of the body.
(b) Kidney It is called as the ‘magic filters’. It helps in the removal of unwanted substances like urea from the blood.
(c) Blood platelets This component of blood helps in blood clotting and prevents the blood loss from the body.
(d) Heart It is a pumping organ which receives blood from the body through veins and pumps it with enough force into the arteries from where it is carried to the various body parts.
Q8. How is transpiration and translocation different from each other.
Ans: The differences between transpiration and translocation are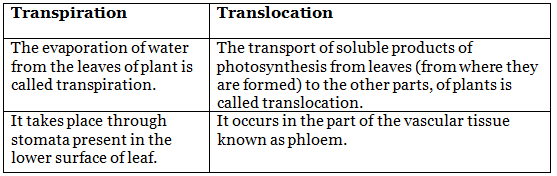
Q9. How does the water move from root to leaves?
Ans: The water moves from root to leaves with the help of specialised cells called vascular tissue. Transport of water and nutrients is done by xylem tissue present in plants.
The heart is an organ which beats continuously as a pump for the transport of blood carrying other substances with it, through a network of tubes or blood vessels. The heart pumps blood throughout our life without stopping or relaxing.
Q10. The given diagram is of human excretory system. Label the marked parts of it.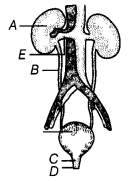 Ans: The various parts of human excretory system are as follows
Ans: The various parts of human excretory system are as follows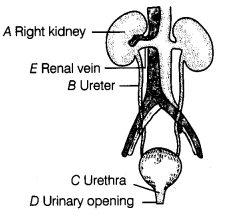
Q11. Why plants absorb a large quantity of water from the soil, then give it off by transpiration?
Ans: Plants absorb a large quantity of water from the soil because they need nutrients which are dissolved in the water. The excess water evaporates through the stomata present on the leaf surface by the process of transpiration.
Q12. Boojho’s uncle was hospitalised and put on dialysis after a severe infection in both of his kidneys.
(a) What is dialysis?
(b) When does it become necessary to take such a treatment?
Ans: The normal functioning of kidney is necessary for good health of a person. But sometime s the kidney may stop working due to infection or injury. This condition of kidney is called kidney failure which may lead to the accumulation of urea in the blood of a person. Since, urea is a toxic substance which must be removed from the blood. Such person having kidney failure cannot survive unless his blood is filtered periodically through the artificial kidney machine to remove urea. The process used for cleaning the blood of a person by separating the waste product urea from it is called dialysis.This machine removes urea and other waste the product periodically.
The long term solution for the patient suffering from kidney failure is kidney transplantation. In this method, the diseased or damaged kidney is removed and matching kidney is donated by a healthy person. The donated kidney is transplanted in its place by performing surgery.
Q13. Explain in brief the main functions of the structural and functional unit of kidney in excretory system.
Ans: Kidney is the major excretory organ which consists of thousands of tiny filters called nephrons. The major functions of nephron are
- To filter blood at high pressure which helps in the separation of nitrogenous waste such as urea from the blood.
- It helps in selective re-absorption of some substances (from the initial filtrate which is filtered at a very high pressure). These substances include glucose, amino acid, salts ancf a major amount of water.
Q14. Blood from heart is carried by certain tube-like structure. What are they? Give the structure and functions of different types of blood carrying tubes.
Ans: These are tubes or pipes that carry blood throughout the body. It runs between the heart and the rest of the body. There are three major types of blood vessels in the body, i.e. arteries, veins and capillaries.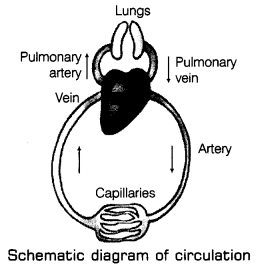
1. Arteries: These carry blood from the heart to all the parts of body. These lie quite deep under our skin and cannot be seen easily. Arteries have thick elastic walls as the blood flows at high pressure due to pumping action from heart through arteries. No valves are present in the arteries. The main artery, i.e. aorta is connected to the left ventricle of the heart. It carries oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to all the parts of body except the lungs. Another artery called pulmonary artery is connected to the right ventricle of the heart and carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs.
Note: The arteries normally carry oxygenated blood from the heart but one artery called pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood from heart to lungs.
2. Veins: These are the blood vessels that carry blood from all the parts of the body back to the heart. These tube-like blood vessels are situated just under the skin and can easily be seen as greenish-blue tubes or lines below the skin. These carry deoxygenated blood from the body parts to heart. Veins have thin walls and blood flows at low pressure through the veins. Therefore, veins have valves in them which allow the blood to flow in one direction and prevent the back flow of blood in veins.
Usually veins carry deoxygenated blood but pulmonary vein that is connected to the left atrium of the heart, carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart.
Functions of Blood
Various functions of blood are
- It transports substances like digested food from the small intestine to the other parts of the body.
- It carries water to all the parts of the body.
- It carries oxygen and CO2 during circulation.
- It carries waste products like urea from liver to kidney for excretion in urine.
- It protects the body from disease.
Q15. Like humans and animals, transportation of water, mineral and nutrients also take place in plants. How?
Ans:
Transport of Substances in Plants:
Plants take up water and dissolved minerals from the soil through their roots and transport it to their leaves. The leaves use this water and mineral for synthesising their food by the process called photosynthesis.The food produced by green plants in transported back to all the parts of plant body.
Therefore, it is clear that plants also need a transport system for carrying water, minerals and food through various parts of their body.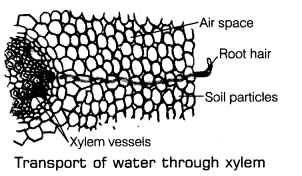
Transport of Water and Minerals:
Plant root absorbs the water and mineral from the soil. The roots possess root hair which increase the surface area of the root for absorption of water and minerals nutrient that is dissolved in the water. It is moved from roots up to the stem and leaves through the tube-like tissue called as xylem.
Absorption and flow of water is a continuous process through the xylem tissue. Xylem tissues are the continuous network of channels which connect roots to the leaves through the stem and branches. It thus transports water and minerals to the leaves of the entire plant.
Transport of Food Material:
The food manufactured in the leaf is transported to different parts of plants. This transportation of food material from leaves to the other parts of plants is carried out by the tissue called phloem and the process of transport of food material is called translocation. The phloem consists of vessels that are known as sieve tubes.
Q16. What is blood? What does it consists of?
Ans: Blood is the fluid circulating through the heart, arteries, veins. It carries oxygen and nutrients to the cells of the body and removes waste materials and carbon dioxide from the body. Blood consists of the liquid, i.e., plasma, red blood cells (RBCs), white blood cells (WBCs) and platelets.
Q17. What do you mean by dialysis?
Ans: If the kidneys of a person fail to function due to infection or injury, blood is filtered periodically by using an artificial kidney to eliminate the wastes from the blood. This process is called dialysis.
Q18. Explain the removal of urine from the body.
Ans: After filtration, the urine reaches the urinary bladder by passing through ureter; it gets stored in the bladder. Whenever required, it gets eliminated through an opening called urethra.
Q19. How does the absorption of water and minerals take place in the plants?
Ans: With the help of roots, plants absorb water and minerals. Roots contain root hair which are fine threadlike structures made of a single cell. Water and minerals from the soil enter root hair, pass through the secondary root and reach the vascular tissue, xylem. From xylem it is transported to all parts of the plant.
Q20. What is translocation. Where does it take place?
Ans: Translocation is the process of transport of soluble products of photosynthesis from leaves to other parts. It occurs in phloem.
Q21. Where do plants store their waste products?
Ans:
- Plants store their waste products like gums and resins in the old xylem.
- Plants store wastes in vacuoles and leaves that fall off.
Q22. What is the use of a stethoscope? Explain its structure as well.
Ans: Stethoscope is used by doctors to amplify the sound of the heart. It consists of two earpieces, a chest piece and a tube that joins these parts. With the help of this device, doctors can check out a disease by listening carefully to the heartbeat.
Q23. What are the functions of blood?
Ans: The functions of blood are:
- It transports oxygen to all parts of the body from the lungs.
- It transports the digested food to all parts of the body from the small intestine.
- It helps in removing waste products and carbon dioxide from the cells.
Q24. What kind of blood flows in the arteries and veins?
Ans: Arteries carry oxygen-rich blood, whereas veins transport carbon dioxide-rich blood. Exceptionally, pulmonary artery carries carbon dioxide-rich blood (i.e., impure) and veins carry oxygen-rich blood (i.e., pure).
Q25. Write the importance of heartbeat.
Ans: The rhythmic contraction and relaxation constitute a heartbeat. Heartbeat helps in pumping the blood throughout the body.
Q26. Why the heart has different chambers?
Ans: Blood has to transport both oxygen and carbon dioxide. Hence the heart has different chambers to prevent mixing of oxygen-rich blood and carbon dioxide-rich blood with each other.
Q27. Explain the formation of urine.
Ans: Blood contains nitrogenous wastes. These have to be removed from the body, since they are toxic and so are harmful for the body. The elimination is done by the kidneys.
Blood contains both useful and harmful substances. When it reaches the kidney, the filtration is done by its unit called nephron. The useful substances are absorbed back, whereas the harmful substances get eliminated as urine.
Q28. Write one function each of blood platelets and heart.
Ans:
- Blood platelets: They help in clotting of blood.
- Heart: It receives impure blood from veins, purifies it and then pumps the blood with sheer forces so that it could go to all parts of the body.
Q29. Write the structures and functions of blood vessels.
Ans: The structures and functions of blood vessels are given as follows:
Arteries:
- Structure: Arteries have thick elastic wall because they carry blood from the heart at a high pressure to other parts of the body.
- Function: They carry oxygen-rich blood from the heart to all parts of the body.
Veins:
- Structure: They have thin walls comparatively to arteries because the blood flows with less pressure. Rather they have valves which prevents back flow of blood.
- Function: They carry carbon dioxide-rich blood from all parts of the body to the heart.
Capillaries:
- Structure: These are very thin blood vessels, having walls one cell thick.
- Function: Across the thin wall of the capillaries, the exchange of gases and nutrients take place between the blood and the surrounding cells.
Q30. Draw a well labelled diagram of human heart.
Ans: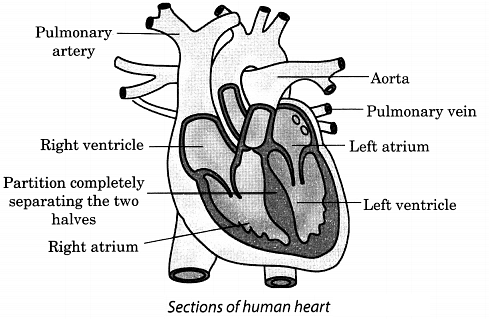
Q31. Explain the excretion in birds, fishes, lizards, dogs and humans.
Ans: The way of the elimination of waste products from the body of animals depends on the availability of water. Animals like birds and lizards excrete a white coloured, semi-solid product, known as uric acid. Aquatic animals (like fish) excrete the waste materials (i.e., ammonia) in the gaseous form which directly dissolve with water. Dogs and human beings excretes urea.
Q32. Explain the working of heart.
Ans:
- Deoxygenated blood from all parts of the body enters the right chamber of the heart called right artium or auricle through superior and inferior vena cava.
- As the atrium contracts deoxygenated blood flows from right atrium to right ventricle through tricupsid valve.
- When ventricle is full tricupsid valve shuts to prevent backflow of blood into atrium.
- The ventricle then contracts blood into pulmonary artery to reach the lungs where it get oxygenated.
- Oxygenated blood then returns to the left atrium of heart through pulmonary veins.
- As the atrium contracts, oxygenated blood flows from left atrium to left ventricle through mirtal valve.
- And when ventricle contracts, blood leaves the heart through aortic valve to the arteries. Arteries circulate blood throughout the body.
Q33. What are the various components of blood. Write function of each component.
Ans: Blood has four main components, i.e., plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. Function of various components are:
- Plasma: Plasma is the watery component of blood. It suspends other components of blood. It contain many important dissolved substances, such as protein, electrolytes, nutrients, gases and waste products. It maintain the exact pressure of the blood.
- Red blood cells: RBC contain haemoglobin protein, whose main function is to carry oxygen to all parts of the body and to bring carbon dioxide to the lungs.
- White blood cells: Main function of WBC is to fight against infections diseases and foreign invaders.
- Platelets: It helps in clotting of blood during injuries and thus, prevent excess loss of blood from our body.
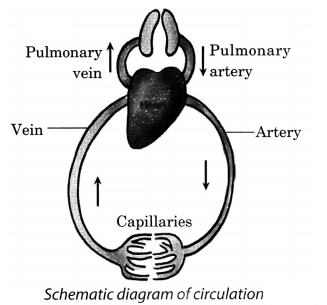
Q34. Explain human circulatory system with a well labelled diagram.
Ans: Circulatory system is the life support system of our body that provides our body cells with nutrients and oxygen. It takes away waste product from the body cells. Our circulatory system comprises of the heart, blood, blood vessels and lungs.
- Blood is the fluid that carries oxygen and nutrients to various parts of the body and takes away wastes and carbon dioxide from the cell for elimination.
- Blood vessels comprises of arteries, veins and Capillaries. Arteries carry oxygen-rich blood from the heart to various parts of the body. Capillaries are single-walled vessels which exchange gases and nutrients from the cells.
- Veins carry carbon dioxide-rich blood from different parts of the body to the heart.
- Heart is a muscular organ with four chambers which pumps blood throughout the body. It pumps carbon dioxide-rich blood to the lungs for purification.
- When it receives oxygen-rich blood from the lungs it again pump this blood to arteries for transportation to various body parts.
- Lungs helps in exchange of gases between air we breathe in and the blood. It helps in elimination of carbon dioxide from blood and making it rich in oxygen content.
|
112 videos|435 docs|28 tests
|





















