Class 7 Science Chapter 12 Question Answers - Forests - Our Lifeline
Q1. Forests are valuable resources. Explain.
Ans: Forests are essential resources that contribute significantly to our lives. They provide:
- Food: Includes cereals, pulses, and fruits.
- Fuel: Firewood for cooking and heating.
- Materials: Fibre for textiles and construction materials.
- Industrial Products: Such as tannins, lubricants, dyes, resins, and perfumes.
- Medicinal Resources: Many plants have healing properties.
Additionally, forests are home to diverse wildlife, which is crucial for maintaining the ecosystem. Thus, forests are invaluable resources.
Q2. Forests are called green lungs. Why?
Ans: Forests are often referred to as green lungs because they play a vital role in providing oxygen for us to breathe.
- Forests absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
- Through the process of photosynthesis, they produce oxygen.
- Deforestation reduces the number of trees, leading to less oxygen.
Thus, preserving forests is essential for maintaining our oxygen supply.
Q3. Write the differences between decomposers and scavengers.
Ans: The difference between decomposers and scavengers is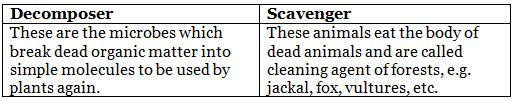
Q4. Plants are known as the producers of a food chain. Give reason.
Ans: Plants are known as the producers of a food chain. Green plants, also known as autotrophs, produce their own food through a process called photosynthesis. This process involves:
- Using carbon dioxide and water.
- Requiring sunlight and chlorophyll.
As a result, plants provide essential food for all living organisms in the ecosystem, forming the foundation of the food chain.
Q5. How could a pipal sapling have grown on a side wall of some old buildings?
Ans: A pipal sapling can grow on a wall due to several natural processes:
- Animals, particularly birds, often disperse seeds through their droppings.
- When a pipal seed lands on a wall, it may come into contact with water and nutrients.
- These conditions can allow the seed to germinate and develop into a sapling.
Q6. State the role of scavengers in cleaning our environment.
Ans: Scavengers play a vital role in maintaining a clean environment by consuming dead animals. This process helps to:
- Act as natural cleaners of ecosystems.
- Prevent the spread of disease by removing decaying matter.
- Recycle nutrients back into the soil, promoting plant growth.
- Common scavengers include: Vultures, Crows, Jackals, Hyenas, Various insects, etc
Q7. Explain how the root system of plants helps prevent floods.
Ans: The root system of plants plays a crucial role in preventing floods by:
- Allowing water to seep into the ground effectively.
- Maintaining the water table throughout the year.
- Binding the soil together, which helps to prevent erosion.
These functions collectively reduce the risk of flooding during heavy rainfall.
Q8. Life would be impossible without plants. Explain how.
Ans: Life would be impossible without plants. Plants play a crucial role in our existence:
- Producers: All green plants produce food through photosynthesis, using water, carbon dioxide, and sunlight.
- Food Source: Animals, including humans, rely on plants for food. Without plants, there would be no food.
- Oxygen Supply: During photosynthesis, plants release oxygen. Without them, we would lack this essential gas.
These two fundamental needs—food and oxygen—highlight the importance of plants in sustaining life.
Q9. What happens when an animal dies in the forest?
Ans: When an animal dies in the forest:
- The body is consumed by scavengers such as vultures, jackals, and hyenas.
- This process helps to clean the forest environment.
- It demonstrates that in nature, nothing goes to waste.
Q10. Is it possible to construct a food chain without a producer? State the reason to support your answer.
Ans: No, it is not possible to construct a food chain without a producer. Here’s why:
- Producers, such as plants, are essential as they create food through photosynthesis.
- All living organisms rely on producers for energy and nutrients.
- If producers are absent, there is no energy flow, making a food chain impossible.
Q11. If one component of the forest is removed, what would its effect be on the ecosystem?
Ans: Every component of the forest relies on the others. Removing one can disrupt the entire ecosystem:
If top carnivores, lions or tigers, are removed:
- Herbivore populations will increase.
- Overgrazing will occur, leading to a decline in plant life.
- This disruption can cause significant ecological imbalance.
Thus, the removal of any single component can have far-reaching effects on the entire ecosystem.
Q12. The crown is different from the canopy. Explain how.
Ans: The crown of a tree refers to the part that includes its branches and leaves. In contrast, the canopy is formed when the crowns of tall trees create a roof-like cover over other plants in the forest.
- The crown is the upper part of a tree.
- The canopy is the layer formed by overlapping crowns of trees.
- The canopy provides shade and habitat for various organisms.
Q13. Sketch a diagram to show how plants maintain the balance between carbon dioxide and oxygen in the atmosphere.
Ans: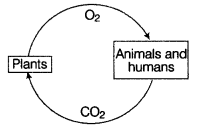
Q14. Write the major steps by which we can conserve the forest.
Ans: Forests play a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance. To conserve them, we can take the following steps:
- Planned harvesting: This involves selectively cutting down some trees while leaving others intact. The remaining trees help prevent soil erosion and produce seeds for new growth, ensuring the forest remains healthy.
- Afforestation: This is the process of planting new trees in areas where forests have been depleted. Both government and private organisations are actively involved in afforestation efforts, which not only restore forests but also provide timber for construction.
- Protection from fire: Forest fires can devastate large areas. These fires may be caused by human negligence, lightning, or natural friction. To combat this, fire-fighting solutions can be deployed from aircraft, and wind direction can be altered using powerful blowers.
Q15. Cycling of papers helps conserve forests. Justify.
Ans: Cycling of papers helps conserve forests. Papers are made from wood pulp, which comes from trees. By recycling paper instead of letting it decompose, we can:
- Reduce the need to cut down trees for new paper.
- Help preserve forests and the environment.
Growing a tree takes years, while cutting it down takes only minutes. Therefore, we must:
- Think carefully before cutting any tree.
- Encourage paper recycling in our communities and worldwide.
Q16. Differentiate between autotrophs and heterotrophs.
or
Differentiate between producer and consumer.
Ans: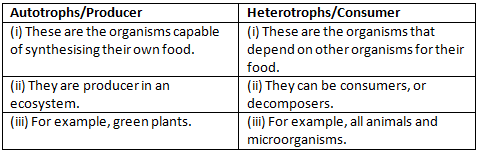
Q17. Give an example of a food chain.
Ans: Example of a food chain:
- Grass is eaten by insects.
- Insects are consumed by frogs.
- Frogs are preyed upon by snakes.
- Snakes can be eaten by eagles.
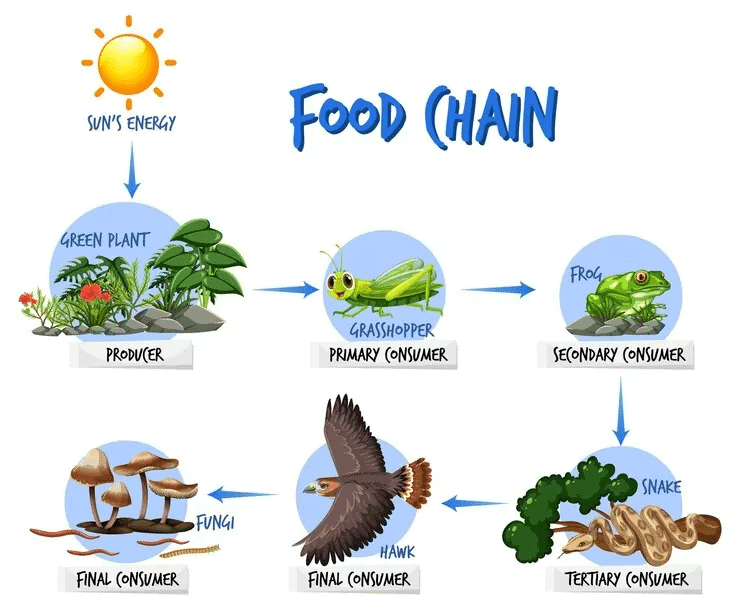 This sequence illustrates a simple food chain.
This sequence illustrates a simple food chain.
Q18. How do forests prevent soil erosion? Explain.
Ans: Soil erosion is the removal of the top layer of fertile soil by wind, rivers, or rain. This process can transform fertile land into deserts, particularly in areas lacking vegetation like trees and plants. Forests play a crucial role in preventing soil erosion through the following mechanisms:
- The roots of plants and trees bind soil particles together, making it difficult for strong winds and flowing water to displace them.
- During heavy rainfall, the forest canopy intercepts rainwater, slowing its descent through the stems, branches, and leaves. This reduces the impact on the forest floor.
- The forest floor, covered with fallen leaves and twigs, absorbs water effectively, preventing it from flowing and thus reducing erosion.
Q19. What does the forest floor look like?
Ans: The forest floor looks dark-coloured and covered with a layer of dead and decaying fruits, plants, leaves, twigs and small herbs, which is quite moist and warm.
Q20. What do you mean by deforestation? Give some causes of deforestation.
Ans: The excessive cutting of trees for personal or commercial purposes is called deforestation.
Two causes of deforestation are as follows:
- The land is required to be cleared for cultivation, construction of houses, roads, etc.
- Forest fires cause huge loss of forest cover, which may be natural or by man.
- Overpopulation, too, directly affects forest cover with the expansion of its habitat.
- The reckless felling of trees to obtain timber also causes deforestation.
Q21. What is the importance of dense bushes and tall grasses for animals living in the forests?
Ans: Dense bushes and tall grasses are crucial for animals in forests because they offer:
- Food: Many animals rely on these plants for nourishment.
- Shelter: They provide a safe space for animals to hide from predators.
- Protection: These dense areas help herbivores evade carnivores.
Q22. Why is it dark inside a forest?
Ans: The interior of a forest is often dark due to several factors:
- Sunlight struggles to reach the ground because of the dense canopy formed by tall trees.
- The leaves create a roof that blocks much of the light.
- Various climbers and creepers further obstruct light penetration.
Q23. How do forests help in bringing rain?
Ans: Trees play a crucial role in the water cycle by:
- Absorbing water from the soil through their roots.
- Releasing excess water into the atmosphere via transpiration as water vapour.
- Allowing this water vapour to form clouds, which eventually lead to rainfall.
Q24. How do forests sustain a large variety of animals?
Ans: Forests support a wide range of animals by providing essential resources and habitats. Here’s how:
- Habitat Variety: Different animals, such as herbivores, carnivores, and scavengers, find suitable living conditions in forests.
- Food Sources:
Herbivores consume plants.
Carnivores prey on herbivores.
Scavengers, like vultures and eagles, feed on dead animals. - Decomposers: Microorganisms break down dead plants and animals, turning them into humus, which enriches the soil.
- Nutrient Cycling: The decomposition process ensures that nutrients are recycled, supporting new plant growth.
Thus, forests create a dynamic ecosystem that sustains diverse animal life.
Q25. As an active citizen, elaborate on your role in protecting the forests.
Ans: At my level, I will do the following things to protect the forest:
- Use less paper and try to recycle it.
- Do not buy any products made up of or obtained from the killing of wild animals.
- Try to plant as many trees as I can.
- Aware people of the importance of forests in our lives.
- Reduce the use of artificial items as they also create stress for the forest.
|
112 videos|286 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Class 7 Science Chapter 12 Question Answers - Forests - Our Lifeline
| 1. Why are forests considered our lifeline? |  |
| 2. How do forests help in maintaining the balance of nature? |  |
| 3. What are the threats faced by forests today? |  |
| 4. How can individuals contribute to the conservation of forests? |  |
| 5. What are the benefits of sustainable forest management? |  |





















