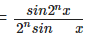Trigonometric Functions Chapter Notes | Mathematics (Maths) Class 11 - Commerce PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Angle |

|
| Functions of Negative Angles |

|
| Transformation Formulae |

|
| Product of Trigonometric Ratios |

|
Angle
Angle is a measure of rotation of a given ray about its initial point. The original ray is called the initial side and the final position of ray after rotation is called terminal side of the angle. The point of rotation is called vertex. If the direction of rotation is anti-clockwise, the angle is said to be positive and if the direction of rotation is clockwise, then the angle is negative.
Measuring Angles
There are two systems of measuring angles
- Sexagesimal system (degree measure): If a rotation from the initial side to terminal side is (1/360)th of a revolution, the angle is said to have a measure of one degree, written as 1°.
One sixtieth of a degree is called a minute, written as 1′ and one-sixtieth of a minute is called a second, written as 1″
Thus, 1° = 60′ and 1′ = 60″ - Circular system (radian measure): A radian is an angle subtended at the centre of a circle by an arc, whose length is equal to the radius of the circle. We denote 1 radian by 1°.
Relation Between Radian and Degree
We know that a complete circle subtends at its centre an angle whose measure is 2π radians as well as 360°.
2π radian = 360°.
Hence, π radian = 180°
or 1 radian = 57° 16′ 21″ (approx)
1 degree = 0.01746 radian
Six Fundamental Trigonometric Identities
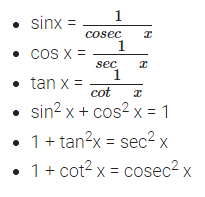
Trigonometric Functions
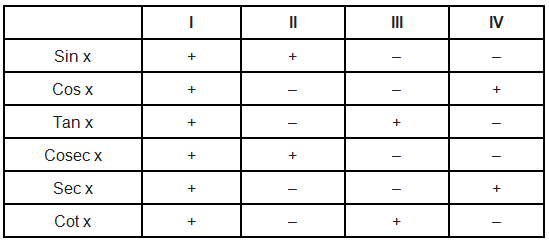
Trigonometric ratios are defined for acute angles as the ratio of the sides of a right angled triangle. The extension of trigonometric ratios to any angle in terms of radian measure (real number) are called trigonometric function. The signs of trigonometric function in different quadrants have been given in following table.
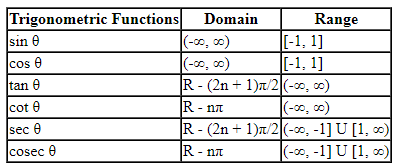
Domain and Range of Trigonometric Functions
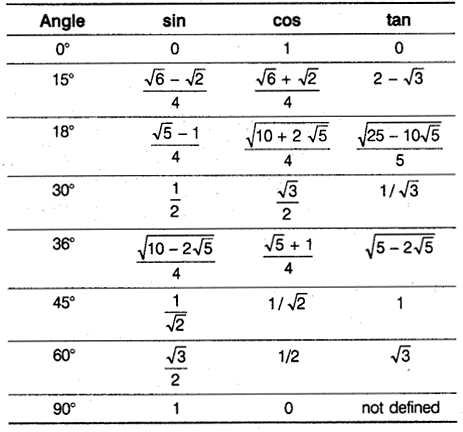
Sine, Cosine, and Tangent of Some Angles Less Than 90°
Allied or Related Angles
The angles 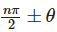 are called allied or related angle and θ ± n × (2π) are called coterminal angles. For general reduction, we have following rules, the value of trigonometric function for
are called allied or related angle and θ ± n × (2π) are called coterminal angles. For general reduction, we have following rules, the value of trigonometric function for 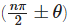 is numerically equal to
is numerically equal to
- the value of the same function, if n is an even integer with the algebraic sign of the function as per the quadrant in which angle lies.
- the corresponding co-function of θ, if n is an odd integer with the algebraic sign of the function for the quadrant in which it lies, here sine and cosine, tan and cot, sec and cosec are cofunctions of each other.
Functions of Negative Angles
For any acute angle of θ.
We have,
- sin(-θ) = – sinθ
- cos (-θ) = cosθ
- tan (-θ) = – tanθ
- cot (-θ) = – cotθ
- sec (-θ) = secθ
- cosec (-θ) = – cosecθ
Some Formulae Regarding Compound Angles
An angle made up of the sum or difference of two or more angles is called compound angles. The basic results in direction are called trigonometric identities as given below:
(i) sin (x + y) = sin x cos y + cos x sin y
(ii) sin (x – y) = sin x cos y – cos x sin y
(iii) cos (x + y) = cos x cos y – sin x sin y
(iv) cos (x – y) = cos x cos y + sin x sin y
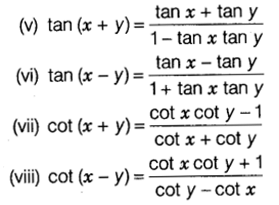
(ix) sin(x + y) sin (x – y) = sin2 x – sin2 y = cos2 y – cos2 x
(x) cos (x + y) cos (x – y) = cos2 x – sin2 y = cos2 y – sin2 x
Transformation Formulae
- 2 sin x cos y = sin (x + y) + sin (x – y)
- 2 cos x sin y = sin (x + y) – sin (x – y)
- 2 cos x cos y = cos (x + y) + cos (x – y)
- 2 sin x sin y = cos (x – y) – cos (x + y)
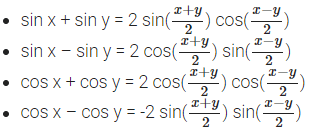
Trigonometric Ratios of Multiple Angles
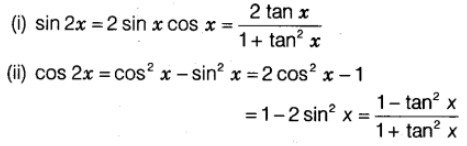
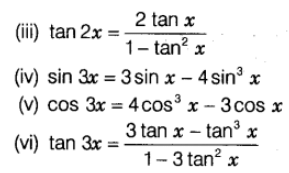
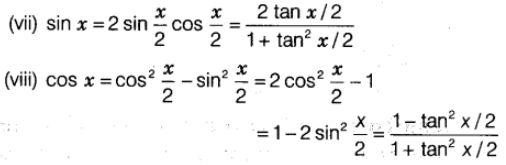
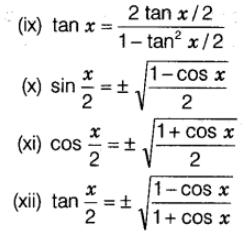
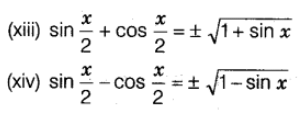
Product of Trigonometric Ratios
- sin x sin (60° – x) sin (60° + x) = 1/4 sin 3x
- cos x cos (60° – x) cos (60° + x) = 1/4 cos 3x
- tan x tan (60° – x) tan (60° + x) = tan 3x
- cos 36° cos 72° = 1/4
- cos x . cos 2x . cos 22x . cos 23x … cos 2n-1

Sum of Trigonometric Ratio, if Angles are in A.P.
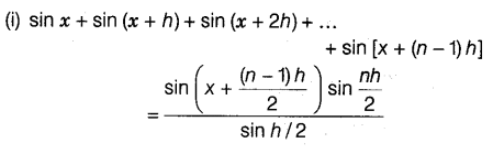
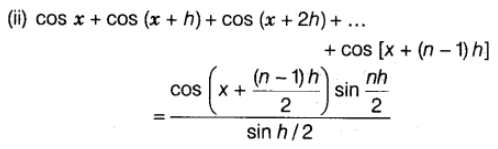
Trigonometric Equations
Equation which involves trigonometric functions of unknown angles is known as the trigonometric equation.
Solution of a Trigonometric Equation
A solution of a trigonometric equation is the value of the unknown angle that satisfies the equation.
A trigonometric equation may have an infinite number of solutions.
Principal Solution
The solutions of a trigonometric equation for which 0 ≤ x ≤ 2π are called principal solutions.
General Solutions
A solution of a trigonometric equation, involving ‘n’ which gives all solution of a trigonometric equation is called the general solutions.
General Solutions of Trigonometric Equation
- sin x = 0 ⇔ x = nπ, n ∈ Z
- cos x = 0 ⇔ x = (2n + 1) π/2 , n ∈ Z
- tan x = 0 ⇔ x = nπ, n ∈ Z
- sin x = sin y ⇔ x = nπ + (-1)n y, n ∈ Z
- cos x = cos y ⇔ x = 2nπ ± y, n ∈ Z
- tan x = tan y ⇔ x = nπ ± y, n ∈ Z
- sin2 x = sin2 y ⇔ x = nπ ± y, n ∈ Z
- cos2 x = cos2 y ⇔ x = nπ ± y, n ∈ Z
- tan2 x = tan2 y ⇔ x = nπ ± y, n ∈ Z
Basic Rules of Triangle
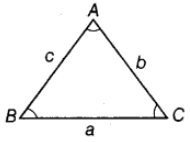
In a triangle ABC, the angles are denoted by capital letters A, B and C and the lengths of sides of opposite to these angles are denoted by small letters a, b and c, respectively.
Sine Rule
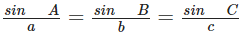
Cosine Rule
a2 = b2 + c2 – 2bc cos A
b2 = c2 + a2 – 2ac cos B
c2 = a2 + b2 – 2ab cos C
Projection Rule
- a = b cos C + c cos B
- b = c cos A + a cos C
- c = a cos B + b cos A
|
74 videos|239 docs|91 tests
|