Class 7 Maths Chapter 6 Question Answers - Lines and Angles
Q1. The adjacent angles on a straight line are (5x−6)o and 7(x + 6)o . Find the value of x.
Ans:
Given that, (5x−6)o and 7(x+6)o are adjacent angles on a straight line.
Since the sum of adjacent angles on a straight line =180o
We can write,, (5x−6)o +7(x+6)o =180o
⇒ 5x − 6 + 7x + 42 = 180
⇒ 12x = 180−36
⇒ x = 144/12
⇒ x = 12
The adjacent angles are as follows:
(5x−6)o = (5×12−6)o
= (60−6)o
= 54o
And, 7(x+6)o
= 7(12+6)o
= 7×18o
= 126o
Q2. The measures of two adjacent angles on a straight line are xo and (2x−27)o . Find the smallest angle.
Ans:
Given: xo and (2x−27)o are adjacent angles on a straight line.
Now, xo +(2x−27)o
=180o ...(Since adjacent angles on a straight line = 180o)
⇒ 3x = 180 + 27
⇒ 3x = 207
⇒ x= 207 /3
⇒ x = 69
The ajacent angles are as follows:
xo = 69o = Smallest angle
And, 2x − 27o = 2 × 69 − 27
= 138 − 27 = 111o
Q3. Prove that the bisectors of a pair of vertically opposite angles are on the same straight line.
Ans:
Let AB and CD be straight lines intersecting at O.
Also, let OX be the bisector of ∠AOC and OY be the bisector of ∠BOD
OY is the bisector of ∠BOD
∴ ∠1 = ∠6....(i)
OX is the bisector of ∠AOC
∴ ∠3 = ∠4.....(ii)
∠2 and ∠5 are vertically opposite angles.
∴ ∠2 = ∠5.....(iii)
We know that, sum of all angles = 360o
∴ ∠1 + ∠2 + ∠3 + ∠4 + ∠5 + ∠6 = 360o
Using the relations from (i), (ii) and (iii), we get
∠1 + ∠2 + ∠3 + ∠3 + ∠2 + ∠1 = 360o
2∠1+2∠2+2∠3=360o
⇒ ∠DOY + ∠AOD + ∠AOX = 180o
But, ∠DOY + ∠AOD + ∠AOX = ∠XOY
∴ ∠XOY = 180o
Since, ∠XOY = 180o, both OX and OY are on the same straight line.
[Hence proved]
Q4. Prove that if the sum of two adjacent angles is 180o, then the non-common arms are two opposite rays.
Ans:
Given: Two adjacent angles are ∠AOC and ∠BOC and ∠AOC + ∠BOC = 180o
To prove: OA and OB are two opposite rays.
Construction: Let OA and OB are not two opposite rays.
Then, draw a ray OE opposite to OA such that AOE is a straight line.
Proof:
∠AOC + ∠BOC = 180o .....(1)
∠AOC + ∠COE = 180o ....(2) (Linear pair)
∠AOC + ∠EOC = ∠AOC + ∠BOC (From equation 1 and 2)
∴ ∠EOC = ∠BOC
 This is possible only if OE and OB coincide. Hence, OA and OB are two opposite rays.
This is possible only if OE and OB coincide. Hence, OA and OB are two opposite rays.
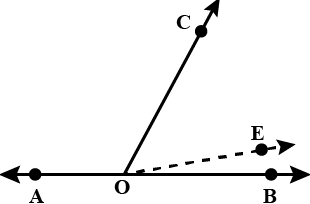
Q5. By observing above figure, comment on nature of straight line AB and CD Ans:
Ans:
In the figure, alternate angles are not equal.
It is property of parallel lines that when a transversal intersects two parallel lines, its alternate angles are equal.
Q6. It is given that ∠XYZ=64 and XY is produced to point P. Draw a figure from the given information. If ray YQ bisects ∠ZYP, find ∠XYQ and reflex ∠QYP.
Ans:
Given,
∠XYZ = 64∘
YQ bisects ∠ZYP
∠XYZ + ∠ZYP = 180∘(Linear Pair)
⇒ 64∘ + ∠ZYP = 180∘
∠ZYP = 116∘
Also, ∠ZYP = ∠ZYQ + ∠QYP
∠ZYQ = ∠QYP (YQ bisects ∠ZYP)
⇒ ∠ZYP = 2∠ZYQ
⇒ 2∠ZYQ = 116∘
⇒ ∠ZYQ = 58∘
= ∠QYP
Now, ∠XYQ=∠XYZ+∠ZYQ
⇒ ∠XYQ = 64 + 58∘
⇒ ∠XYQ = 122∘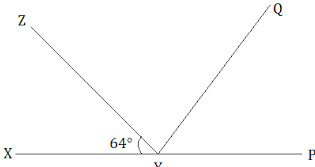 Also, reflex ∠QYP = 180∘ +∠XYQ
Also, reflex ∠QYP = 180∘ +∠XYQ
∠QYP = 180∘ + 122∘
⇒ ∠QYP = 302∘
Q7. Two complementary angles differ by 12o , find the angles?
Ans:
Let x be the one angle.
So, the complement of x = 90o − x.
Given, two complementary angles differ by 20o .
⇒ x − (90o − x)=12o
⇒ x − 90o + x = 12o
⇒ 2x = 12o + 90o
⇒ x = 102o / 2
⇒ x = 51o .
Therefore, complementary of x,
= 90o − x
= 90o − 51o
= 39o .
Hence, 51o and 39o are the complementary angles.
Q8. Show that if a straight line is perpendicular to one of the two or more parallel lines, then it is also perpendicular to the remaining lines.
Ans: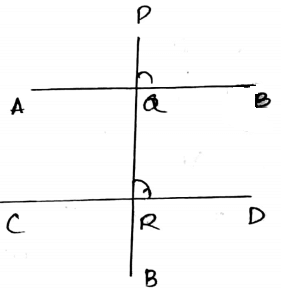
Let us assume that AB∥CD
PQ is perpendicular to AB
We have to prove that PQ is perpendicular to CD
∠PQB = 90o (given)
∴∠QRD = ∠PQB = 90o
Corresponding angles of parallel line
∴ PQ is perpendicular to CD
Q9. Draw diagrams illustrating each of the following situation:
(a) Three straight lines which do not pass through a fixed point.
(b) A point and rays emanating from that point such that the angle between any two adjacent rays is an acute angle.
(c) Two angles which are not adjacent angles, but still supplementary.
(d) Three points in the plane which are equidistant from each other.
Ans:
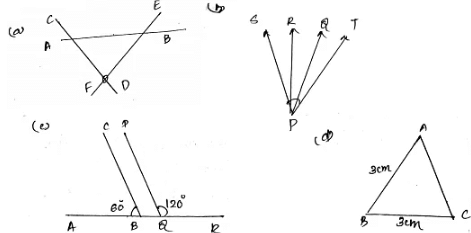
(b) ∠SPQ= Acute Angle
∠QPR= Acute Angle
∠RPT= Acute Angle
Q10. Find the supplementary angle of the given angle(in degrees): 105o
Ans:
Supplementary angles are two angles with a sum of 180o .
One supplement angle is 105o .
⇒ Other supplement angle =180o − 105o
= 75o
Hence, the required supplementary angle is 75o .
Q11. State whether the following statement is True or False.
If two lines intersect each other, then the vertically opposite angles formed are equal.
A. True
B. False
Ans:
When two lines intersect each other, then the vertically opposite angles so formed are equal to each other. Q12. What is the measure of complementary angle of 20∘ ?
Q12. What is the measure of complementary angle of 20∘ ?
(1) 60∘
(2) 70∘
(3) 80∘
Ans:
We know, two angles are complementary when they add up to 90o .
Given, measure of one complementary angle is 20o .
⇒ Measure of other complementary angle =90o −20o
= 70o
∴ Measure of a complementary angle of 20o
=70o.
Therefore, (2) 70o is correct.
Q13. Measure of one angle of linear pair is given. Find the measure of another angle : 85∘
Ans:
180∘ − 85∘
= 95∘
Thus, another angle is 85∘
Q14. Measure of one angle of linear pair is given. Find the measure of another angle: 107∘.
Ans:
180∘ − 107∘
=73
Thus another angle is 73∘
Q15. Measure of one angle of linear pair is given as 50∘ . Find the measure of another angle.
Ans:
We know that sum of angles in linear pair is 180∘
Measure of another angle = 180∘ − 50∘
= 130∘
Thus, another angle is 130∘
|
78 videos|457 docs|39 tests
|
















