Human Eye and Colourful World Class 10 Worksheet Science Chapter 10
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Q1: What is the function of the cornea in the human eye?
(a) It controls the size of the pupil.
(b) It provides most of the refraction of light.
(c) It is a dark muscular diaphragm.
(d) It is the outermost, transparent part.
Ans: (b)
Sol: The cornea is the outermost, transparent part of the eye that provides most of the refraction of light.
Q2: What is the term used to describe the ability of the eye lens to adjust its focal length?
(a) Myopia
(b) Hypermetropia
(c) Accommodation
(d) Astigmatism
Ans: (c)
Sol: Accommodation is the ability of the eye lens to adjust its focal length.
Q3: What causes myopia (near-sightedness)?
(a) Focal length becomes too long.
(b) Eye ball becomes too small.
(c) Excessive curvature of eye lens.
(d) Diminishing flexibility of eye lens.
Ans: (c)
Sol: Myopia is caused by the excessive curvature of the eye lens.
Q4 What is the correction for hypermetropia?
(a) Use of concave lens
(b) Use of convex lens
(c) Use of bifocal lens
(d) Diminishing flexibility of eye lens
Ans: (b)
Sol: Hypermetropia is corrected by using a convex lens of suitable power.
Q5: What phenomenon is responsible for the formation of a rainbow?
(a) Dispersion
(b) Refraction
(c) Total Internal Reflection
(d) All of the above
Ans: (d)
Sol: A rainbow is formed due to the combined effects of dispersion, refraction, and total internal reflection.
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: The ability of the eye lens to adjust its focal length is called ____________.
Ans: Accommodation
Accommodation is the ability of the eye lens to adjust its focal length.
Q2: Presbyopia is a defect of vision that occurs in ____________.
Ans: old age
Explanation: Presbyopia is a defect of vision that causes difficulty in seeing nearby objects clearly in old age.
Q3: The maximum distance at which an object can be seen clearly is called the ____________.
Ans: far point
The far point is the maximum distance at which an object can be seen clearly.
Q4: The phenomenon of twinkling of stars is due to the fluctuation in the ____________ of the Earth's atmosphere.
Ans: refractive index
Twinkling of stars is caused by the fluctuation in the refractive index of the Earth's atmosphere.
Q5: The angle between two adjoining lateral surfaces of a prism is called the ____________.
Ans: angle of prism
The angle between two adjoining lateral surfaces of a prism is called the angle of prism.
Match the Column (In a Table)
Question: Match the following:
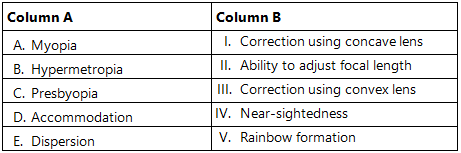
Ans:
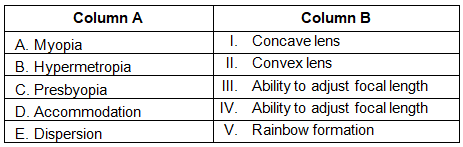
Very Short Answers
Q1: What would have been the colour of sky if the earth had no atmosphere?
Ans: The sky would have looked dark if the earth had no atmosphere as there would not have been any scattering.
Q2: Which great scientist was colour blind?
Ans: Dalton was colour blind.
Q3: On what factor does colour of scattered light depend?
Ans: The colour of scattered light depends on the size of the scattering particle. Very fine particles scatter mainly blue light whereas particles of larger size scatter light of longer wavelengths.
Q4: Why is a small amount of sodium thiosulphate added to water in tank in the activity to understand reddish appearance of sun at sunrise and sunset?
Ans: Sodium thiosulphate is added to water in the tank for precipitating minute colloidal sulphur particles which scatter short wavelengths of light.
Q5: A man is wearing glasses of focal length +1m, what can be defect in the eye?
Ans: As the focal length of glasses is positive, so the power of the lens is also positive which indicates the use of a convex lens. Hence, he is suffering from hypermetropia.
Q6: Why are danger light signals red in color?
Ans: As red light is scattered the least and it covers longer distances. That's why it is used in danger signal.
Q7: Which part of the human eye helps in changing the thickness of lens?
Ans: Ciliary muscles
Q8: Name the light sensitive part of the eye where image of an object is formed.
Ans: Retina
Q9: Which is the range of vision of normal eye?
Ans: 25 cm to infinity.
Q10: What are light sensitive cells?
Ans: Rods and cones.
Case Study Type Questions
A prism is a transparent refracting medium bounded by two plane surfacesinclined to each other at a certain angle. The refraction of light through a prism follows the laws of refraction. In the prism, refraction takes place on its refracting surface it means when the light enters the prism and when the light leaves the prism. The refraction through a prism is shown. Here, <A is the angle of prism, ∠ i is the angle of incidence of the face AB and ∠e is the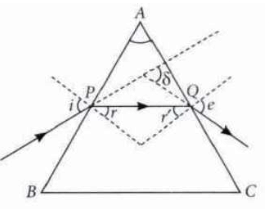
The incident ray suffers a deviation or bending through an angle δ due tothe refraction through prism. This angle is called angle of deviation as shown in figure.
i + e = δ + A
Q1: The angle between the two refracting surfaces of a prism is called
(a) angle of prism
(b) angle of incidence
(c) angle of deviation
(d) angle of emergence
Ans: A
The angle between the two refracting surfaces of a prism is indeed called the angle of prism. This is the angle formed by the two planes of the prism which refract light. Hence, option A is correct.
Q2: The angle between the incident ray and the emergent ray is called
(a) angle of emergence
(b) angle of deviation
(c) angle of incidence
(d) none of these
Ans: B
The angle between the incident ray and the emergent ray in the context of light passing through a prism is known as the angle of deviation. This angle measures how much the light has been deflected from its original path as it passes through the prism. Hence, option B is correct.
Q3: When a ray is refracted through a prism, then
(a) ∠ ∠δ
(b) ∠ i=∠e+∠δ
(c) ∠δ= ∠e
(d) ∠i > ∠r
Ans: D
When a ray is refracted through a prism, the angle of incidence (i) is greater than the angle of refraction (r). This is due to the fact that light slows down and bends towards the normal line (a line perpendicular to the surface of the prism) when it enters the prism. Hence, option D is correct.
Q4: The angle of deviation depends on
(a) refractive index of prism
(b) angle of incidence
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) none of these
Ans: C
The angle of deviation depends on both the refractive index of the prism and the angle of incidence. The refractive index of the prism determines how much the light will bend when it enters the prism. The angle of incidence is the angle at which the light hits the prism. Both these factors together determine the final path of light and therefore the angle of deviation. Hence, option C is correct.
Short Answers Type Questions
Q1: In a human eye, name the following parts.
i. A thin membrane which allows light to enter into the eye?
ii. The muscles which help in changing the focal length of the eye lens?
Ans: i. Cornea is the thin transparent membrane.
ii. Ciliary muscles help in changing the focal length of the eye lens.
Q2: The image formed on retina is inverted but we see the object erect. Why?
Ans: The image formed on retina is inverted, this image is formed on the light sensitive cells called rods and cones of the retina which generates electrical signals. This signal reaches brain via optic nerve. It is the brain that interprets this image and while processing the image it helps in perceiving objects as they are.
Q3: Why danger signals are red?
Ans: Danger signals are of red colour, as it scatters the least and can be seen from the maximum distance.
Q4: Why does sky look blue on a clear day?
Ans: White light scatters due to atmospheric refraction. White light is made up of seven colours out of which, blue light scatters the most hence the sky looks blue.
Q5: Why do you take time to see objects when you enter a dim lighted room from outside in the sun?
Ans: In the sun light the size of pupil, is small but when one enters the dim light, it takes some time for iris to adjust the size of pupil and the light sensitive cells take some time to get activated.
Q6: When white light enters the prism, which colour of light deviates/bends the least and which colour bends the most?
Ans: The light that bends the least is red colour and the light that bends the maximum is violet colour light.
Long Answers Type Questions
Q1: A person is unable to read a book properly. From which defect is he suffering? How to correct this defect?
Ans: The person is suffering from hypermetropia or long-sightedness.
A long sighted person can see distant objects clearly, but cannot see distinctly objects lying closer than a certain distance. Thus, he cannot see clearly an object lying at 25 cm which is the least distance of distinct vision for a normal eye. His far point is farther from the eye than 25 cm, say at 75 cm or so.
- Causes of the defect: This defect is due to either :
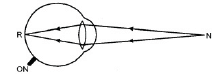
- Normal eye: It is able to focus the rays from normal near point (25 cm from eyes)
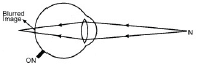
- Defective eye: Due to eye ball getting short or an increase in focal length of eye lens, the rays do not focus on retina.
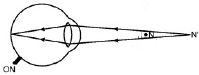
- Defective eye: is able to form image at retina when object is moved from N to N' the near point of defective eye.
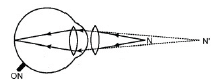
- Corrected eye: A convex (or any convergent) lens of suitable focal length converges the rays to match those coming from N'. Hypermetropic eye.
- Normal eye is able to focus on retina the rays emerging out from N.
- However, the defective eye is not able to focus the rays from near point of normal eye i.e. N.
- It can focus the rays from near point of defective eye. i.e. N'.
- From fig. we conclude that more inclined rays are not focused on retina whereas less inclined rays from N' get focused on retina.
- Correction of this Defect: Such a defect is corrected by placing a convex or converging lens of suitable focal length before the eye so that the rays diverging from N appear to come, after refraction, from the near point N'.
- the size of the eye ball becoming too short.
- the lens becoming too thin, so that its focal length becomes abnormally large.
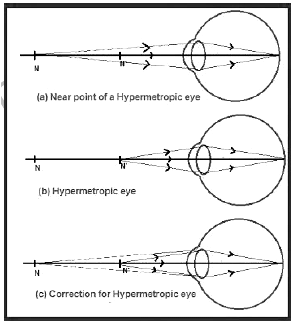
Q2: Make a diagram to show how hypermetropia is corrected. The near point of hypermetropic eye is 1 m. What is the power of the lens required to correct this defect? Assume that the near point of normal eye is 25 cm.
Ans: For diagram of correction of hypermetropia,
Numerical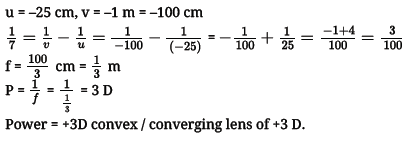
Q3: With the help of well labeled diagram, explain the construction and working of human eye.
Ans:
- Human eye is the most remarkable and most delicate optical instrument.
- Though in principle, it is similar to a photographic camera, it is far most delicate and perfect than the finest camera ever designed by human ingenuity.
- Structure : The human eye consists of nearly spherical ball of about 2.5 cm diameter.
- Its outermost coating is made of a tough and opaque white substance known as SCLEROTIC. Sclerotic preserve the shape of eye and protects it against external injury.
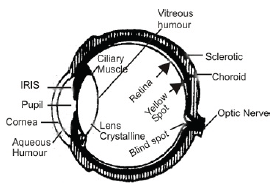
- Front portion of sclerotic is transparent and slightly bulged outwards and known as CORNEA.
- There is a layer of black tissues, below sclerotic and is called CHOROID. It serves to absorb any stray light and thus avoids blurring of the image by reflection from the eye-ball.
- In font of eye, choroids merge into a coloured diaphragm known as iris which a hole in the middle called PUPIL. When we refer to the colour of eyes of a person, we refer to the colour of iris of the person. This iris corresponds to the stop in the camera. By means of involuntary muscle control, it regulates the amount of light entering the eye.
- In strong light, the pupil contracts so as to admit less light whereas in dim light, it expands so as to admit as much light as required.
- Behind iris is a crystalline lens with jelly-like layers. The lens is held in position with the help of ciliary muscles. The lens divides the eye ball into two chambers – the front chamber called anterior chamber and other between lens and the retina called posterior chamber. Anterior chamber is filled with a fluid called aqueous humour while the posterior chamber is filled with a jelly like substance called vitreous humour.
- The innermost coating of the eye, covering the rear of inner surface, is a very delicate membrane called the retina. It is richly supplied with blood vessels and nerve fibres and serves as a light-sensitive screen to receive the image. The sensation of vision in the retina is carried to the brain by a nerve called optic nerve. The most sensitive part of retina is known as the yellow spot. It is a slightly raised portion with a slight depression known as the fovea centralis. The point where the optic nerve enters the eye is totally insensitive to light and is known as the blind spot.
- Eye Lids are provided to control the amount of light falling on the eye. Lids also protect the eyes from dust etc.
- How does the eye focus: In eye, the distance between lens and the retina remains the same, while crystalline lens automatically changes its focal length by changing its curvature due to pull or push of ciliary muscles according to the distance of the object so as to bring the image to a sharp focus upon the retina. While seeing the far objects such as distant tree, the eye lens becomes thinner and flatter so as to increase its focal length. To see the objects close to the eyes, such as printed page, the lens becomes thicker so as to decrease its focal length. The process by which the eye can adapt itself to see objects at different distances is called accommodation.
- Range of vision: The most distant point upto which a fully relaxed eye can see is called the far point. For normal eye, far point is infinity. The point at the shortest distance from the eye upto which the eye can accommodate itself and therefore, can see clearly is known as the near point. It is about 15 cm for a normal eye. The distance between far and near points is called range of vision or accommodation. Within the range of vision, there is a certain distance where the object is most clearly seen. The distance for a normal eye is about 25 cm and is known as the least distance of distinct vision.
- Persistence of vision: Time for which the impression of the object seen by the eye remains on the retina even after the removal of the object is called the persistence of vision.
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Human Eye and Colourful World Class 10 Worksheet Science Chapter 10
| 1. How does the human eye work? |  |
| 2. What is the role of the cornea in vision? |  |
| 3. How do we perceive different colors? |  |
| 4. Can the human eye see all colors? |  |
| 5. How does the human eye adjust to different lighting conditions? |  |
















