Class 7 Science Chapter 8 HOTS Questions - Reproduction in Plants
Q1: When you keep food items like bread and fruits outside for a long time especially during the rainy season, you will observe a cottony growth on them.
(a) What is this growth called?
(b) How does the growth take place?
Ans:
(a) The cottony growth observed on food items like bread and fruits is known as bread mould, which is a type of fungus.
(b) This growth of fungus takes place by spores present in air, which when comes in the contact with moisture in bread germinates and grow to produce new cells.
Q2: A student was given a flower. He was asked to pick the different whorls of flower by the forcep. He pulled each part of the flower and laid them on the chart paper in a sequence and named them W, X, Y, Z (from outer to inner whorl). He was unable to name them.
Help the student to name the different parts of a flower. Also help him to tell which part produces male gamete and female gametes.
Ans: The four whorls of the flower are outermost whorl ‘W’ is green part which is called sepal. Inside sepal the next whorl is X which is coloured and attractive part of the flower called petals. The Y is the inner whorl of flower called stamen. It is the male reproductive part of flower. It consist of two parts, i.e. anther and filament. The anther contains male gametes called pollen grain. The whorl ‘Z’ is the innermost part of the flower called pistil. It is the female reproductive part of flower. It consist of three parts, i.e. stigma, style and ovary. The ovary produces ovule which contains the female gametes or egg cell.
Q3: Investigate the role of different agents like wind, water, and animals in seed dispersal. How does each agent contribute to the survival and spread of plant species?
Ans: Role of different agents are:
- Wind dispersal: Seeds are carried by the wind, allowing plants in open areas to spread their seeds widely. However, this can result in seeds landing in unsuitable locations.
- Water dispersal: Seeds travel via water, such as rivers or streams. This method helps plants establish in new areas, particularly near water sources, but they often remain close to these water bodies.
- Animal dispersal: Animals assist in spreading seeds by carrying them on their fur or ingesting them. After digestion, seeds are excreted in different locations, promoting plant growth in diverse areas. In return, animals benefit from the plants as a food source.
Q4: The process of layering is commonly used in jasmine for reproduction. Explain how this process of layering is performed in jasmine.
Ans: Layering is a method of vegetative reproduction in branches.
In this method, a mature branch of parent plant is bent down and covered with soil.
The tip of the branch is kept above the ground. After few days the roots are developed from the branch buried under the soil and develops into a new plant. This method is done in the plants that have long and slender branches, e.g. jasmine.
Q5: Coconut is a large and heavy fruit. How is it adapted for dispersal by water?
Ans: The seeds of some plants that have an outer fibrous or spongy covering are dispersed through water. They have the ability to float in the water and drift along with its flow, e.g. seeds of water lily, lotus, chestnut (singhara) and coconut are dispersed through water. The coconut fruits have a fibrous outer coat which enables them to float in water and carried away by flowing water to far off places.
Q6: Explore the concept of vegetative propagation and its applications in agriculture . Discuss its advantages and limitations compared to sexual reproduction in plants.
Ans: Vegetative propagation allows plants to reproduce asexually from vegetative parts like stems, roots, or leaves, producing genetically identical offspring. This method is advantageous for preserving desirable traits in agriculture and horticulture, such as disease resistance or fruit quality, but it lacks the genetic diversity provided by sexual reproduction. Farmers can use techniques like cutting, grafting, or tissue culture to propagate plants efficiently and maintain uniformity in cultivated crops.
Q7: In the figure of a flower given below, label the parts whose functions are given below and give their names.
(a) The part which contains pollen grains.
(b) The part where the female gamete is formed.
(c) The female reproductive part, where pollen grains germinate.
(d) The colourful part of flower which attracts insects
 Ans: The various parts of a flower whose functions are mentioned above are labelled as follows :
Ans: The various parts of a flower whose functions are mentioned above are labelled as follows :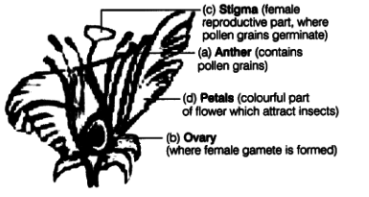
Q8: How do the plants like sugarcane, potato and rose reproduce when they cannot produce seeds?
Ans: Sugarcane and rose are propagated by stem cutting that is a method of vegetative propagation, in which stem is capable of growing into a mature independent plants that are identical to their parents.
Potato is an underground modified stem having bud called eyes, which sprout and develop into a new identical plant.
Thus, the plants which cannot produce seeds, can be propagated vegetatively with the help of vegetative parts such as stem, roots, buds and leaves.
Q9: Multiple choice Questions
1. What is one way animals help spread seeds?
a) They eat the seeds and keep them safe.
b) They play with the seeds for fun.
c) They bury the seeds underground.
d) They ignore the seeds completely.
Ans: a) They eat the seeds and keep them safe.
Explanation: Animals help spread seeds by carrying them on their fur or in their stomachs after eating them. This helps the seeds to be transported to new locations.
2. How can humans help plants spread their seeds?
a) By cutting down forests
b) By avoiding planting new trees
c) By disturbing natural habitats
d) By planting more trees and protecting wildlife
Ans: d) By planting more trees and protecting wildlife
Explanation: Humans can help plants spread their seeds by planting more trees, creating safe spaces for animals, and protecting helpful insects like bees. These actions support natural seed dispersal processes.
Q10: Analyze the significance of pollination in plant reproduction. Discuss the mechanisms of self-pollination and cross-pollination?
Ans: Pollination is essential for plant reproduction as it enables the transfer of pollen, which contains male gametes, to the stigma of a flower. This process is crucial for fertilisation.
- Self-pollination occurs when pollen is transferred within the same flower or between flowers of the same plant. This method ensures reproductive success but can limit genetic diversity.
- Cross-pollination involves pollen transfer between flowers of different plants. This promotes genetic variation and typically requires pollinators such as insects, birds, or wind for effective transfer.
|
112 videos|435 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Class 7 Science Chapter 8 HOTS Questions - Reproduction in Plants
| 1. What are the main types of reproduction in plants? |  |
| 2. How do flowering plants reproduce? |  |
| 3. What is vegetative propagation, and how does it benefit plants? |  |
| 4. What role do seeds play in plant reproduction? |  |
| 5. How do environmental factors influence plant reproduction? |  |

















