Multiple Choice Questions
Q1: In which form, do the water molecules have less kinetic energy?
(a) Ice
(b) Water
(c) Steam
(d) All of them have equal kinetic energy
Ans: (a)
Ice has less kinetic energy as compared to water and steam.
Q2: Which of the following describes the liquid phase?
(a) It has a definite shape and a definite volume.
(b) It has a definite shape but not definite volume.
(c) It has a definite volume but not a definite shape.
(d) It has neither a definite shape nor a definite volume.
Ans :(c)
Liquids have definite volume but not a definite shape. They take the shape of the container in which they are kept.
Q3: Which of these choices is defined “Standard Pressure”?
(a) 14.7 psi
(b) 1 atm
(c) 760 torr
(d) All of these
Ans: (d)
All the units are used as standard units for pressure. 1 atm = 760 torr = 14.7 pounds per square inch (psi.)
Q4: The process of evaporation causes:
(a) heating
(b) cooling
(c) increase in temperature
(d) none of these
Ans: (b)
Evaporation causes cooling due to escape of high energy particles.
Q5: Ice floats on the surface of water because:
(a) it is heavier than water
(b) the density of both water and ice is the same
(c) ice is lighter than water
(d) none of these
Ans: (c)
Due to presence of open spaces in the cage like structure of ice its density is less than water, hence ice is lighter than water.
Q6: Which of the following statements is not correct?
(a) Matter is continuous in nature.
(b) Inter-particle spaces are maximum in the gaseous state of a substance.
(c) Particles which constitute the matter follow a zigzag path.
(d) Solid state is the most compact state of a substance.
Ans: (c)
Only in gaseous state the particles follow a zigzag path.
Q7: Kinetic energy of molecules is directly proportional to
(a) temperature
(b) pressure
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) atmospheric pressure
Ans: (a)
With increase in temperature, the kinetic energy of the particles also increases.
Q8: The inter-particle force are the strongest in
(a) hydrogen
(b) methyl alcohol
(c) water
(d) sodium chloride
Ans: (d)
Sodium chloride is a crystalline solid and inter-particle force are the strongest in it.
Q9: The substance having the maximum tendency to flow is
(a) water
(b) sodium
(c) sodium chloride
(d) chlorine
Ans: (d)
Chlorine being a gas, has maximum fluidity
Q10: If a few spoons of salt are dissolved in pure water then
(a) its b.pt. becomes less than 100ºC
(b) its b.pt. becomes more than 100ºC
(c) its freezing point becomes more than ºC
(d) none of these
Ans: (b)
Impurities increase the boiling point of a liquid.
Q11: A gas can be best liquefied
(a) by increasing the temperature
(b) by lowering the pressure
(c) by increasing the pressure and reducing the temperature
(d) none of these
Ans: (c)
A gas can be liquefied by increasing the pressure and reducing the temperature.
Q12: The evaporation of a liquid can be best carried out in a(a) beaker
(b) China dish
(c) test tube
(d) flask
Ans: (b)
China dish has the maximum surface area available for evaporation.
Q13: The state of matter which consists of super energetic particles in the form of ionized gases is called
(a) gaseous state
(b) liquid state
(c) Bose-Einstein condensate
(d) plasma state
Ans: (d)
Plasma state consists of super energetic and super excited particles.
Q14: Which of the following pair of gases cannot be separated by diffusion method?
(a) SO2 and H2
(b) CO2 and NO2
(c) NH3 and N2
(d) CO2 and H2
Ans: (b)
Both CO2 and NO2 have same molecular weights and densities. Therefore, they cannot be separated by diffusion.
Q15: Sugar syrup, usually used to coat sweets with sugar, becomes hard when cooled. From this we can conclude that sugar syrup is:
(a) a saturated solution
(b) an unsaturated solution
(c) not a solution
(d) none of these
Ans: (a)
From sugar syrup, solid sugar separates out as solid cooling and syrup becomes hard indicating that syrup is saturated solution.
Q16: To separate the solids which are insoluble in liquids such that solid is heavier than liquid:
(a) sedimentation and decantation
(b) evaporation and condensation
(c) filtration
(d) condensation and crystallization
Ans: (a)
Solids which are insoluble in liquids but heavier that liquids can be allowed to sediment and the liquid can be decanted.
Q17: Which changes of state occur during distillation?
(a) Boiling followed by filtration
(b) Boiling followed by condensation
(c) Condensation followed by boiling
(d) Filtration followed by boiling
Ans: (b)
In distillation, boiling followed by condensation of vapours takes place.
Q18: A saturated salt water solution was heated and allowed to cool without adding any more salt. What will happen?
(a) Some salt appears to settle at the bottom.
(b) Some more salt can be dissolved now.
(c) No change takes place.
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Ans : (c)
Normally, a saturated solution on heating, some more solute gets dissolved but on cooling again that extra solute dissolved crystallizes out. But as no more salt is added no change takes place
Q19: When liquid starts boiling, further heat energy which is supplied
(a) is lost to the surroundings as much
(b) increases the temperature of the liquid
(c) increases the kinetic energy of the particles in the liquid
(d) is absorbed as latent heat of vaporisation by the liquid.
Ans: (d)
Heat energy is absorbed as latent heat of vaporisation, hence there is no change in temperature till the complete liquid is converted to vapours.
Q20: The forces of attraction between the particles of matter is maximum in
(a) iron rod
(b) kerosene oil
(c) glycerine
(d) dry air
Ans: (a) iron rod
In iron rod (solid) there is maximum force of attraction between the particles.
Q21: You can separate a mixture of sand, salt and water by:
(a) filtration and distillation
(b) decantation and evaporation
(c) filtration and decantation
(d) decantation and crystallization
Ans: (b)
By decantation, sand can be separated from salt solution in water. Salt solution on evaporation leaves a residue of salt.
Q22: The substance with least inter-particle space is
(a) methanol
(b) acetic acid
(c) copper
(d) oxygen
Ans: (c)
Solid particles have least inter-particle space between them.
Q23: Large volume of Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) is available in small cylinders to us due to its property of
(a) high inflammability
(b) easy availability
(c) high compressibility
(d) low density
Ans: (c)
Due to its high compressibility, large volumes of a gas can be compressed into a small cylinder and transported easily.
Q24: Alcohol exists as a liquid at room temperature because
(a) the intermolecular forces are strong enough to keep its particles bound to each other
(b) its melting point is below room temperature
(c) it is highly compressible
(d) both (a) and (b)
Ans: (d) both (a) and (b)
In alcohol, the intermolecular forces of attraction between the particles bind them to one another such that if flows.
Q25: Which of the following statement is NOT true?
(a) A mixture of water and milk can be separated by filtration.
(b) A mixture of powdered salt and sugar can be separated by fractional crystallisation.
(c) Loading is a process which involves alum.
(d) Salt from sea water is obtained by evaporation.
Ans: (a)
A mixture of water and milk cannot be separated by filtration as both get filtered.
A mixture of powdered salt and sugar can be separated by fractional crystallisation.
Loading is a process which involves alum.
Salt from sea water is obtained by evaporation.
Fill in the blanks.
Q26: A mixture of sulphur and charcoal can be separated by .......... method.
Ans : solvent extraction
A mixture of sulfur and charcoal can be separated by the solvent extraction method. This is because sulfur is soluble in carbon disulfide, a type of solvent, while charcoal is not. Hence, when the mixture is added to carbon disulfide, sulfur dissolves while charcoal remains undissolved.
Q27: Magnesium sulphate in water is a .......... mixture.
Ans : homogeneous
Magnesium sulphate in water forms a homogeneous mixture, which means that the substances are uniformly distributed throughout the mixture and cannot be distinguished from each other.
Q28: A mixture of iodine and sand are separated by method of ..........
Ans: sublimation
A mixture of iodine and sand can be separated by the method of sublimation. This is because iodine sublimes, i.e., it changes directly from solid to gas state on heating, leaving behind sand.
Q29: During separation of CO2 and hydrogen gas by diffusion the gas that diffuses rapidly is ..........
Ans: hydrogen
During separation of CO2 and hydrogen gas by diffusion, hydrogen gas diffuses rapidly. This is due to its lighter weight compared to CO2, hence it moves faster.
Q30: .......... can be classified chemically into pure substance and mixtures.
Ans: Matter
Matter, which includes everything around us that has mass and occupies space, can be classified chemically into pure substances and mixtures. Pure substances are made up of only one kind of particles, while mixtures have more than one kind of particles.
Q31: During distillation of iodine and methyl alcohol the non-volatile substance is ..........
Ans : iodine
During the distillation of iodine and methyl alcohol, iodine is the non-volatile substance. This means that iodine does not easily convert into gas at normal temperature and pressure, whereas methyl alcohol does, and thus can be separated by this method.
Q32: Compounds are formed by chemically combining elements in a .......... proportion by weight.
Ans: definite
Compounds are formed by chemically combining elements in a definite proportion by weight. This indicates that the ratio of the weights of the elements in a compound remains constant.
Q33: The number of atoms present in the molecules of an element is called its ..........
Ans: atomicity
The number of atoms present in the molecules of an element is referred to as its atomicity. For instance, in an oxygen molecule (O2), the atomicity is 2, as it consists of two oxygen atoms.
Q34: During the separation of CO2 and O2 by the process of preferential liquefaction, the component .......... liquefies.
Ans: CO2
During separation of CO2 and O2 by the process of preferential liquefaction, CO2 liquefies. This is because CO2 has a lower boiling point and turns into liquid form before oxygen does.
Q35: Soda water can be separated by .......... the pressure.
Ans: lowering
Soda water can be separated by lowering the pressure. This is because soda water is a mixture of water and carbon dioxide gas under pressure. When the pressure is reduced, the gas escapes, leaving behind water.
True/False
Q36: A homogeneous mixture of two liquids can be separated using fractional distillation method.
Ans : True
Homogeneous mixtures of two liquids with different boiling points can be separated using fractional distillation. This method uses the differences in boiling points to selectively boil off and separate the components.
Q37: The melting and boiling points of a mixture is fixed depending on the proportions of its components it is made of.
Ans : True
The melting and boiling points of a mixture are dependent on the proportions of its components. Different mixtures of the same substances can have different melting and boiling points based on their composition.
Q38: A mixture of glucose water can be separated by the method of evaporation.
Ans: True
A mixture of glucose and water can be separated by the method of evaporation. In this process, the water evaporates, leaving behind the solid glucose.
Q39: The components of a mixture can never be separated by physical methods.
Ans: False
The components of a mixture can be separated by various physical methods such as filtration, evaporation, distillation, etc., depending on the nature of the components.
Q40: The properties of compounds are same from those of the elements of which they are made.
Ans: False
The properties of compounds are different from those of the elements from which they are made. This is due to the chemical changes that occur during the formation of the compound.
Q41: Sand and sawdust can be separated by gravity method.
Ans : True
Sand and sawdust can be separated by gravity method. This method uses the principle of gravity to separate heavier components (sand) from lighter ones (sawdust).
Q42: Separation of CCl4 from CS2 can be carried out by separating funnel method.
Ans : False
The separation of Carbon Tetrachloride (CCl4) from Carbon Disulfide (CS2) cannot be carried out by the separating funnel method as both are miscible liquids (they mix completely), and this method is used for separating immiscible liquids.
Q43: A handful of soil is homogeneous mixture of solids.
Ans: False
Soil is not a homogeneous mixture. It contains different components like sand, clay, organic matter, etc., which are not uniformly distributed.
Q44: Distilled water cannot be separated into its constituents by physical methods.
Ans: True
Distilled water is a pure substance and cannot be separated into its constituents (hydrogen and oxygen) by physical methods. It requires a chemical method (electrolysis) for separation.
Q45: Baking soda is a compound.
Ans: True
Baking soda, or Sodium Bicarbonate (NaHCO3), is a compound. It is made up of multiple elements - Sodium, Hydrogen, Carbon, and Oxygen, combined in a fixed ratio.
Matching Questions
Direction: In the section, each question has two matching lists. Choices for the correct combination of elements from List-I and List-II are given as options (a), (b), (c) and (d) out of which one is correct.
Q46:
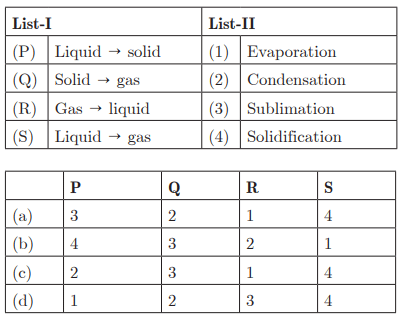 Ans: (b) P - 4, Q - 3, R - 2, S - 1
Ans: (b) P - 4, Q - 3, R - 2, S - 1
Q47:
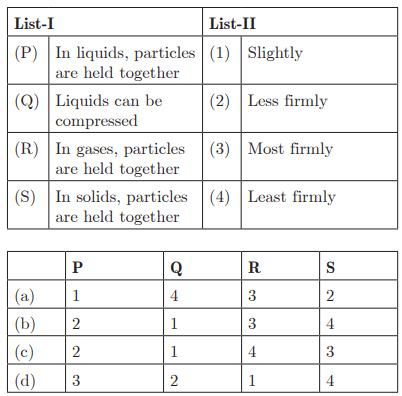 Ans: (c) P - 2, Q - 1, R - 4, S - 3
Ans: (c) P - 2, Q - 1, R - 4, S - 3
Q48:
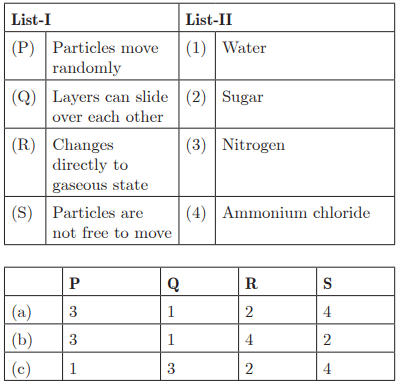
 Ans: (b) P - 3, Q - 1, R - 4, S - 2
Ans: (b) P - 3, Q - 1, R - 4, S - 2
Q49:
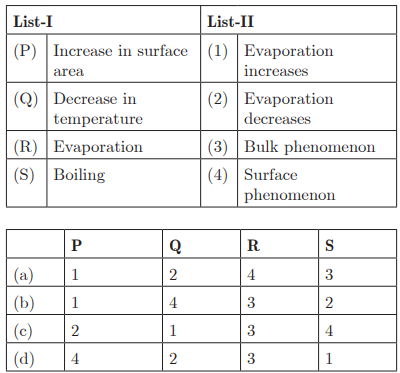 Ans: (a) P - 1, Q - 2, R - 4, S - 3
Ans: (a) P - 1, Q - 2, R - 4, S - 3
Q50:
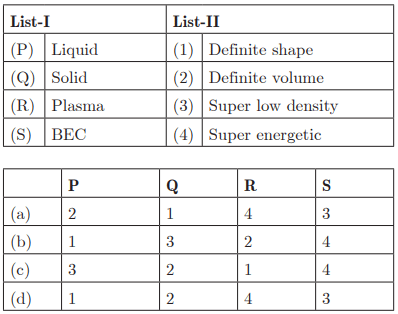 Ans: (a) P - 2, Q - 1, R - 4, S - 3
Ans: (a) P - 2, Q - 1, R - 4, S - 3
 Ans: (b) P - 4, Q - 3, R - 2, S - 1
Ans: (b) P - 4, Q - 3, R - 2, S - 1 Ans: (c) P - 2, Q - 1, R - 4, S - 3
Ans: (c) P - 2, Q - 1, R - 4, S - 3
 Ans: (b) P - 3, Q - 1, R - 4, S - 2
Ans: (b) P - 3, Q - 1, R - 4, S - 2 Ans: (a) P - 1, Q - 2, R - 4, S - 3
Ans: (a) P - 1, Q - 2, R - 4, S - 3 Ans: (a) P - 2, Q - 1, R - 4, S - 3
Ans: (a) P - 2, Q - 1, R - 4, S - 3


























