Some Application of Trigonometry Class 10 Worksheet Maths
Multiple Choice Questions
Q1: If the length of the shadow of a tree is decreasing then the angle of elevation is:
(a) Increasing
(b) Decreasing
(c) Remains the same
(d) None of the above
Q2. The angle of elevation of the top of a building from a point on the ground, which is 30 m away from the foot of the building, is 30°. The height of the building is:
(a) 10 m
(b) 30/√3 m
(c) √3/10 m
(d) 30 m
Q3: If the height of the building and distance from the building foot’s to a point is increased by 20%, then the angle of elevation on the top of the building:
(a) Increases
(b) Decreases
(c) Do not change
(d) None of the above
Q4: If a tower 6m high casts a shadow of 2√3 m long on the ground, then the sun’s elevation is:
(a) 60°
(b) 45°
(c) 30°
(d) 90°
Q5: The angle of elevation of the top of a building 30 m high from the foot of another building in the same plane is 60°, and also the angle of elevation of the top of the second tower from the foot of the first tower is 30°, then the distance between the two buildings is:
(a) 10√3 m
(b) 15√3 m
(c) 12√3 m
(d) 36 m
Q6: The angle formed by the line of sight with the horizontal when the point is below the horizontal level is called:
(a) Angle of elevation
(b) Angle of depression
(c) No such angle is formed
(d) None of the above
Q7: The angle formed by the line of sight with the horizontal when the point being viewed is above the horizontal level is called:
(a) Angle of elevation
(b) Angle of depression
(c) No such angle is formed
(d) None of the above
Q8: From a point on the ground, which is 15 m away from the foot of the tower, the angle of elevation of the top of the tower is found to be 60°. The height of the tower (in m) standing straight is:
(a) 15√3
(b) 10√3
(c) 12√3
(d) 20√3
Q9: The line drawn from the eye of an observer to the point in the object viewed by the observer is said to be
(a) Angle of elevation
(b) Angle of depression
(c) Line of sight
(d) None of the above
Q10: The height or length of an object or the distance between two distant objects can be determined with the help of:
(a) Trigonometry angles
(b) Trigonometry ratios
(c) Trigonometry identities
(d) None of the above
Solve the following Questions
Q1: Two poles of equal heights are standing opposite to each other on either side of the road which is 80m wide. From a point between them on the road the angles of elevation of the top of the poles are 60°and 30°.find the height of the poles and the distances of the point from the poles.
Q2: A tree standing on a horizontal plane leaning towards east. At two points situated at distances a and b exactly due west on it, the angles of elevation of the top are respectively α and β .Prove that the height of the top from the ground is  .
.
Q3: A man sitting at a height of 20m on a tall tree on a small island in the middle of the river observes two poles directly opposite to each other on the two banks of the river and in line with the foot of tree. If the angles depression of the feet of the poles from a point at which the man is sitting on the tree on either side of the river are 60° and 30° respectively. Find the width of the river.
Q4: Consider right triangle ABC, right angled at B. If AC = 17 units and BC = 8 units determine all the trigonometric ratios of angle C.
Q5: If C and Z are acute angles and that cos C = cos Z prove that ∠C = ∠Z.
Q6: In triangle ABC, right angled at B if sin A = 1/2 . Find the value of
1. sin C cos A – cos C sin A
2. cos A cos C + sin A sin C
Q7: In triangle ABC right angled at B, AB = 12cm and ∠CAB = 60°. Determine the lengths of the other two sides.
Q8: If θ is an acute angle and  find θ.
find θ.
Q9: Find the value of x in each of the following.
(i) cosec 3x = 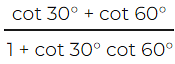
(ii) cos x = 2 sin 45° cos 45° – sin 30°
Q10: Given sin A = 12/37, find cos A and tan A.
You can access the solutions to this worksheet here.
|
126 videos|457 docs|75 tests
|
FAQs on Some Application of Trigonometry Class 10 Worksheet Maths
| 1. What are the basic trigonometric ratios used in solving problems? |  |
| 2. How can trigonometry be applied to real-life situations? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of the unit circle in trigonometry? |  |
| 4. How do you calculate the height of a tree using trigonometry? |  |
| 5. What are some common trigonometric identities that are useful in solving problems? |  |























