Class 9 History Chapter 5 Practice Question Answers - Pastoralists in the Modern World
Multiple Choice Questions
Q1: In Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh the dry plateau was covered with stone and grass inhabited by:
(a) Cattle herders
(b) Goat herders
(c) Sheep herders
(d) Camel herders
Ans: (c)
The sheep herders inhabited the dry plateau in Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh.
Q2: Who were Gollas?
(a) Cattle herded tribe of dry central plateau region.
(b) Sheep herded tribe of dry central plateau region.
(c) Camel herded tribe of dry central plateau region.
(d) Goat herded tribe of dry central plateau region.
Ans: (a)
Gollas were cattle herded tribe of dry central plateau region.
Q3: Banjaras are well-known groups of graziers and found in the villages of:
(i) Madhya Pradesh
(ii) Punjab
(iii) Rajasthan
(iv) Uttar Pradesh
(v) Maharashtra
(vi) Haryana
(a) (i), (v), (vi)
(b) (ii), (v), (vi)
(c) (i), (ii), (iii), (v)
(d) (iv), (v), (vi)
Ans: (c)
Banjaras were well known groups of graziers and found in the villages of all the above.
Q4: Which of the following is the immediate impact of the colonial rule on the life of the pastoralists?
(a) Their grazing ground increased
(b) They were paid rent free land
(c) Their agriculture stock increased
(d) Their grazing ground shrunked and their agricultural stock, trade and crafts were adversley affected.
Ans: (d)
By the colonial rule the life of the pastoralists were adversely affected. Their grazing ground shrunked and agricultural stock, trade and crafts were affected.
Q5: The colonial Government in India in 1871 enacted an Act. Name it.
(a) Forest Conservation Act
(b) The Criminal Tribal Act
(c) The Scientific Forestry
(d) The Tribal Act
Ans: (b)
In 1871, the colonial government enacted an act called ‘The Criminal Tribal Act’. Other Acts were introduced in different years.
Q6: Nomads are the people:
(a) who do not live at one place but move from one to another to earn their living.
(b) who temporary shift from one place to another.
(c) who live at one place and move from place to place to earn their living.
(d) who are very brave.
Ans: (a)
People who move from one place to another to earn their livings are called nomads.
Q7: Which tribe did not evolve pastoral activity in South Africa?
(a) Massai
(b) Gonds
(c) Boran
(d) Turkene
Ans: (b)
Gonds did not evolve pastoral activity in South Africa. They were an Indian tribe.
Q8: Which tribe combined cultivators with pastoralism in India?
(a) Raikas
(b) Maru
(c) Gujjars
(d) Gaddi
Ans: (a)
Raikas combined cultivators with pastoralism in India.
Q9: What is referred as Bhabar?
(a) A wet forest area below the foothills of Garhwal and Kumaun.
(b) A moderate area having plenty of vegetation.
(c) A dry area which is sparsely populated.
(d) A dry forest area below the foothills of Garhwal and Kamaun.
Ans: (d)
A dry forest area below the foothills of Garhwal and Kamaun was known as Bhabar.
Q10: Gaddi Shepherds came down from the high meadow in:
(a) September
(b) February
(c) October
(d) Mid of October.
Ans: (a)
During the month of September Gaddi Shepherds came down from the high meadows.
Fill in the blanks.
Q11: By April, the Gujjar shepherds moved north and spent the summer in Lahul and …………….
Ans: Spilts
The Gujjar shepherds, who are known for their pastoral lifestyle, migrate seasonally in search of pastures for their livestock. By April, these shepherds move northward, and spend the summer in Lahul and Spiti. Spiti is a cold desert mountain valley located in the Indian state of Himachal Pradesh, which provides suitable grazing grounds for their animals during the summer.
Q12: ……………. and vast meadows in the high mountains.
Ans: Bugyal
Bugyals are the alpine pasture lands, or vast meadows found in the higher elevation of the Himalayas. These meadows which stay covered with snow in winter, offer lush green pastures in summer, making them an excellent grazing ground for the pastoral communities and their livestock.
Q13: The ……………. could not tolerate the wet monsoon conditions.
Ans: Sheep
Sheep, a major part of pastoral communities, are unable to withstand the wet monsoon conditions. The humid and wet conditions during the monsoon can lead to health issues in sheep, including various bacterial and fungal infections. Therefore, shepherds often move their flocks to drier areas during this season.
Q14: In the deserts of Rajasthan lived the ……………. .
Ans: Raikas
The Raikas are traditional camel breeders who reside in the deserts of Rajasthan. This community is particularly found in the arid regions of the Thar Desert. The Raikas have adapted to the harsh desert conditions and have developed unique practices for camel rearing and breeding.
Q15: The colonial state wanted to transform all ……………. lands into cultivated land.
Ans: Grazing
The colonial state aimed to transform all grazing lands into cultivated lands. This was part of the colonial agenda to increase revenue by promoting agriculture and reducing the nomadic pastoral lifestyle. The transformation of grazing lands into cultivated fields also led to the sedentarization of many nomadic communities.
True/False
Q16: Gujjar Bakarwals of Jammu and Kashmir are great herders of goat and sheep.
Ans: True
The Gujjar Bakarwals of Jammu and Kashmir are indeed great herders of goat and sheep. They are a nomadic tribe that moves with their livestock depending on the season, to the higher mountains during summers and to the lower valleys during the winters. They have a deep knowledge of the routes and the pastures along them.
Q17: The Gaddi shepherds of Punjab had a similar cycle of seasonal movement of the Gujjars.
Ans: False
The Gaddi shepherds are from Himachal Pradesh, not Punjab. Also, their pattern of movement is different from the Gujjars. The Gaddis begin their march upwards to the higher pastures in the summer and come down by winter, unlike the Gujjars who move to the lower valleys in winter.
Q18: Bhabar is a dry forested area below the foothills of Garhwal and Kumaun.
Ans: True
Bhabar is an alluvial, rock-strewn, dry and forested area located at the foothills of the Shivalik range in the Himalayas. It stretches from the Indus River to the Brahmaputra River, passing through the Garhwal and Kumaun regions. It is known for its dry riverbeds and boulders.
Q19: Dhangars were an important pastoral community of Himachal Pradesh.
Ans: False
Dhangars are a major pastoral community but they are from Maharashtra, not Himachal Pradesh. They are primarily sheep and goat herders and are known for their knowledge of the landscape, grazing lands, and water resources.
Q20: After the Kharif harvest was cut at this time, the fields had to be fertilised and made ready for rabi harvest.
Ans: True
After the Kharif harvest, which is the summer crop, is cut around September-October, the fields do need to be fertilised and prepared for the Rabi harvest, which is the winter crop. This is a standard agricultural practice to ensure the soil retains its nutrients for the next crop cycle.
Matching Questions
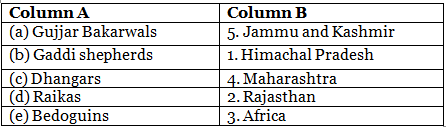
Q21:
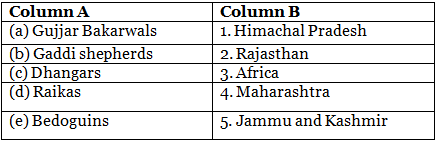
Ans: