Long Questions: Light, Shadow and Reflections | NCERT Summary: UPSC PDF Download
Q1: Explain the construction of a pinhole camera.
Ans: A pinhole camera is made up of two boxes that may simply slide into each other without leaving any gaps. Each box has one side ripped out. A small pinhole is formed in the centre of the larger box's opposite surface. A little square is glued on the opposite surface of the smaller box. A translucent paper is used to cover the sliced portion. The pinhole in the smaller box is facing the square strip as it is slid into the larger box. The open face of the little box is used to observe a distant object while keeping light from behind blocked out. The smaller box is dragged forward or backwards until the object's picture is obtained on the larger box screen that is translucent.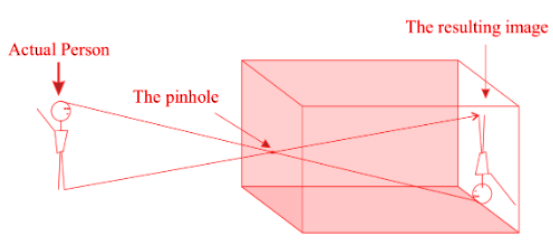
Q2: Explain the concept of light and its sources. Differentiate between natural and artificial sources of light, providing examples for each.
Ans:
- Light is a form of energy that enables us to see objects. It travels in straight lines and can be reflected, refracted, or blocked. There are two types of light sources:
- Natural Sources of Light: These sources produce light naturally. The most significant natural source of light is the Sun, which provides sunlight. Other natural sources include stars and lightning.
- Artificial Sources of Light: These sources are created by humans. Examples include bulbs, candles, and lanterns. These sources emit light when they are heated or connected to a power source.
Q3: Describe how shadows are formed. Explain the conditions required for the formation of shadows and how the size of the shadow changes with the distance of the object from the screen. Provide examples to illustrate your explanation.
Ans: Shadows are formed when an opaque object comes in the path of light.
The conditions for shadow formation are:
- The object should be opaque (does not allow light to pass through).
- There should be a source of light.
- A screen or surface is needed to project the shadow.
The size of the shadow changes with the distance of the object from the screen. When the object is closer to the screen, the shadow appears larger. As the object moves away, the shadow becomes smaller.
Example: If you hold your hand close to a wall with a light source, you'll see a larger shadow. When you move your hand away, the shadow becomes smaller.
Q4: Explain the concept of reflection of light. Describe the difference between regular and irregular reflection with examples of each.
Ans: Reflection is the bouncing back of light when it strikes the surface of an object.
There are two types of reflection:
- Regular Reflection: In regular reflection, light rays are reflected uniformly, creating a clear image. Mirrors have smooth surfaces that cause regular reflection.
- Irregular Reflection: In irregular reflection, light rays are scattered in different directions, creating a blurry or diffuse reflection. Most surfaces, like paper or a wooden table, cause irregular reflection.
- Example: When you look at yourself in a mirror, you see a clear and regular reflection. When you look at your reflection on a rough surface like a wooden table, the reflection is irregular and unclear.
Q5: Describe the working principle of a periscope. Explain how a periscope helps in observing objects from a hidden position. Provide a step-by-step explanation of the path of light inside a periscope.
Ans: A periscope is an optical instrument used to observe objects from a hidden position. It uses the principle of multiple reflections to achieve this.
Working Principle:
- Light enters the top mirror at one end of the periscope.
- The top mirror reflects the light rays downward at a 90-degree angle.
- The light then strikes the bottom mirror at the other end of the periscope.
- The bottom mirror reflects the light rays horizontally, allowing you to observe the object from a hidden position.
A periscope helps you see objects above or around obstacles without being directly visible.
Q6: Explain the concept of a pinhole camera. Describe the construction and working of a pinhole camera, including the formation of an inverted image. Provide examples of real-life applications of a pinhole camera.
Ans: A pinhole camera is a simple camera without lenses, using a small hole to project an image onto a surface.
Construction and Working:
- Take a box with one side covered by an opaque material, except for a small hole (pinhole).
- Place the object you want to capture in front of the hole.
- An inverted (upside-down) image of the object is formed on the opposite inside wall of the box.
- This happens because light travels in straight lines and crosses over at the pinhole.
Example: A room with a small hole in the window during daylight acts as a pinhole camera. An inverted image of the outside scene forms on the opposite wall.
Real-Life Applications: Pinhole cameras are used for educational purposes to understand optics and for fun experiments to create artistic images with unique effects.
Q7: Explain the terms 'opaque', 'transparent', and 'translucent'. Provide examples of materials that fall under each category.
Ans:
- Opaque: Opaque materials do not allow light to pass through. Light is completely blocked. Examples include wood, metal, and cardboard.
- Transparent: Transparent materials allow light to pass through clearly, enabling objects to be seen. Examples include glass, clear plastic, and clean water.
- Translucent: Translucent materials allow some light to pass through but scatter it, making objects on the other side appear blurred. Examples include frosted glass, wax paper, and tissue paper.
Q8: Describe the concept of lateral inversion in reflection. Provide examples to illustrate the phenomenon and explain how lateral inversion affects the perception of reflected text.
Ans: Lateral inversion is a phenomenon where the left and right sides of an object appear reversed in a mirror reflection. This means that the image appears flipped horizontally.
Example: If you hold up a sign with the word "OPEN" in front of a mirror, the reflection will show "NEPO," demonstrating lateral inversion.
In lateral inversion, the image's orientation changes left to right, while the top-bottom orientation remains the same. This phenomenon affects how we perceive mirrored text, making it appear backward in a reflection.
Q9: Explain the concept of a kaleidoscope. Describe its construction and working, including the role of multiple mirrors in creating intricate patterns. Provide examples of situations where kaleidoscopes are used.
Ans: A kaleidoscope is an optical instrument that creates beautiful symmetrical patterns using multiple mirrors and colorful objects.
Construction and Working:
- A kaleidoscope contains three mirrors arranged in a triangular shape.
- One end is filled with small, colorful objects like glass pieces or beads.
- When you look through the other end and rotate the kaleidoscope, the objects create intricate symmetrical patterns due to the multiple reflections.
Example: Kaleidoscopes are used as toys to engage and entertain children. They are also used as decorative items, producing visually appealing patterns.
Q10: Describe the concept of dispersion of light. Explain how a glass prism disperses white light into its component colors and the formation of a rainbow. Provide examples of everyday situations where dispersion is observed.
Ans: Dispersion of light is the separation of white light into its component colors when passing through a prism. This occurs because different colors of light bend by different amounts while passing through the prism.
Formation of a Rainbow:
- Raindrops act like tiny prisms, dispersing sunlight into its colors.
- The colors are then reflected inside the raindrop's surface and exit as a rainbow.
Examples: When sunlight passes through a glass of water, a spectrum of colors can be seen on the other side due to dispersion. This effect is also observed when light passes through a crystal or a diamond, creating colorful reflections.
|
666 docs
|















