Textbook Solution: Chemical and Chemical Changes | Class 7 Oxford Science: Chapter Notes, Worksheets & Tests PDF Download
A. Choose the correct option.
1.
Ans: (c)
2.
Ans: (a)
3.
Ans: rust
4.
Ans: (b)
5.
Ans: (d)
6.
Ans: (a)
B. Fill in the blanks with the correct words.
1.
Ans: Molecules are formed when two or more atoms join together.
2.
Ans: Chemical symbol for the element silver is Ag.
3.
Ans: Elements with atomicity two are called diatomic.
4.
Ans: Rusting is an example of a chemical change.
5.
Ans: Crystals are the solids having a definite geometrical shape.
C.
1.
Ans: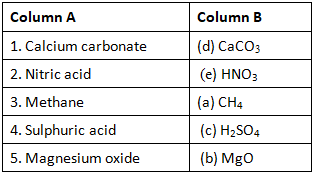
D. Name the following.
1.
Ans: A substance that is made up of only one kind of atom - Element
2.
Ans: The abbreviations used to represent elements - Chemical symbols
3.
Ans: The number of atoms present in one molecule of an element - Atomicity
4.
Ans: The representation of a chemical reaction using symbols and formulae for reactants and products - Chemical equation
5.
Ans: Type of change in which a new substance is produced - Chemical Change
6.
Ans: The process by which a compound is converted into its crystal - Crystallization
E. Answer the following questions.
1.
Ans: Elements are pure substances that are made up of only one type of atom and cannot be broken down further. Examples include Gold (Au), Silver (Ag), and Aluminium (Al). Compounds are pure substances that are formed when two or more elements combine chemically. For example, water (H2O) is a compound formed by the combination of Hydrogen and Oxygen.
2.
Ans: An atom is the smallest most stable particle of a chemical substance. It is the basic unit of a chemical element, and the smallest unit that defines the chemical properties of an element.
3.
Ans: The elements represented by the following symbols are: Ba - Barium, Fe - Iron, Zn - Zinc, S - Sulphur, Au - Gold.
4.
Ans: The chemical symbols for the following elements are: Aluminium - Al, Iodine - I, Flourine - F, Mercury - Hg, Potassium - K.
5.
Ans: Atomicity is the number of atoms present in one molecule of an element. For example, Helium (He) and Neon (Ne) are monoatomic elements as they exist as single atoms. Hydrogen (H2), Nitrogen (N2), Oxygen (O2), and Chlorine (Cl2) are diatomic elements as they exist as molecules consisting of two atoms.
6.
Ans: (a) Two atoms of the element helium - He2
(b) A molecule of the element phosphorus - P4
(c) A molecule of the compound water - H2O
(d) Four molecules of the compound carbon dioxide - 4CO2
7.
Ans: The chemical formulae for the following compounds are: Sulphuric acid - H2SO4, Nitric acid - HNO3, Hydrochloric acid - HCl.
8.
Ans: The elements present in the following compounds are:
CO - Carbon and Oxygen
NaCl - Sodium and Chlorine
CH4 - Carbon and Hydrogen
MgO - Magnesium and Oxygen
9.
Ans: Crystals are solid forms of a compound that have a definite geometrical shape. Impure copper sulphate can be purified by dissolving it in boiling water to form a saturated solution, then filtering to remove insoluble impurities. The filtered solution is left undisturbed, allowing pure copper sulphate crystals to form.
10.
Ans: (a) Iron objects turn reddish-brown when exposed to air due to the formation of rust or iron oxide, which occurs when iron reacts with air and moisture.
(b) The cut surface of fruits and vegetables turn brown due to a chemical reaction between the cut surface and atmospheric oxygen, forming a brown pigment called melanin.
(c) The blue-coloured copper sulphate solution turns sea green when iron filings are added due to a chemical reaction between copper sulphate and iron, forming green-coloured iron sulphate and a brown deposit of copper.
11.
Ans: The gas evolved in the reaction between baking soda and vinegar is carbon dioxide. When this gas is passed through lime water, it turns the lime water milky.
12.
Ans: (a) Burning of magnesium in presence of oxygen - Magnesium + Oxygen -> Magnesium Oxide
(b) Rusting of iron - Iron + Oxygen + Water -> Iron Oxide (rust)
(c) Reaction of copper sulphate solution with iron filings - Copper Sulphate + Iron -> Iron Sulphate + Copper
13.
Ans: Iron filings acquire a reddish-brown deposit when dropped in copper sulphate solution because a chemical reaction occurs between the iron and the copper sulphate, producing a green-coloured iron sulphate solution and a deposit of copper on the iron filings.
|
138 videos|151 docs|18 tests
|
FAQs on Textbook Solution: Chemical and Chemical Changes - Class 7 Oxford Science: Chapter Notes, Worksheets & Tests
| 1. What are some examples of chemical changes? |  |
| 2. How can you differentiate between a physical change and a chemical change? |  |
| 3. What are some signs that a chemical change has occurred? |  |
| 4. Can you reverse a chemical change? |  |
| 5. How do chemical changes impact our daily lives? |  |
















