Best Study Material for Class 7 Exam
Class 7 Exam > Class 7 Notes > Class 7 Oxford Science: Chapter Notes, Worksheets & Tests > Textbook Solution: Time and Motion
Textbook Solution: Time and Motion | Class 7 Oxford Science: Chapter Notes, Worksheets & Tests PDF Download
A. Choose the correct option.
1.Ans: (a)
2.
Ans: (a)
3.
Ans: (c)
4.
Ans: (b)
B. Fill in the blanks with the correct words.
1.Ans: Kilometres per hour
2.
Ans: An hourglass is a type of clock.
3.
Ans: The time period of a pendulum depends on the length of the string.
4.
Ans: Metre per second is the SI unit of speed.
5.
Ans: In uniform motion, speed remains the same.
C. Match the Following.
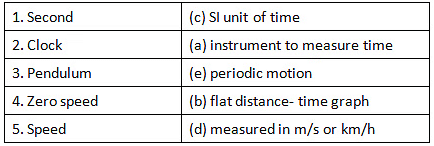
1.
Ans:
 |
Download the notes
Textbook Solution: Time and Motion
|
Download as PDF |
Download as PDF
D. Answer the following questions.
1.
Ans: Three instruments used to measure time are: a clock, a sundial, and an hourglass.
2.
Ans: Periodic motion is used to measure time by identifying an event that repeats itself at regular intervals. This event should have a constant and predictable periodic motion.
Examples of periodic motion include the to-and-fro movement of a compressed spring, the rotation and revolution of the Earth, the revolution of the moon around the Earth, and the oscillation of a pendulum. This predictable motion is used to construct various types of clocks, such as a pendulum clock.
3.
Ans: Two units of time larger than a day are: a week and a year.
4.
Ans: One clock that uses the movement of the sun to keep time is a sundial.
5.
Ans: Speed is defined as the distance travelled by an object in unit time. It refers to how fast or slow an object is moving. The SI unit of speed is metres per second (m/s).
E. Numerical Problems.
1.
Ans: A vehicle travels 25 km in 15 minutes. To calculate its speed in km/h, first convert minutes to hours. There are 60 minutes in an hour, so 15 minutes is 15/60 = 0.25 hours. Speed = distance/time = 25 km/0.25 h = 100 km/h.
2.
Ans: A commercial aircraft travels at 900 km/h. To calculate the distance it travels in 5 hours, multiply the speed by the time: distance = speed x time = 900 km/h x 5 h = 4500 km.
3.
Ans: Seismic waves travel at about 8 km/s on the Earth's crust. To calculate the distance it travels in 10 s, multiply the speed by the time: distance = speed x time = 8 km/s x 10 s = 80 km.
4.
Ans:
(a) 30 s to minutes: 30 s / 60 = 0.5 minutes
(b) 72 hours to days: 72 h / 24 = 3 days
(c) 90 km/h to m/s: 90 km/h * (1000 m/1 km) * (1 h/3600 s) = 25 m/s
(d) 75 m/s to km/h: 75 m/s * (1 km/1000 m) * (3600 s/1 h) = 270 km/h.
The document Textbook Solution: Time and Motion | Class 7 Oxford Science: Chapter Notes, Worksheets & Tests is a part of the Class 7 Course Class 7 Oxford Science: Chapter Notes, Worksheets & Tests.
All you need of Class 7 at this link: Class 7
|
140 videos|108 docs|18 tests
|
FAQs on Textbook Solution: Time and Motion - Class 7 Oxford Science: Chapter Notes, Worksheets & Tests
| 1. What is the concept of time and motion in physics? |  |
| 2. How are time and motion related in scientific experiments? |  |
Ans. Time is often used to measure the duration of motion in scientific experiments, helping scientists analyze the speed, distance, and acceleration of objects.
| 3. Can time and motion be accurately measured in experiments? |  |
Ans. Yes, time can be measured using clocks or timing devices, while motion can be tracked using tools like motion sensors or cameras to ensure accurate measurements in experiments.
| 4. How does understanding time and motion help in predicting outcomes in scientific research? |  |
Ans. By understanding time and motion, scientists can predict the behavior of objects, calculate trajectories, and make accurate predictions about the outcomes of experiments in various scientific research fields.
| 5. What are some real-world applications of studying time and motion in physics? |  |
Ans. Studying time and motion in physics has real-world applications in fields such as engineering, robotics, sports science, and transportation, where understanding the relationship between time and motion is crucial for designing efficient systems and improving performance.
Related Searches

























