Solids, Liquids and Gases - 2 Class 4 Worksheet Science
Q1: Fill in the blanks.
(i) All matter has _____ and _____.
Ans: mass, takes up space
All matter has mass, which is the amount of matter in an object, and takes up space, which is its volume.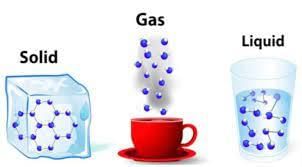
(ii) Matter is made up of tiny particles called _____.
Ans: molecules
Matter is composed of tiny particles called molecules, which are made up of atoms.
(iii) The three states of matter are _____, _____, and _____.
Ans: solid, liquid, gas
The three states of matter are solid, liquid, and gas, each with different properties and arrangements of molecules.
(iv) Liquids take the shape of the _____ they are poured into.
Ans: container
Liquids take the shape of the container they are poured into, as they have no fixed shape.
(v) Gases do not have a definite shape or _____.
Ans: volume
Gases do not have a definite shape or volume, and their molecules are very far apart.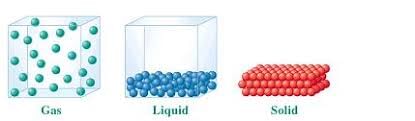
Q2: Match the column.
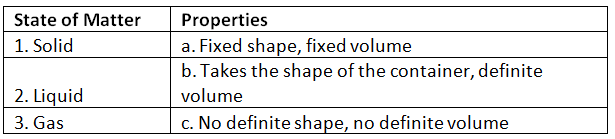 Ans: 1. Solid - Fixed shape, fixed volume
Ans: 1. Solid - Fixed shape, fixed volume
Solids have a fixed shape and volume due to closely packed molecules.
2. Liquid - Takes the shape of the container, definite volume
Liquids take the shape of the container they are poured into but have a fixed volume.
3. Gas - No definite shape, no definite volume
Gases have no fixed shape or volume and can expand to fill any available space.
Q3: True or False.
(i) Solids have a definite shape and volume.
Ans: True
Solids have a fixed shape and volume because their molecules are tightly packed.
(ii) Gases are often visible.
Ans: False
Gases are often invisible, and we cannot see them directly.
(iii) Melting is the process of changing a liquid to a solid.
Ans: False
Melting is the process of changing a solid to a liquid upon heating, not the other way around.
(iv) Water can exist in all three states: solid, liquid, and gas.
Ans: True
Water can exist in all three states: solid (ice), liquid (water), and gas (water vapor).
(v) Soluble substances dissolve in water.
Ans: True
Soluble substances like sugar dissolve in water, while insoluble substances like tea leaves do not dissolve in water.
Q4: Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs).
(i) What is the state of matter of water at room temperature?
(a) Solid
(b) Liquid
(c) Gas
(d) None of these
Ans: (b)
At room temperature, water is in its liquid state.
(ii) Which of the following substances is a solute?
(a) Water
(b) Salt
(c) Coffee
(d) None of these
Ans: (b)
Salt is a solute that dissolves in a solvent (such as water) to form a solution.
(iii) What happens to water when it is boiled in a kettle?
(a) It freezes into ice
(b) It evaporates into steam
(c) It turns into a solid
(d) None of these
Ans: (b)
When water is boiled, it turns into steam, which is a gas.
(iv) How can insoluble solids be separated from liquids?
(a) Filtration
(b) Evaporation
(c) Condensation
(d) None of these
Ans: (a)
Insoluble solids can be separated from liquids using the filtration method.
(v) Which of the following is NOT a property of gases?
(a) Definite shape
(b) No definite volume
(c) Often invisible
(d) None of these
Ans: (a)
Gases do not have a definite shape, but they can expand to fill the space available to them.
Q5: Short Answer Questions.
(i) Explain the three states of matter with examples.
Ans: The three states of matter are solid, liquid, and gas.
- Solids: Solids have a fixed shape and volume. Examples of solids are a pencil, a slice of bread, and a piece of wood.
- Liquids: Liquids take the shape of the container they are poured into and have a definite volume. Examples of liquids are water, juice, and milk.
- Gases: Gases do not have a definite shape or volume and are often invisible. Examples of gases are the air we breathe and the air filled in balloons.
(ii) Describe the process of evaporation.
Ans: Evaporation is the process by which a substance changes from the liquid state into its vapor form upon heating. When water is heated in a kettle, it starts boiling, and steam escapes from the water. This steam is water vapor. Evaporation occurs because the heat energy provided to the water overcomes the forces of attraction between the water molecules, allowing them to escape into the air as gas.
(iii) What is a solution? Give an example.
Ans: A solution is a mixture formed when a solute dissolves in a solvent. The substance that dissolves in the liquid is called the solute, and the liquid in which the solute dissolves is called the solvent. An example of a solution is saltwater, where salt (solute) dissolves in water (solvent) to form a saltwater solution.
(iv) How can insoluble solids be separated from liquids?
Ans: Insoluble solids can be separated from liquids by two methods:
- Filtration: In this method, the mixture is poured through a sieve or filter paper. The solid particles are trapped on the filter paper, while the liquid passes through, resulting in the separation of the insoluble solid from the liquid.
- Sedimentation and decantation: In this method, the mixture is allowed to stand for some time. The solid particles settle at the bottom due to gravity, and the liquid can be poured off carefully without disturbing the settled solid, resulting in the separation of the insoluble solid from the liquid.
|
48 videos|225 docs|34 tests
|
FAQs on Solids, Liquids and Gases - 2 Class 4 Worksheet Science
| 1. What are the three states of matter? |  |
| 2. What is the main difference between solids and liquids? |  |
| 3. How do solids, liquids, and gases differ in terms of particles? |  |
| 4. Can matter change from one state to another? Give an example. |  |
| 5. How does temperature affect the states of matter? |  |
















