Weather and Climate - 2 Class 5 Worksheet SST
| Table of contents |

|
| True or False |

|
| Find the Odd One Out and Give Reason |

|
| Match the Following |

|
| Real-Life Application-Based Questions |

|
True or False
(i) Weather refers to the long-term atmospheric conditions of a place.
Ans: False
Weather refers to short-term atmospheric conditions, while climate refers to long-term patterns.
(ii) The Sun’s rays fall more directly at the Equator than at the poles.
Ans: True
The Equator receives direct sunlight, resulting in warmer temperatures. In contrast, the poles receive slanted rays, which spread heat over a larger area, leading to cooler conditions.
(iii) Altitude does not affect the climate of a place.
Ans: False
As altitude increases, temperature decreases, which means mountainous regions are generally cooler than lowland areas.
(iv) The monsoon is a type of rainfall pattern that affects India.
Ans: True
The monsoon is a specific type of rainfall pattern that significantly affects India. Monsoon winds contribute to heavy rainfall in the region, playing a crucial role in shaping its climate and supporting agriculture.
(v) All coastal areas experience extreme climates.
Ans: False
Coastal areas typically experience moderate climates due to the influence of the sea. This results in smaller temperature variations when compared to inland areas.
(vi) Humidity is the amount of moisture present in the air.
Ans: True
Humidity is the amount of moisture present in the air. It refers to the water vapour in the atmosphere and influences how hot or cold a place feels.
(vii) Frigid zones receive the most sunlight and have the highest temperatures.
Ans: False
Frigid zones are located near the North and South Poles and receive less direct sunlight. This results in extremely cold temperatures.
(viii) Chennai and Mumbai have extreme climates like deserts.
Ans: False
Chennai and Mumbai are coastal cities, which means they experience a moderate climate. This contrasts with deserts, which have extreme temperature variations.
(ix) Distance from the sea does not affect the climate of a place.
Ans: False
Places near the sea tend to have moderate climates, while areas far from the sea often experience extreme climates.

Find the Odd One Out and Give Reason
(i) Equator, Frigid Zone, Monsoon, Temperate Zone
Ans: Monsoon
The other three (Equator, Frigid Zone, Temperate Zone) are climatic zones, whereas Monsoon refers to a seasonal wind pattern that brings rainfall.
(ii)Temperature, Rainfall, Wind Speed, Earthquake
Ans: Earthquake
Temperature, Rainfall, and Wind Speed are elements of weather, whereas an Earthquake is a geological event unrelated to atmospheric conditions.
(iii) Latitude, Altitude, Distance from the Sea, Rain Gauge
Ans: Rain Gauge
Latitude, Altitude, and Distance from the Sea are factors affecting climate, while a Rain Gauge is an instrument used to measure rainfall.
(iv) Tropical Zone, Desert Climate, Frigid Zone, Temperate Zone
Ans: Desert Climate
The other three are climatic zones, whereas Desert Climate refers to a specific type of climate found in various zones.
(v) Sunlight, Humidity, Glacier, Air Pressure
Ans: Glacier
Sunlight, Humidity, and Air Pressure are elements of weather, while Glacier is a landform formed by ice accumulation.
Match the Following
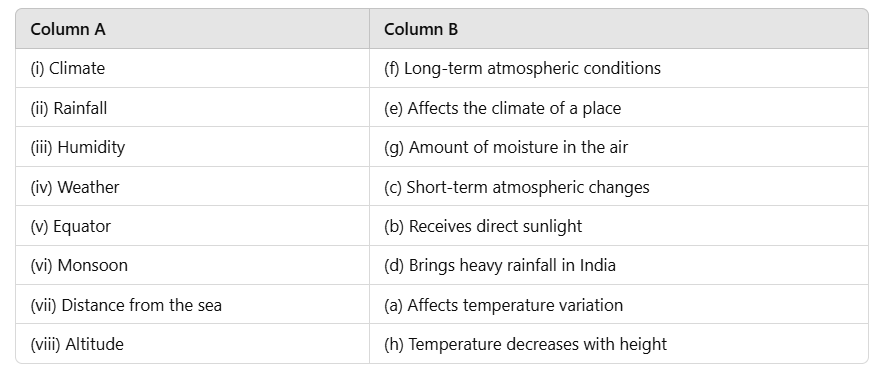
Ans:
Real-Life Application-Based Questions
(i) Why do people living near coastal areas experience less temperature variation than those living in deserts or inland areas?
Ans: People living near coastal areas experience less temperature variation compared to those in deserts or inland areas due to the presence of large water bodies. Coastal regions have a moderate climate because water takes longer to heat up and cool down than land. As a result, places near the sea experience smaller temperature differences between day and night.
(ii) Why is the Equator hotter than the Polar regions?
Ans: The Equator is hotter than the Polar regions primarily because it receives direct sunlight throughout the year. In contrast, the Polar regions are exposed to slanted rays of sunlight, which spread the heat over a larger area. This difference in sunlight intensity results in the Polar regions being significantly colder.
(iii) Why do farmers check the weather forecast before sowing their crops?
Ans: Farmers depend on rainfall and temperature for successful crop growth.
Checking the weather forecast enables them to:
- Plan irrigation effectively.
- Avoid droughts that could harm their crops.
- Protect crops from extreme weather conditions such as storms or frost.
(iv) Why does Chennai experience a more moderate climate than Delhi, even though both are in India?
Ans: Chennai is a coastal city, which contributes to its moderate climate due to the influence of the sea. In contrast, Delhi is located inland, far from any large water body, resulting in an extreme climate characterized by very hot summers and cold winters.
|
33 videos|264 docs|50 tests
|
FAQs on Weather and Climate - 2 Class 5 Worksheet SST
| 1. What is the difference between weather and climate? |  |
| 2. How do meteorologists predict the weather? |  |
| 3. What are the main factors that influence climate? |  |
| 4. Why is understanding climate change important? |  |
| 5. What are some examples of extreme weather events? |  |




















