Real Numbers Class 10 Notes Maths Chapter 1
Some Important Definitions
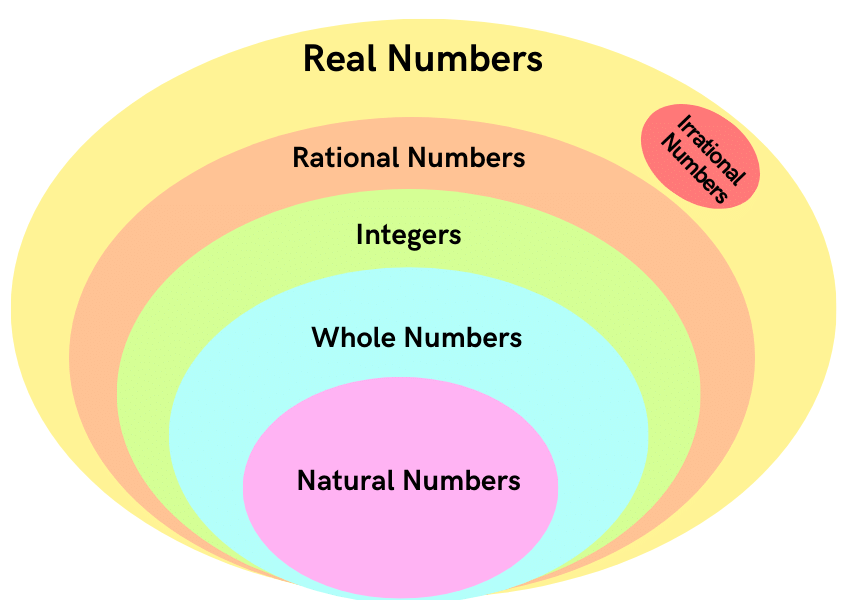
- Real Numbers(R): All rational and irrational numbers are called real numbers.
- Integers(I): All numbers from (…-3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3…) are called integers.
- Rational Numbers(Q):Real numbers of the form p/q, q ≠ 0, p, q ∈ I are rational numbers.
- All integers can be expressed as rational, for example, 5 = 5/1.
- Decimal expansion of rational numbers terminating or non-terminating recurring.
- Irrational Numbers(Q’ ): Real numbers which cannot be expressed in the form p/q and whose decimal expansions are non-terminating and non-recurring.
- Roots of primes like √2, √3, √5 etc. are irrational
- Natural Numbers(N): Counting numbers are called natural numbers. N = {1, 2, 3, …}
- Whole Numbers(W): Zero along with all natural numbers are together called whole numbers. {0, 1, 2, 3,…}
- Even Numbers: Natural numbers of the form 2n are called even numbers. (2, 4, 6, …}
- Odd Numbers: Natural numbers of the form 2n -1 are called odd numbers. {1, 3, 5, …}
Remember this!
- All Natural Numbers are whole numbers.
- All Whole Numbers are Integers.
- All Integers are Rational Numbers.
- All Rational Numbers are Real Numbers.
Prime Numbers
The natural numbers greater than 1 which are divisible by 1 and the number itself are called prime numbers, Prime numbers have two factors i.e., 1 and the number itself For example, 2, 3, 5, 7 & 11 etc.
Note: 1 is not a prime number as it has only one factor.
Composite Numbers
The natural numbers which are divisible by 1, itself and any other number or numbers are called composite numbers. For example, 4, 6, 8, 9, 10 etc.
Note: 1 is neither prime nor a composite number.
Constructing a factor tree
Step 1: Write the number as a product of prime number and a composite number.
Step 2: Repeat the process till all the primes are obtained.
Example : Factorize 8190
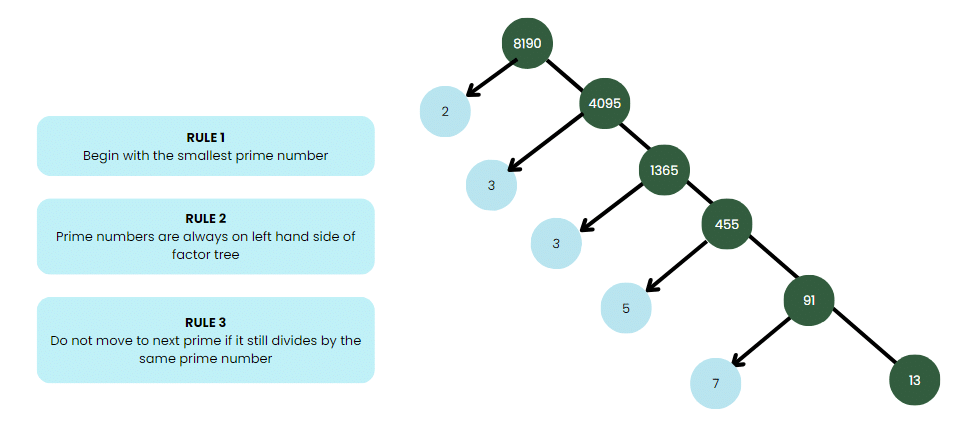
So we have factorised 8190 as 2 × 3 × 3 × 5 × 7 × 13 as a product of primes, i.e., 8190 = 2 × 32 × 5 × 7 × 13 as a product of powers of primes
Fundamental theorem of Arithmetic
Every composite number can be expressed as a product of primes, and this expression is unique, apart from the order in which they appear.
Applications:
- To locate HCF and LCM of two or more positive integers.
- To prove irrationality of numbers.
- To determine the nature of the decimal expansion of rational numbers.
Algorithm to locate HCF and LCM of two or more positive integers
Step 1: Factorize each of the given positive integers and express them as a product of powers of primes in ascending order of magnitude of primes.
Step 2: To find HCF, identify common prime factor and find the least powers and multiply them to get HCF.
Step 3: To find LCM, find the greatest exponent and then multiply them to get the LCM.
To prove Irrationality of numbers
- The sum or difference of a rational and an irrational number is irrational.
- The product or quotient of a non-zero rational number and an irrational number is irrational.
To determine the nature of the decimal expansion of rational numbers
- Let x = p/q, p and q are co-primes, be a rational number whose decimal expansion terminates. Then the prime factorization of’q’ is of the form 2m5n, m and n are non-negative integers.
- Let x = p/q be a rational number such that the prime factorization of ‘q’ is not of the form 2m5n, ‘m’ and ‘n’ being non-negative integers, then x has a non-terminating repeating decimal expansion.
|
127 videos|584 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Real Numbers Class 10 Notes Maths Chapter 1
| 1. What are prime numbers and how are they different from composite numbers? |  |
| 2. What is Euclid’s Division Lemma and how is it applied? |  |
| 3. How do you construct a factor tree for a number? |  |
| 4. What is the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic? |  |
| 5. How can you determine the nature of the decimal expansion of rational numbers? |  |