Class 10 Geography Chapter 2 Previous Year Questions - Forest and Wildlife Resources
Previous Year Questions 2025
Q1: Which of the following characteristics of the Indian Wild Life (Protection) Act are correct? (1 Mark)
Characteristics:
I. To make provisions for habitat for wild animals.
II. To publish list of protected species.
III. To ban hunting to save endangered species.
IV. To include important subjects like forests and wildlife in the Union List.
(a) Only I, II and III are correct.
(b) Only I, II and IV are correct.
(c) Only II, III and IV are correct.
(d) Only I, III and IV are correct.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Only I, II and III are correct.
The Indian Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972 provided provisions for protecting habitats, published an all-India list of protected species, and banned hunting to save endangered species. But forests and wildlife are not mentioned in the Act as Union List subjects in the chapter.
Q2: Choose the correctly matched pair from the following: (1 Mark)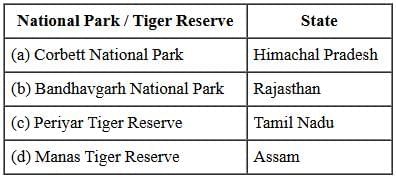
 View Answer
View Answer 
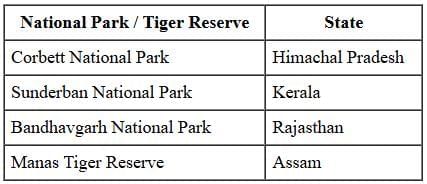
Ans: (d) Manas Tiger Reserve - Assam
- Manas Tiger Reserve is located in Assam. The other pairs are incorrectly matched:
- Corbett National Park → Uttarakhand
- Sunderban National Park → West Bengal
- Bandhavgarh National Park → Madhya Pradesh
Or
Choose the correctly matched pair: (1 Mark)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d) Manas Tiger Reserve - Assam
Q3: Match Column I with Column II and choose the correct option: (1 Mark)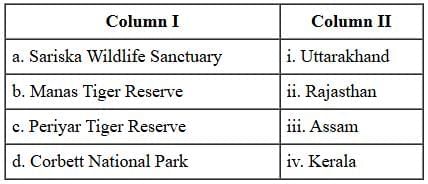
(a) a-i, b-ii, c-iii, d-iv
(b) a-ii, b-iii, c-iv, d-i
(c) a-iv, b-i, c-iii, d-ii
(d) a-ii, b-i, c-iv, d-iii
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) a-ii, b-iii, c-iv, d-i
The table below shows the correct matching of each national park or wildlife sanctuary with its respective state: 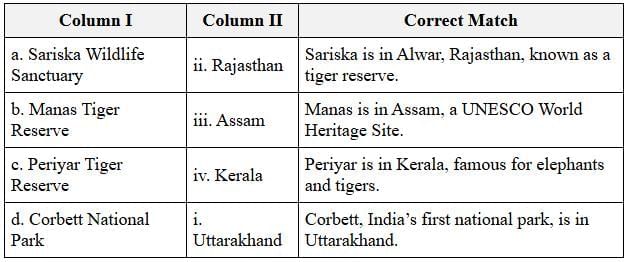
The correct mapping is:
- a-ii (Sariska - Rajasthan)
- b-iii (Manas - Assam)
- c-iv (Periyar - Kerala)
- d-i (Corbett - Uttarakhand)
Thus, option (b) is correct.
Q4: Read the given source and answer the questions that follow: (4 Marks)
Sacred Groves - a wealth of diverse and rare species
Nature worship is an age-old tribal belief based on the premise that all creations of nature have to be protected. Such beliefs have preserved several virgin forests in pristine form called Sacred Groves (the forests of God and Goddesses). These patches of forest or parts of large forests have been left untouched by the local people and any interference with them is banned. Certain societies revere a particular tree which they have preserved from time immemorial. The Mundas and the Santhal of Chota Nagpur region worship mahua (Bassia latifolia) and kadamba (Anthocaphalus cadamba) trees, and the tribals of Odisha and Bihar worship the tamarind (Tamarindus indica) and mango (Mangifera indica) trees during weddings. To many of us, peepal and banyan trees are considered sacred. Indian society comprises several cultures, each with its own set of traditional methods of conserving nature and its creations. Sacred qualities are often ascribed to springs, mountain peaks, plants, and animals which are closely protected. You will find troops of macaques and langurs around many temples. They are fed daily and treated as a part of temple devotees. In and around Bishnoi villages in Rajasthan, herds of blackbuck (chinkara), nilgai, and peacocks can be seen as an integral part of the community and nobody harms them.
(i) How do sacred groves show the inter-connectivity of spirituality and ecology? (1 Mark)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
(i) Sacred groves show the inter-connectivity of spirituality and ecology because nature is worshipped as divine, leading to protection of forests, trees, springs, plants, and animals.
(ii) How do tribal practices promote conservation of forests? (1 Mark)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
(ii) Tribal practices promote conservation as communities like Mundas, Santhals, and tribals of Odisha and Bihar preserve and worship trees like mahua, kadamba, tamarind, and mango, leaving forests untouched and banning interference.(iii) Why is conservation of wildlife important for all of us? Explain. (2 Marks)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Conservation of wildlife is important because it preserves ecological diversity and life-support systems (water, air, soil). It also maintains genetic diversity of plants and animals, supporting agriculture, fisheries, and overall human survival.
Q5: Which state of India has the maximum area under permanent forest? (1 Mark)
(a) Haryana
(b) Himachal Pradesh
(c) Punjab
(d) Madhya Pradesh
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d) Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh has the largest area under permanent forests, constituting about 75% of its total forest area.
Previous Year Questions 2024
Q1: Read the following passages and answer the questions that follow: (CBSE 2024)Nature worship is an age-old tribal belief based on the premise that all creations of nature have to be protected. Such beliefs have preserved several virgin forests in pristine form called Sacred Groves (the forests of God and Goddesses). These patches of forest or parts of large forests have been left untouched by the local people and any interference with them is banned. Certain societies revere a particular tree which they have preserved from time immemorial. The Mundas and the Santhal of Chota Nagpur region worship mahua (Bassia latifolia) and kadamba (Anthocaphalus cadamba) trees, and the tribals of Odisha and Bihar worship the tamarind (Tamarindus indica) and mango (Mangifera indica) trees during weddings. To many of us, peepal and banyan trees are considered sacred. Indian society comprises several cultures, each with its own set of traditional methods of conserving nature and its creations. Sacred qualities are often ascribed to springs, mountain peaks, plants and animals which are closely protected. You will find troops of macaques and langurs around many temples. They are fed daily and treated as a part of temple devotees. In and around Bishnoi villages in Rajasthan, herds of blackbuck, (chinkara), nilgai and peacocks can be seen as an integral part of the community and nobody harms them.
(i) How does the sacred grove relate to the belief in nature worship?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Many cultures, especially Indian tribal communities, hold sacred groves in high regard as places where the natural world's divinity is recognised and honored. These groves serve as physical representations of the idea that all natural objects are sacred and deserve preservation.
(ii) How do communities incorporate trees into their cultural practices? Explain with an example.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Communities include trees in their cultural practices in a variety of ways, primarily by giving sacred or symbolic meaning. For example, certain trees, like the tamarind, mango, kadamba, and mahua, have great significance and are worshipped during weddings and other ceremonies in many Indian tribal communities. Similarly, sacred trees like banyan and peepal are frequently connected to places of worship like temples.
(iii) Explain the cultural values that contribute to the coexistence of nature.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (1) Numerous societies have customs regarding the preservation of particular natural regions, like sacred woods, where particular species of trees or ecosystems are respected. These places hold rituals and ceremonies that uphold the cultural value of honoring and protecting the natural world.
(2) Natural elements such as trees, animals, and other features are frequently symbolic in cultural belief systems. For instance, groups of macaques and langurs that surround numerous temples receive daily food and are regarded as members of the temple community. Herds of blackbuck, nilgai, and peacocks are regarded as essential members of the community in certain villages of Rajasthan.
This perspective demonstrates a shared understanding of how crucial it is to coexist with nature.
Previous Year Questions 2023
Q2: Which of the following options represent potential measures that can be taken to mitigate the threats posed on the tiger population and biodiversity?(I) Banning hunting, giving legal protection to their habitats, and restricting trade in wildlife.
(II) Prohibiting the visit of public into forest area.
(III) Establishing wildlife sanctuaries and National Parks.
(IV) Converting forests into Reserved and Protected forests. (CBSE SQP 2023)
Options:
(a) Statements (I) and (II) are correct.
(b) Statements (II), (III) and (IV) are correct.
(c) Statement (II) is correct.
(d) Statements (I), (III), and (IV) are correct.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
Statement (I) suggests banning hunting and protecting tiger habitats, which helps in conserving the tiger population and maintaining biodiversity.
Statement (III) about establishing wildlife sanctuaries and national parks provides safe areas for tigers and other wildlife to thrive, promoting biodiversity.
Statement (IV) on converting forests into reserved and protected forests ensures that these areas are safeguarded from exploitation and development.
Statement (II), which proposes prohibiting public visits to forest areas, might not be practical or beneficial for conservation efforts. Allowing controlled visits can raise awareness and support for wildlife protection.
Previous Year Questions 2022
Q3: Which of the following descriptions of forest is NOT correct? (2022)(a) Reserved Forest - Reservation of more than half of forests
(b) Protected Forest - Reservation of 1/3 of the forests
(c) Unclassed Forest - Reservation of forest under government and private individuals.
(d) Permanent Forest - Reserved and unclassed forest for the production of timber.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
Reserved and protected forests are referred to as permanent forest. It is maintained for the purpose of prod ucing ti mber and ot her forest product.
Q4: Match the items in Column A with those of Column B. (Delhi Gov. SQP 2022)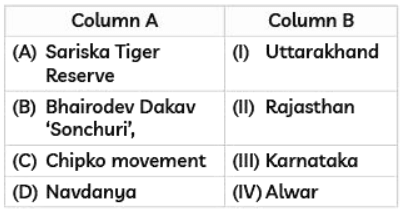 (a) (A)-(III), (B)-(I), (C)-(IV), (D)-(II)
(a) (A)-(III), (B)-(I), (C)-(IV), (D)-(II)
(b) (A)-(II), (B)-(III), (C)-(IV), (D)-(I)
(c) (A)-(II), (B)-(IV), (C)-(I), (D)-(III)
(d) (A)-(III), (B)-(IV), (C)-(II), (D)-(I)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
(A) Sariska Tiger Reserve is located in (II) Rajasthan. It is a well-known tiger reserve famous for its tiger population.
(B) Bhairodev Dakav 'Sonchuri' is in (IV) Alwar, which is part of Rajasthan, and this area is noted for its unique wildlife and conservation efforts.
(C) Chipko movement began in (I) Uttarakhand as a grassroots movement to protect trees and forests.
(D) Navdanya is an organization that promotes biodiversity and organic farming, and it is associated with (III) Karnataka.
Q5: How do human beings influence the ecology of a region? (Delhi Gov. SQP 2022)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Human beings influence the ecology of a region in several ways:
- Breathing: Humans inhale oxygen and exhale carbon dioxide, which are essential for plant life.
- Anthropogenic activities: Actions such as agriculture, grazing, and industrial development permanently alter the ecology of a region.
- Consumption: Humans use various products from plants and animals, affecting their demand and consequently altering ecosystems.
Q6: What is a wildlife sanctuary? How is it different from national parks? (Delhi Gov. SQP 2022)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: A protected area set aside for the preservation and conservation of wildlife and their habitats is known as a wildlife sanctuary. Governments or private organisations created these areas with the intention of protecting biodiversity, fostering ecological balance, and offering refuge to threatened or endangered species.
The difference between wildlife sanctuaries and national parks are: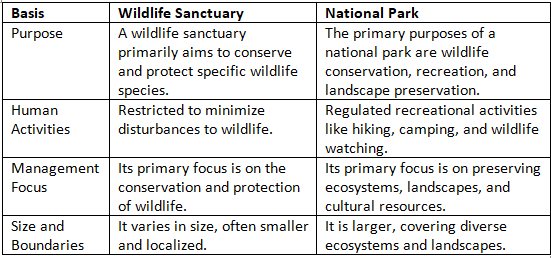
Q7: The destruction of forests and wildlife is not just a biological issue. The biological loss is strongly correlated with the loss of cultural diversity." Explain the statement by giving relevant examples. (Delhi Gov. SQP 2022)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The destruction of forests and wildlife is not just a biological issue. The biological loss is strongly correlated with the loss of cultural diversity.
This can be proved using the following points:
- Marginalisation: The loss of biological diversity has pushed many native and forest communities into poverty, as they rely on forests for food, shelter, and livelihoods.
- Cultural Impact: These communities have lifestyles and cultures that are deeply tied to the forests. When forests disappear, their cultures are directly affected.
- Gender Disparity: Women, who are primarily responsible for gathering produce, fuel, fodder, and water, face greater challenges. Their increased workload affects their health and family roles.
- Generational Loss: As women struggle, they may neglect their children, leading to a loss of cultural transmission and values.
- Traditional Practices: Many communities have unique rituals linked to forests, such as worship and marriage ceremonies. The loss of forests can mean the disappearance of these important traditions.
Previous Year Questions 2017
Q8: In which year was the 'Indian Wildlife Protection Act' implemented in India? Describe the main thrust area of this program. (2017) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (i) In the 1960s and 1970s, the conservationists demanded some rules to protect the wildlife. Conceding to their demand, the government enacted the Indian Wildlife (Protection) Act 1972. Under this act, an all-India list of protected species was published.
(ii) Hunting was banned to protect the remaining population of some endangered species.
(iii) Trade in wildlife was restricted and the habitats of wildlife were given legal protection. Many national parks and wildlife sanctuaries were established by central state governments and the state governments.
(iv) Several projects were announced for protecting specific animals, e.g. Project Tiger. Project Tiger was launched in 1973 to protect tigers from becoming extinct.
Q9: What is biodiversity? Why is biodiversity important for human lives? Analyse. (2017)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Biodiversity refers to diverse flora and fauna that exist in a given area. Plants, animals and human beings are interdependent. It is necessary for human beings as we get fresh air, water, food etc., from them. Thus, the existence of human beings depends on them.
Biodiversity boosts ecosystem productivity where each species, no matter how small, all have an important role to play. For example, a larger number of plant species means a greater variety of crops. Greater species diversity ensures natural sustainability for all life forms. Healthy ecosystems can better withstand and recover from a variety of disasters. And so, while we dominate this planet, we still need to preserve the diversity in wildlife. Each species depends on the services provided by other species to ensure survival. It is a type of cooperation based on mutual survival that is provided by a balanced eco system. That is why when the ecosystem is disturbed survival of the species becomes difficult.
Previous Year Questions 2016
Q10: 'Forests and wildlife are vital to the quality of life and environment'. Justify the statement by giving three reasons. (2016) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Forests and wildlife are vital to the quality of life and environment. This is because the destruction of forests and wildlife leads to:
- Loss of cultural diversity: Communities relying on forest products suffer greatly due to the decline of flora and fauna.
- Impact on women: In rural areas, women are responsible for gathering firewood, fodder, and water. The depletion of these resources increases their workload and can lead to health issues.
- Poverty: When tribal populations cannot access basic supplies, they must purchase them, creating greater economic strain.
Q11: 'Large-scale development projects have also contributed significantly to the loss of forests'. Justify this statement with relevant examples. (2016)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (i) Since 1951, over 5000 sq km of forest was cleared for River Valley Projects.
(ii) Clearing of forests is still continuing with projects like the Narmada Sagar Project in Madhya Pradesh which would inundate 40,000 hectares of forest.
(iii) Mining is another important factor behind deforestation.
Previous Year Questions 2015
Q12: Analyse any four reasons for the depletion of forest resources in India. (2015) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Reasons for the depletion of forest resources in India are:
(i) Extensive use of forest products such as wood, barks, leaves, rubber, medicines, dyes, food, fuel, fodder, manure etc.
(ii) Agricultural expansion, development of railways, mining, commercial and social forestry.
(iii) Substantial forests in the tribal belts of northeastern states have been degraded by shifting cultivation (Jhumming) or slash and burn agriculture.
(iv) Large scale developmental projects like Narmada Sagar Project of Madhya Pradesh which would inundate 40,000 hectares of forests.
(v) Mining is another important factor, as in the Buxa Tiger Reserve in West Bengal is seriously threatened by dolomite mining. It has disturbed the natural habitat of many species and migration route of animals, especially the great Indian elephant.
Q13: Describe the steps taken to conserve the flora and fauna of the country. (2015,2014)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The various steps taken to conserve the flora and fauna of the country include:
- Implementation of the Indian Wildlife Protection Act 1972.
- Controlling deforestation and promoting afforestation programmes.
- Providing legal protection to animals by enforcing laws against hunting and poaching.
- Raising public awareness about the importance of forests and their biodiversity.
- Establishing biosphere reserves; India has set up 18 such reserves.
- Offering financial and technical support to various botanical gardens.
- Implementing focused projects like Project Tiger, Project Rhino, and Project Great Indian Bustard.
- Creating 106 national parks and 565 wildlife sanctuaries to protect natural heritage.
Previous Year Questions 2014
Q14: Explain any three factors responsible for the depletion of flora and fauna in India. (2014) View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Three major reasons which are responsible for the depletion of flora and fauna in India:
(i) Agricultural expansion: After Independence agricultural expansion became the major cause of depletion of forest resources. Between 1951 and 1980, according to the Forest Survey of India, over 26,200 sq. km of fore are was converted into agricultural land all over India
(ii) Mining: It is another major factor responsible for deforestation, eg. dolomite mining has been seriously three attended the Buxa Tiger Reserve in West Bengal. This ongoing mining has disturbed the natural habitat and blocked the migration route of a great Indian elephant.
(iii) Large-scale development projects: Since 1951, over 5000 sq km of forest was cleared for River Valley Projects Large hydro projects have inundated large forest areas.
|
95 videos|815 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Geography Chapter 2 Previous Year Questions - Forest and Wildlife Resources
| 1. What are the main types of forest ecosystems found in India? |  |
| 2. How does deforestation impact wildlife resources? |  |
| 3. What measures are taken to conserve forest and wildlife resources in India? |  |
| 4. What role do forests play in combating climate change? |  |
| 5. How can individuals contribute to forest and wildlife conservation? |  |

















