Basic Geometrical Ideas Class 6 Notes Maths Chapter 4
| Table of contents |

|
| Points |

|
| Line Segment |

|
| Line |

|
| Intersecting Lines |

|
| Parallel Lines |

|
| Ray |

|
| Curves |

|
| Polygons |

|
| Angles |

|
Points
It is a position or location on a plane surface, which are denoted by a single capital letter.
Line Segment
It is a part of a line with the finite length and 2 endpoints.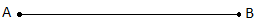
The points A and B are called the endpoints of the segment.
It is named as: 
Line
It is made up of infinitely many points with infinite length and no endpoint.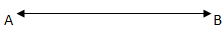
It extends indefinitely in both directions. Named as: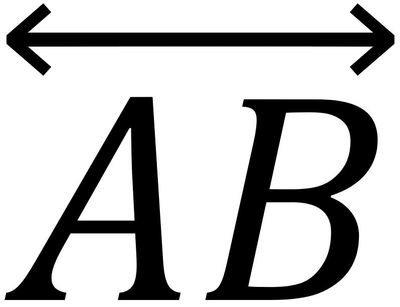
Intersecting Lines
The two lines that share one common point are called Intersecting Lines. This shared point is called the point of intersection.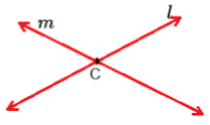
Here, line l and m are intersecting at point C.
Real life example of intersecting lines: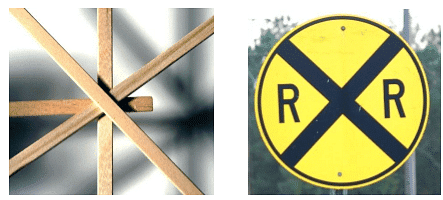
Parallel Lines
Two or more lines that never intersect (Never cross each other) are called Parallel Lines.
Real life examples of parallel lines: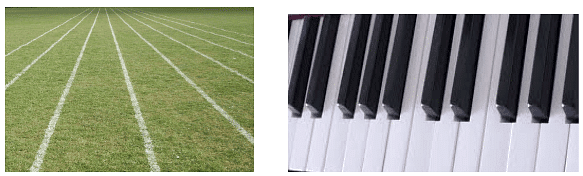
Ray
It is a part of a line with one starting point whereas extends endlessly in one direction.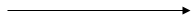
Real life examples of the ray are:
Curves
Anything which is not straight is called a curve.
1. Simple Curve – A curve that does not cross itself.
2. Open Curve – Curve in which its endpoints do not meet.
3. Closed Curve – Curve that does not have an endpoint and is an enclosed figure.
A closed curve has 3 parts which are as follows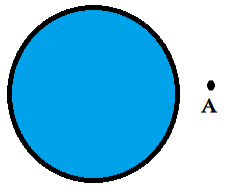
1. Interior of the curve
It refers to the inside/inner area of the curve.
The blue coloured area is the interior of the figure.
2. The exterior of the curve.
It refers to the outside / outer area of the curve.
The point marked A depicts the exterior of the curve.
3. The boundary of the curve
It refers to the dividing line thus it divides the interior and exterior of the curve.
The black line which is dividing the interior and exterior of the curve is the boundary.
The interior and boundary of the curve together are called the curves “region”.
Polygons
It is a 2d closed shape made of line segments / straight lines only.
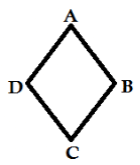
- Sides –It refers to the line segments which form the polygon, as in the above figure AB, BC, CD, DA are its sides.
- Vertex – Point where 2 line segments meet, as in the above figure A, B, C and D are its vertices.
- Adjacent Sides – If any 2 sides share a common endpoint they are said to be adjacent to each other thus called adjacent sides, as in the above figure AB and BC, BC and CD, CD and DA, DA and AB are adjacent sides.
- Adjacent Vertices – It refers to the endpoints of the same side of the polygon. As in the above figure A and B, B and C, C and D, D and A are adjacent vertices.
- Diagonals – It refers to the joins of the vertices which are not adjacent to each other. As in the above figure, AC and BD are diagonals of the polygon.
Angles
A figure formed from 2 rays which share a common endpoint is called Angle.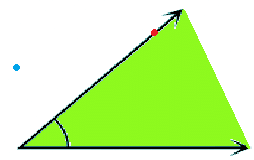
The rays forming the angle are known as its arms or sides.
The common endpoint is known as its vertex.
An angle is also associated with 3 parts
- Interior - It refers to the inside/inner area.
The green coloured area is the interior of the angle. - Angle/boundary - It refers to the arms of the angle.
The red point is on the arm of the angle. - Exterior - It refers to the outside / outer area.
The blue point depicts the exterior of the figure.
Naming an Angle
While naming an angle the letter depicting the vertex appears in the middle.
Example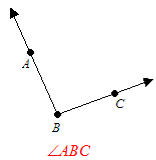 The above angle can also be named as ∠CBA.
The above angle can also be named as ∠CBA.
Triangle
It is a 3 sided polygon. It is also the polygon with the least number of the sides.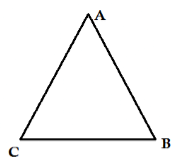
Vertices: A, B and C
Sides: AB, BC and CA
Angles: ∠A, ∠B and ∠C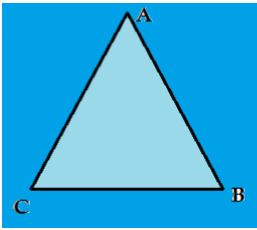
- Here, the light blue coloured area is the interior of the angle.
- The black line is the boundary.
- Whereas, the dark blue area is the exterior of the angle.
Quadrilaterals
It is a 4 sided polygon
Vertices: A, B, C, D
Sides: AB, BC, CD, DA
Angle: ∠A, ∠B, ∠C, ∠D
Opposite Sides: AB and DC, BC and AD
Opposite Angles: ∠B and ∠D, ∠A and ∠C
Adjacent Angles: ∠A and ∠B, ∠B and ∠C, ∠C and ∠D, ∠D and ∠A.
Circles
It is a simple closed curve and is not considered as a polygon.
Parts of Circles
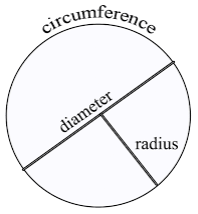
- Radius: It is a straight line connecting the centre of the circle to the boundary of the same. Radii is the plural of ‘radius’.
- Diameter: It is a straight line from one side of the circle to the other side passing through the centre.
- Circumference: It refers to the boundary of the circle.
- Chord: Any line that connects two points on the boundary of the circle is called Chord. Diameter is the longest chord.

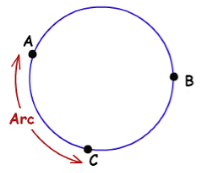
- Arc: It is the portion of the boundary of the circle.
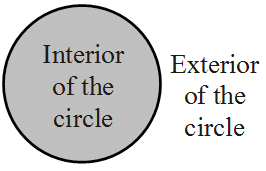
- Interior of the Circle: Area inside the boundary of the circle is called the Interior of the Circle.
- The Exterior of the Circle: Area outside the boundary of the circle is called the Exterior of the Circle.
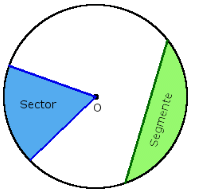
- Sector: It is the region in the interior of a circle enclosed by an arc on one side and a pair of radii on the other two sides.
- Segment: It is the region in the interior of the circle enclosed by an arc and a chord.
Semi-circle
A diameter divides the circle into two semi-circles. Hence the semicircle is the half of the circle, which has the diameter as the part of the boundary of the semicircle.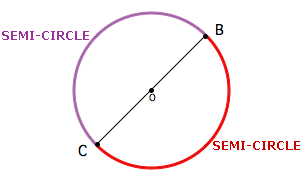
|
435 docs|98 tests
|
FAQs on Basic Geometrical Ideas Class 6 Notes Maths Chapter 4
| 1. What is the difference between a line segment and a line? |  |
| 2. What are intersecting lines and how do they differ from parallel lines? |  |
| 3. What is a ray in geometry? |  |
| 4. How can we define a polygon and what are its characteristics? |  |
| 5. What are angles and how are they measured? |  |
















