Important Points: Is matter around us Pure? | Science Class 9 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Pure Substances |

|
| Mixture |

|
| Alloys |

|
| Solution |

|
| Solubility |

|
| Suspension |

|
| Tyndall Effect |

|
| Elements |

|
| Compounds |

|

Pure Substances
- Pure substances consist of only one type of particle and have uniform chemical properties throughout.
- A pure substance cannot be separated into other substances by any physical process.
Mixture
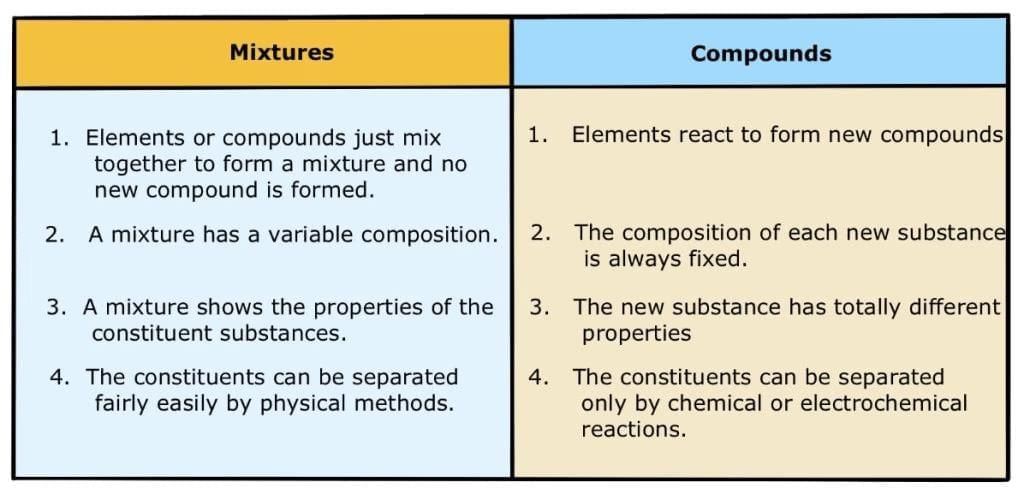
- A mixture is a substance in which two or more elements or compounds are simply mixed together in any proportion.
- Examples include air, which is a mixture of oxygen, nitrogen, carbon dioxide, and water vapour.
Types of Mixture:
Mixture is categorised into two types:
- Homogeneous Mixture: These mixtures have no visible boundaries of separation between their constituents. Example: Sugar in water.
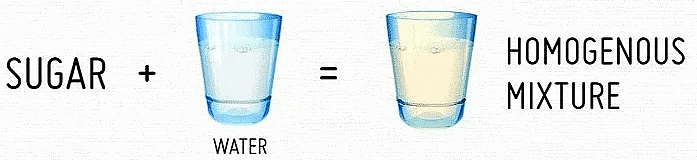
- Heterogeneous Mixture: These mixtures have visible boundaries of separation between their constituents. Example: Mixture of sugar and sand.
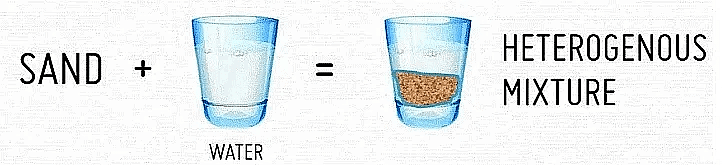
Alloys
- Alloys are homogeneous mixtures of two or more metals, or a metal and a non-metal.
- Although they cannot be separated by simple physical methods, they are considered mixtures because they exhibit the properties of their constituents and have variable composition.
- For example, brass is a mixture of approximately 30% zinc and 70% copper.
Solution
A solution is a homogeneous mixture made up of two components: the solute (the substance that is dissolved) and the solvent (the substance in which the solute is dissolved).
Examples
(i) A solution of sugar in water is a solid in a liquid solution. In this solution, sugar is the solute and water is the solvent.
(ii) A solution of iodine in alcohol known as ‘tincture of iodine’ has iodine (solid) as the solute and alcohol (liquid) as the solvent.
(iii) Aerated drinks like soda water, etc., are gases in liquid solutions. These contain carbon dioxide (gas) as solute and water (liquid) as solvent.
(iv) Air is a mixture of gas in gas. Air is a homogeneous mixture of a number of gases. Its two main constituents are: oxygen (21%) and nitrogen (78%). The other gases are present in very small quantities.
Properties of a Solution
- A solution is a homogeneous mixture.
- The particles of a solution are smaller than 1 nm (10-9 m) in diameter. So, they cannot be seen with naked eyes.
- A solution does not scatter light, and the path of light is not visible through it.
- Solution particles cannot be separated by filtration.
Concentration
- Concentration refers to the amount of a substance in a defined space or as the ratio of solute in a solution to the solvent or the total solution.
- Three methods of expressing concentration are mass by mass percentage, mass by volume percentage and Volume by volume percentage.

Saturated and Unsaturated Solutions
A saturated solution is one where no more solute can be dissolved at a given temperature.
An unsaturated solution can dissolve more solute at the same temperature.
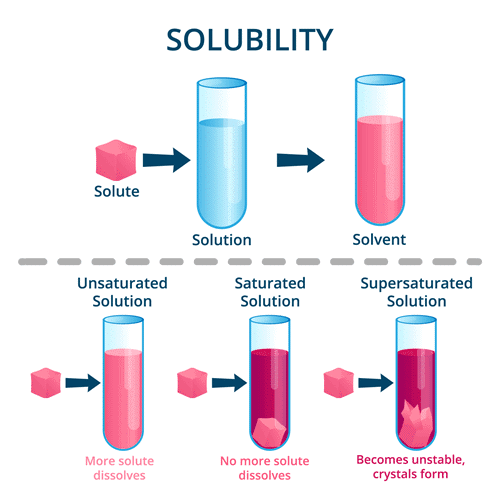
Solubility
Solubility is the maximum amount of solute that can be dissolved in a given amount of solvent at a particular temperature to form a saturated solution.Suspension
- Suspension is a heterogeneous mixture in which solute particles do not mix with the solvent.
- Particles tend to settle down and can be separated using filtration.
Colloidal Solution (Colloid)
- A colloid is a heterogeneous mixture in which the particle size is intermediate between those in true solutions and suspensions. The particles are small enough to remain dispersed but large enough to scatter light.
- Colloids are stable and cannot be separated by filtration.
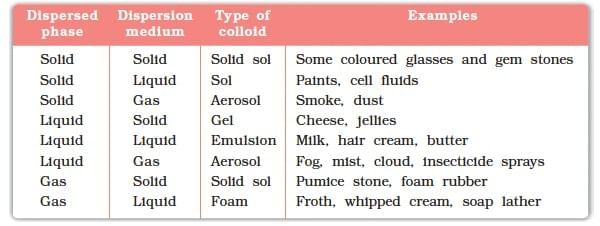
Dispersed Phase:
The component of a colloidal solution that is present in a smaller amount and is dispersed throughout the medium is called the dispersed phase. It is similar to the solute in a true solution.Dispersed Medium:
The component of a colloidal solution in which the dispersed phase is spread out or dispersed is called the dispersed medium. It is similar to the solvent in a true solution.
Tyndall Effect
When light passes through a colloid, the particles scatter the light, making the path of light visible.
Methods of Separation of Mixtures
- Evaporation: Used to separate a soluble solid from a liquid by evaporating the liquid.
- Centrifugation: Separates substances based on density when a mixture is rotated rapidly.
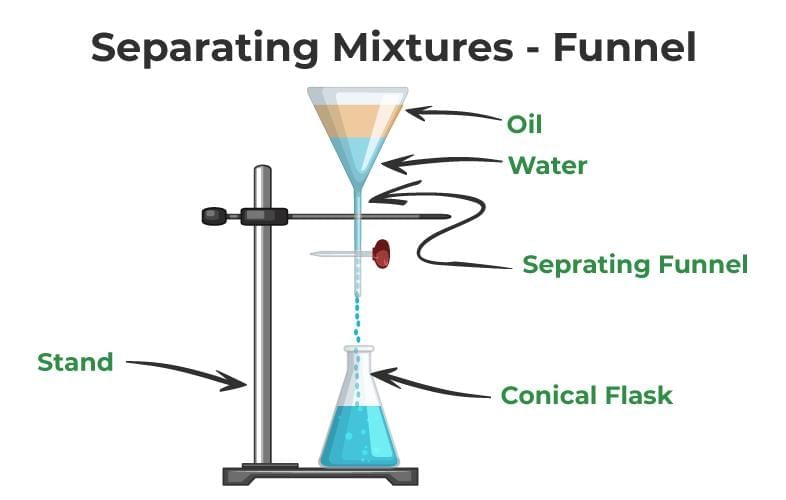
- Separating Funnel: Separates immiscible liquids.
- Sublimation: Separates substances where one sublimes (directly converts to a gas from a solid).
- Chromatography: Separates coloured components using an adsorbent.
- Distillation: Separates miscible liquids with different boiling points.
- Crystallisation: Used to obtain pure crystals of a substance from its solution by slow evaporation or cooling.
Physical Properties
Properties like rigidity, colour, fluidity, boiling point, melting point, density, and hardness are observable and known as physical properties.Physical Change
A physical change is a change in the physical state or appearance of a substance without changing its chemical composition.Chemical Change
A chemical change results in the formation of new substances with different properties from the original substances.Elements
The simplest form of matter that cannot be broken down into other elements by chemical reactions.Categorised as metals, non-metals, and metalloids.
- Metals: Lustrous, conduct heat and electricity, have varied colours, can be hammered into thin sheets (malleability), can be converted into wires (ductility), and produce a ringing sound when hit (sonorous).
- Non-Metals: Do not conduct heat and electricity, are not sonorous, lustrous, or ductile, and have varied colours.
- Metalloids: Show properties of both metals and non-metals.
Facts about elements
- The number of known elements is more than 100. Ninety-two elements are naturally occurring, and the rest are man-made.
- The majority of the elements are solid.
- Eleven elements are in the gaseous state at room temperature.
- Two elements are liquid at room temperature—mercury and bromine.
- Elements gallium and caesium become liquid at a temperature slightly above room temperature (303 K).
Compounds
Compounds are pure substances composed of two or more elements chemically combined in fixed proportions.
|
84 videos|544 docs|60 tests
|
FAQs on Important Points: Is matter around us Pure? - Science Class 9
| 1. What is matter, and how is it classified? |  |
| 2. What are pure substances and how do they differ from mixtures? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between a solution and a suspension? |  |
| 4. What is solubility, and what factors affect it? |  |
| 5. What is the Tyndall Effect and how is it observed? |  |





















