Main Orders of Modern Gymnosperms | Botany Optional for UPSC PDF Download
Orders of Modern Gymnosperms
Modern gymnosperms are categorized into four main orders:
- Cycadales
- Ginkgoales
- Coniferales
- Gnetales
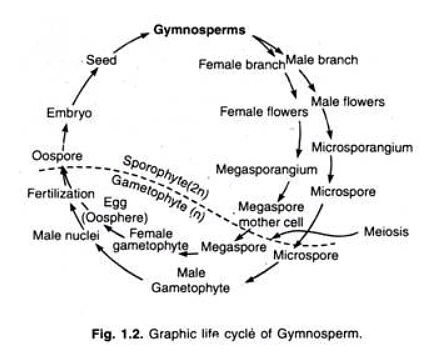 Both Cycadales and Ginkgoales include living members that have a long fossil history, often referred to as "living fossils." Ginkgoales, which were once widely distributed in the early Mesozoic era, are now represented by a single species, Ginkgo biloba.
Both Cycadales and Ginkgoales include living members that have a long fossil history, often referred to as "living fossils." Ginkgoales, which were once widely distributed in the early Mesozoic era, are now represented by a single species, Ginkgo biloba.
Similarly, Cycadales thrived during the Mesozoic era and are now represented by nine well-defined genera limited to specific tropical and subtropical regions around the world.
Coniferales are the most prominent order among living gymnosperms and include plants like Pinus, Cedrus, Abies, Juniperus, Cupressus, Biota, and more. Some conifers are known for being the world's tallest and longest-lived plants. For example, Sequoia gigantea can live for up to 4,000 years and reach heights of 300 to 400 feet. Conifers are found in various regions across the northern and southern hemispheres, forming extensive forests.
Gnetales are represented by three living genera: Gnetum, Ephedra, and Welwitschia. Welwitschia is monotypic, represented by W. mirabilis, and is found in the deserts of South-West Africa. Ephedra includes around 30 to 40 species distributed in tropical and temperate regions of Asia, Africa, and South America.
These gymnosperm plants have various uses and significance. For instance, Cycas revoluta yields sago from its pith, earning it the name "sago palm." The seeds of Pinus gerardiana, known as chilgoza, are edible and found in the dry arid zones of the Himalayas. Ephedrine, a well-known drug, is obtained from different species of the genus Ephedra. Additionally, the young leaves and strobili of Gnetum are consumed as vegetables. Coniferous forests also provide a pleasant climate, making them suitable for health resorts and sanatoria where people seek recreation and treatment.
Evolution of Gymnosperms
The evolution of gymnosperms has been shaped by various factors and challenges, which have led to their unique characteristics and limited advantages compared to other plant groups.
Some key points regarding the evolution and characteristics of gymnosperms are as follows:
- Gymnosperms lack vegetative means of reproduction, such as cuttings or layering, which makes their propagation slower and less efficient.
- Their means of dispersal are limited to wind and human intervention, which restricts their ability to adapt to varied habitats.
- Gymnosperms lack vessels in their xylem and companion cells in their phloem, which are features found in angiosperms (flowering plants).
- These plants are unisexual, meaning they have separate male and female cones or reproductive structures, reducing the chances of self-fertilization. Wind pollination is the primary method of pollen transfer, resulting in a significant waste of pollen.
- Gymnosperms have unprotected ovules and seeds, making them vulnerable to environmental factors and predation.
- Their decline in abundance may also be attributed to the exhaustion of their genetic potential for adapting to changing environments and the emergence of harmful mutations and chromosomal alterations.
- Economically, gymnosperms are less important compared to angiosperms, which dominate the plant kingdom and include most of the world's economically significant crops.
Gymnosperms are among the most ancient seed plants, with their origin dating back to the late Palaeozoic era, approximately 350 million years ago. While they originated during this period, they flourished particularly during the Mesozoic era. Gymnosperms display a diverse array of evolutionary lines within the group, with many species exhibiting fern-like appearances and foliage. These primitive plants often had seeds attached to their pinnatifid fronds, as seen in examples like Medullosa noei.
|
179 videos|143 docs
|
















