Simple Equations Class 7 Notes Maths Chapter 4
| Table of contents |

|
| Algebraic Expressions |

|
| Variable |

|
| Equation |

|
| Balanced Equation |

|
| The Solution of an Equation |

|
| From a Solution to the Equation |

|
| Applications of Simple Equations to Practical Situations |

|
Algebraic Expressions
It is an expression involving constant, variable and some operations like addition, multiplication etc.
Variable
Variable is an unknown number which could have a different numerical value. It is called Variable as it can vary.
It is represented by different letters like x, y, a, b etc.
Equation
An equation is a condition on a variable. It says that two expressions are equal.
Important Points Related to the Equation
- One of the expressions must have a variable.
- LHS of the equation is equal to the RHS of the equation.
- An expression does not have equality sign but an equation always has an equality sign.
- If we interchange the position of the expression from LHS to RHS or vice versa, the equation remains the same.
5x + 7 = 2
2 = 5x + 7Both the above equations are same.
How to form equations using statements?
1. The sum of four times of x and 12 is equal to 35.
4x + 12 = 35
2. Half of a number is 3 more than 8.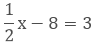
Balanced Equation
When the LHS = RHS of an equation, then it is said to be a balanced equation.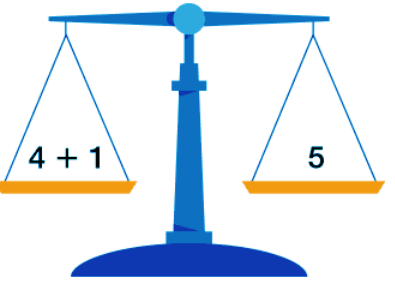
1. If we add the same number to both the sides.
We can add the same number on both the sides of a balanced equation, the equation will remain the same.
12 – 8 = 3 + 1
If we add 3 to both the sides,
12 – 8 + 3 = 7
3 + 1 + 3 = 7
LHS = RHS
2. If we subtract the same number from both sides.
We can subtract the same number from both the sides of a balanced equation, the equation will remain the same.
12 – 8 = 3 + 1
If we subtract 3 from both the sides,
12 – 8 - 3 = 1
3 + 1 -3 = 1
LHS = RHS
3. If we multiply the same number to both the sides.
We can multiply the same number on both the sides of a balanced equation, the equation will remain the same.
12 – 8 = 3 + 1
If we multiply 3 to both the sides,
(12 – 8) × 3 = 36 – 24 = 12
(3 + 1) × 3 = 9 + 3 = 12
LHS = RHS
4. If we divide the same number from both sides.
We can divide the same number from both the sides of a balanced equation, the equation will remain the same.
12 – 8 = 3 + 1
If we divide both the sides by 2,
(12 – 8) ÷ 2 = 4 ÷ 2 = 2
(3 + 1) ÷ 2 = 4 ÷ 2 = 2
LHS = RHS
The Solution of an Equation
Any value of the variable which satisfies the equation is the solution of the equation.
There are two methods to solve an equation
1. By adding or subtracting the same number to both the sides of the equation as we have above seen that the equation will remain the same.
Example 1: x + 11 = 35
Sol: Subtract 11 from both the sides.
x + 11 – 11 = 35 – 11
x = 24
Here, x = 24 is the solution of the given equation.
Example 2: 25y = 125
Sol: Divide both the sides by 25.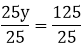
y = 5
1. Transposing Method
In this method, we transpose the numbers from one side of the equation to the other side so that all the terms with variable come on one side and all the constants come on another side. While transposing the numbers the sign of the terms will get changed. i.e. Negative will become positive and positive will become negative.
Example: x + 11 = 35
Sol: Now we will transfer 11 from LHS to RHS and its sign will get reversed.
x = 35 – 11
x = 24
From a Solution to the Equation
As we solve the equation to get the solution, we can get the equation also if we have the solution.
Any equation has only one solution but if we make an equation from a solution then there could be many equations.
Example
Given x = 7
3x = 21 (multiply both sides by 3)
3x + 8 = 29 (add 8 to both the sides)
This is not the only possible equation. There could be other equations also.
Applications of Simple Equations to Practical Situations
If we have statements related to a practical situation then first we have to convert it in the form of the equation then solve it to find the solution.
Example 1: Radha’s Mother’s age is 5 years more than three times Shikha’s age. Find Shikha’s age, if her mother is 44 years old.
Sol: Let Shikha’s age = y years
Her mother’s age is 3y + 5 which is 44.
Hence, the equation for Shikha’s age is 3y + 5 =44
3y + 5 = 44
3y = 44 – 5 (by transposing 5)
3y = 39
y = 13 (by dividing both sides by 3)
Hence, Shikha’s age = 13 years
Example 2: A number consists of two digits. The digit in the tens place is twice the digit in the units place. If 18 be subtracted from the number, the digits are reversed. Find the number.
Sol: Let the digit at units place = y
So, the digit in the tens place = 2y
So, the number is (2y) y.
As it is given that if 18 is subtracted from the number, the digits are reversed.
So, we have
(2y) y - 18 = y(2y)
10 × (2y) + 1 × y - 18 = 10 × y + 1 × (2y)
Solve it
20y + y - 18 = 10y + 2y
21y - 18 = 12y
21y - 18 = 12y
9y = 18 (By dividing both sides by 9)
y = 2
The digit at the units place is y = 2.
And the digit at the tens place is 2y = 2 × 2 = 4
Hence the required number is 42.
|
78 videos|457 docs|39 tests
|
FAQs on Simple Equations Class 7 Notes Maths Chapter 4
| 1. What is an algebraic expression and how is it different from an equation? |  |
| 2. What is a variable in algebra, and why is it important? |  |
| 3. What is a balanced equation, and how can you determine if an equation is balanced? |  |
| 4. What is the solution of an equation, and how do you find it? |  |
| 5. How can simple equations be applied to practical situations? |  |
















